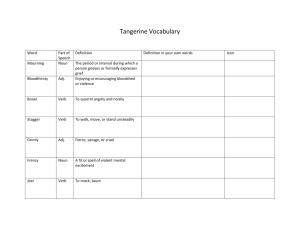
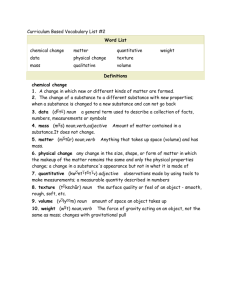
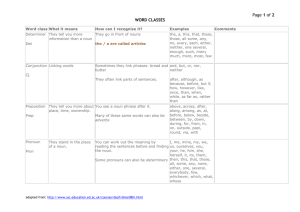
Vocabulary practice for chapter 1
advertisement

Contents Preface v Unit 1 – Context clues for vocabulary Unit 1 objectives Vocabulary list for chapter 1 Activity 1: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 1, pages 1-5) Vocabulary practice for chapter 1 Vocabulary list for chapter 2 Activity 2: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 2, pages 6-8) Vocabulary practice for chapter 2 Vocabulary list for chapter 3 Activity 3: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 3, pages 9-11) Vocabulary practice for chapter 3 Vocabulary list for chapter 4 Activity 4: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 4, pages 12-15) Vocabulary practice for chapter 4 1 1 2 3 5 6 7 9 10 11 12 14 15 17 Unit 2 – More context clues for vocabulary Unit 2 objectives Vocabulary list for chapter 5 Activity 5: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 5, pages 16-20) Vocabulary practice for chapter 5 Vocabulary list for chapter 6 Activity 6: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 6, pages 21-25) Vocabulary practice for chapter 6 19 19 20 21 23 24 25 27 Unit 3 – Adverb phrases and clauses Unit 3 objectives Vocabulary list for chapter 7 Activity 7: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 7, pages 26-31) Vocabulary practice for chapter 7 Vocabulary list for chapter 8 Activity 8: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 8, pages 32-38) Vocabulary practice for chapter 8 29 29 30 31 33 34 35 37 iii Unit 4 – More about before and after Unit 4 objectives Vocabulary list for chapter 9 Activity 9: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 9, pages 39-45) Vocabulary practice for chapter 9 Vocabulary list for chapter 10 Activity 10: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 10, pages 46-50) Vocabulary practice for chapter 10 39 39 40 41 43 44 45 47 Unit 5 – Difficult question forms Unit 5 objectives Vocabulary list for chapter 11 Activity 11: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 11, pages 51-58) Vocabulary practice for chapter 11 Vocabulary list for chapter 12 Activity 12: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 12, pages 59-65) Vocabulary practice for chapter 12 Vocabulary list for chapter 13 Activity 13: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 13, pages 66-70) Vocabulary practice for chapter 13 49 49 50 51 54 56 57 59 60 61 63 iv Preface This book includes materials for teaching grammar, vocabulary, and reading comprehension with the biography, Thomas Alva Edison – Great Inventor by Nancy Smiler Levinson published by Scholastic Inc., 1996, ISBN 0-590-52767-3. The activities in this book have been developed to promote the learning of selected English vocabulary and grammatical structures in a reading comprehension and reading vocabulary course. Students who have studied English for a number of years, but are still encountering significant challenges will find these materials most helpful. Each unit includes a brief introduction to the activities of the unit and the vocabulary needed to understand the biography. The teacher should plan to introduce students to the activities at the start of each unit. Each unit has a particular reading comprehension focus. In addition, all units have vocabulary items for students to learn. The first and second units are designed to teach students to begin to rely on context to make logical guesses about new words and then to verify their guesses with a dictionary if necessary. Unit three includes materials for teaching students to distinguish the semantic and syntactic differences between during and while and to recognize the verb forms that are used with adverb clauses that begin with when and while. The third and fourth units contain materials for teaching students to recognize the sequence of events in the English adverb phrases and clauses introduced by before and after. The fifth unit includes question forms with have, has, had, should, which, how did, and what happened. These forms pose particular difficulties for language learners. Students should plan to read each chapter of the biography two times. The objective of the first reading is to obtain a very general understanding of the content of the chapter. While doing this first reading, students should pay attention to the vocabulary items for that chapter. It is strongly recommended that students keep a vocabulary notebook for new words. The objective of the second reading is to reinforce the vocabulary that is new to the student and to begin to gather the information needed to complete the activity for the chapter. Before moving to the next activity within a unit, students should have an opportunity to discuss their work in small groups with a teacher’s guidance. It