printer-friendly sample test questions
advertisement

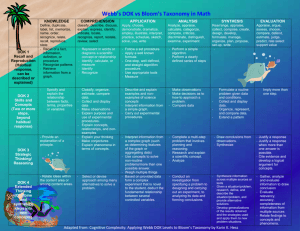
Content Benchmark L.12.C.3 Students know the amount of living matter an environment can support is limited by the availability of matter, energy, and the ability of the ecosystem to recycle materials. E/S Sample Test Questions 1st Item Specification: Explain that different environments have different carrying capacities. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. The following graph shows growth patterns of population over time. Line 2 Population Size Line 1 Line 3 Line 4 Time Which line represents a population that reaches a carrying capacity? A. Line 1 B. Line 2 C. Line 3 D. Line 4 2. Which type of graph represents a population in an environment with limited resources? A. Exponential curve B. Bell curve C. Logistic curve D. Predator/Prey curve Depth of Knowledge Level 2 3. The following table shows the primary productivity of several biomes. The accompanying graph shows the temperature/precipitation relationship of major biomes. Biome Tundra Productivity Kcal/m2/year 600 Grassland 2000 Desert 200 Seasonal Forest Rainforest 6000 Scrubland 1000 9000 (Graph from: (Graph http://www.geology.iastate.edu/gcp/datasets/images/ecosystems.gif) Based on the data given in the graph and table, which environmental factor contributes to greater biodiversity? A. Average temperature B. Available water C. Plant biomass per meter D. Average latitude 4. The following table describes data collected on herbivores living in the same habitat. All four species eat the same food. Deer Species Average size Daily food intake Offspring per Year Species 1 500 kg 12-16kg 1-2 Species 2 320kg 3-5kg 4-6 Species 3 120kg 4-6kg 5-7 Species 4 400kg 9-13kg 3-5 Based on the data given, rank the carrying capacity for the herbivore species from lowest to highest. A. 1-2-3-4 B. 2-3-4-1 C. 3-4-2-1 D. 4-2-1-3 2nd Item Specification: Identify the factors that affect carrying capacity. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 5. Which of the following factors is a density independent limiting factor? A. Competition B. Disease C. Drought D. Predation 6. What happens to a population that exceeds the environmental carrying capacity? A. Death rate and birth rate remain constant. B. Birth rate and death rate decrease. C. Death rate decreases and birth rate increases. D. Birth rate decreases and death rate increases. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 7. Graph A shows the increase in sewage waste and a decrease in oxygen content of a lake. Graph B shows population changes of four species of fish in the lake over the same time period. Graph A Graph B (Modified from Examgen 4.3) Which of the following is a plausible conclusion drawn from the above data? A. The carp were tolerant of the water quality changes. Therefore, the population was able to grow due to decreased competition. B. The walleye were more tolerant of the water quality changes and the population increased from lowered competition from the carp. C. The trout are intolerant of water quality changes but the population remained stable. D. The whitefish were intolerant of water quality changes and the population grew. 8. Which of the following would NOT be a limiting factor to the size of a large, dense population? A. Competition for food, water, space, and sunlight. B. Predation by abundant predators in the area. C. Surviving a natural disaster such as a hurricane. D. Spreading of parasites and other disease agents. 3rd Item Specification: Predict the result of changing a factor on the carrying capacity of an ecosystem. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 9. The moose and wolf populations of Isle Royal National Park are one of the most studied predator/prey relationships. What would be a long term effect of removing the wolves from the park? The moose population will A. increase dramatically due to the lack of predators. B. die off due to disease because the wolves are not removing the sick individuals. C. decrease initially due to disease and then increase dramatically because of lack of predators. D. increase initially due to lack of predators then decrease due to overgrazing. 10. When Rapa Nui (Easter Island) was colonized by a small number of humans it was covered with trees and abundant food types. Within a thousand years the Rapa Nui population disappeared and the island was grassy. Which of the following is the MOST plausible cause of the population crash? As the population increased, A. the different groups warred with each other reducing the overall population. B. the people cut down the trees for shelter and overused the food available faster than the resources were replenished. C. the people used the island as a resting place before moving onto other islands. D. new immigrants brought a disease with them that caused a fatal epidemic. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 11. The following graph illustrates the population of rabbits following the release of a mating pair into an environment without predators. Four possible scenarios are provided in Graphs A through D A. B. 90 80 100 Number of Rabbits Number of Rabbits 120 80 60 40 20 50 40 30 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Years Years D. 90 Number of Rabbits 80 Number of Rabbits 60 10 0 C. 70 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 Years Years Predict what the graph will look like following the introduction of fox at Year 10. A. Graph A B. Graph B C. Graph C D. Graph D Number of Grasshoppers (x1000) 12. A farmer harvests a hay field twice a year. The following graph represents the grasshopper population every summer between harvests. Week 0 is immediately following a harvest. 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Weeks B. 1000 800 600 400 200 Number of grasshoppers (x1000) A. Number of grasshoppers (x1000) The farmer retires immediately after a harvest (Week 0) and the field is left unplowed. 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 0 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Weeks following harvest 5000 D. 4000 3000 2000 1000 Number of grasshoppers (x1000) C. Number of grasshoppers (x1000) Weeks following harvest 1000 800 600 400 200 0 0 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 Weeks following harvest 18 19 20 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Weeks following harvest Which of the following graphs shows the grasshopper’s population growth in Weeks 11-20 without a second harvest? A. Graph A B. Graph B C. Graph C D. Graph D Content Benchmark L.12.C.3 Students know the amount of living matter an environment can support is limited by the availability of matter, energy, and the ability of the ecosystem to recycle materials. E/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 1. C, DOK Level 1 2. C, DOK Level 1 3. B, DOK Level 2 4. B, DOK Level 2 5. C, DOK Level 1 6. D, DOK Level 1 7. A, DOK Level 2 8. C, DOK Level 2 9. D, DOK Level 1 10. B, DOK Level 1 11. C, DOK Level 2 12. A, DOK Level 2