is recommended that quizzes occur frequently and tests occur after each unit. The units in this book are developmentally sequenced. A reasonable level of mastery is needed on earlier units before students can succeed on later units. v THOMAS A. EDISON American inventor Feb. 11, 1847 – Oct. 18, 1931 vi Unit 1 – Context clues for vocabulary This unit will help you learn to figure out meanings of new words by using the context. The context is the sentences and words around the new word. You will learn this skill while reading a biography about Thomas Alva Edison. This biography is in chronological order. It starts when Thomas Alva Edison is a child and ends when he dies. Each chapter in this biography tells a story about part of his life. Unit 1 objectives In this unit, you will learn to: 1. use context to make logical guesses about new words 2. use parts-of-speech to select dictionary definitions 3. use dictionary definitions to check your logical guesses 1 Vocabulary list for chapter 1 adored – Al’s mother adored him. (verb T) bury – The grain started to bury him. (verb T) curiosity –Punishments did not stop Al’s curiosity. (noun U) exploring – Al was playing and exploring. (verb I) frequently – Things frequently went wrong. (adv.) grain – Al fell and landed on the soft grain. (noun U) huge – He was sitting on top of a huge grain elevator. (adj.) locomotives – He wanted to know how locomotives and other machines worked. (noun C) mischief – Al was full of mischief. (noun U) rescued – Someone rescued him. (verb T) stored – People stored grain inside the elevator. (verb T) suffocated – He almost suffocated to death. (verb I) support – The grain couldn’t support him. (verb T) wander – Al was left to wander and play by himself. (verb I) My Study Notes 2 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 1: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 1, pages 1-5) Directions: Read these sentences in your book and read the words that are missing. Then, use the other words in the sentence to figure out the correct meanings of the missing words. Next, select the correct meaning from the word bank at the bottom of the page. If you can’t figure out the meaning, you can use a dictionary. [The part-of-speech will help you use your dictionary.] The first two are already done as examples. 1. (page 1) Al was [adj.] seated on top of a [adj.] large grain elevator, [noun] ______________________ down at tons of grain [verb] _____________________ inside. Al suddenly [verb] ______________________ over the edge. Down, down he fell, [noun] _____________________ on the soft [noun] ______________________. 2. (page 1) But the pile of grain couldn’t [verb] _____________________ him. Al began to [verb] _________________ down. Every time he [verb] _____________________ upward, he only [verb] _____________________ again. 3. (page 1) The grain started to [verb] _____________________ Al. It was hard for him to breathe. He [verb] _____________________. His heart pounded wildly. 4. (page 2) Then Al heard voices, and finally he felt himself being pulled out. He was [verb] _____________________ just in time, before he [verb] _____________________ to death. 5. (page 3) How else could he find out how birds fly or what makes rain turn into snow? How else could he learn how steam engines and [noun] _____________________ work? And [noun] _____________________? And [noun] _____________________? 6. (page 3) It was true that things [adv.] _____________________ went wrong when Al was playing and [verb] _____________________. Ma Edison could not always keep an eye on him. She had so much work to do – cooking, cleaning, [noun] _____________________ the fire, weaving cloth, and sewing. 7. (page 3) His other sister, Harriet Ann, and his brother, William Pitt, [verb] _____________________ him little attention, so Al was often left to [verb] _____________________ and play by himself. Noun - coming down - looking - message machines - seeds of wheat - train engines - watching - wood-sawing machines Verb - choked - climbed - coughed for air - cover - fell - gave - go - hold - kept (saved) - looking for new things - saved - walk around - went down Adjective - large - seated 3 Adverb - in addition to - often 8. (page 3) Their [noun] _____________________ of Milan, Ohio, had wonderful places for a five-year-old boy to poke around. [adv.] _____________________ the grain elevators, there was the lumberyard and the flour [noun] _____________________. There was also the [noun] _____________________ with its boats pulled by [noun] _____________________ of horses. 9. (page 3) Of course, Al didn't mean to tumble down the grain elevator. Another time he didn't mean to fall into the canal while he was watching boats. He was just [adj.] _____________________. 10. (page 3) Although his ma [verb] _____________________ him, she admitted that her son was full of [noun] _____________________ . Neighbors whispered that little Thomas Alva Edison was a(n) [adj.] _____________________ child. 11. (page 4) Al took his punishments bravely, but they did not stop him from poking around. They did not stop his [noun] _____________________. 12. (page 4) [adv.] _____________________ Al was whipped with a [noun] _____________________ for his [noun] _____________________ . His ma and pa hoped to teach him lessons in good behavior. 13. (page 4) One day when Al was six, he went into his family's barn. There were no animals inside. Al lit a small fire "just to see what it would do." Flames [verb] _____________________ and spread quickly. The barn was [adj.] _____________________ . Al escaped just in time, but the barn burned to the ground. 14. (page 4) Al was sorry about what had happened. But Al's whipping was [adj.] _____________________ . When would Al ever learn to behave? Pa asked. Noun - bad behavior - bad behavior - desire to know about things - grinding (crushing) machine - groups - town - tree branch - water way dug by people Verb - loved and admired - went up Adjective - burning - rough and unpleasant - very strange - wanting to know about things 4 Adverb - in addition to - sometimes Vocabulary practice for chapter 1 Directions: Write the meaning for each word in the blank. Use your work from Activity 1. adored __________________________________ bury __________________________________ curiosity __________________________________ exploring __________________________________ frequently __________________________________ grain __________________________________ huge __________________________________ locomotives __________________________________ mischief __________________________________ rescued __________________________________ stored __________________________________ suffocated __________________________________ support __________________________________ wander __________________________________ 5 Vocabulary list for chapter 2 base – The family lived near an army base. (noun C) cemetery – A cemetery was nearby. (noun C) fail – Al’s father owned a business, and the business began to fail. (verb I) goods – Railway cars would carry goods to Port Huron. (noun plural) headed – The family packed their belongings and headed north. (verb I) recover – Luckily, Al began to recover. (verb I) treat – It was hard to treat scarlet fever. (verb T) My Study Notes 6 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 2: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 2, pages 6-8) Directions: Read these sentences in your book and read the words that are missing. Then, use the other words in the sentence to figure out the correct meanings of the missing words. Next, select the correct meaning from the word bank at the bottom of the page. If you can’t figure out the meaning, you can use a dictionary. [The part-of-speech will help you use your dictionary.] 1. (page 6) Pa Edison ran a [noun] _____________________ in Milan. But his business began to [verb] _____________________ . Al's pa decided to sell the house and move to a larger town. 2. (page 6) The family packed their [noun] _____________________ and [verb] _____________________ north. They traveled by [noun] _____________________ , railroad, and steamboat. 3. (page 6) At last, they arrived at Port Huron, Michigan. The town was built on a [noun] __________________ where the river entered Lake Huron. 4. (page 6-7) Ships traveled these waterways, bringing [noun] _____________________ that people needed to live and work. Soon a railroad would be built and would run through Port Huron. Railway cars would carry more [noun] _____________________ to be bought and sold. 5. (page 7) "Business will be [adj.] _____________________ here," Al's pa told the family. He began selling [noun] _______________________ and grain. 6. (page 7) The Edisons rented a large house near the lake and next to a(n) [noun] _______________________. 7. (page 7) There was a(n) [noun] ______________________, a [noun] _______________________ for marching soldiers, and a [noun] _______________________ . 8. (page 7) There was a [noun] _______________________ of pine trees and a vegetable garden in the backyard. 9. (page 7) Al became ill with [noun] _______________________. This illness was hard to [verb] _______________________. There was no medicine to fight it. Noun - a childhood sickness with high fever and red spots on the skin - marching area - piece of land - place to put dead people - place where people in the army live and work - products; things - store that sells wood - strong building for the army - thick (dense) group - things that they owned - things; products - wagon that horses pull - wood Verb - give medical help so someone gets better - lose money - traveled 7 Adjective - very active 10. (page 7) His fever continued to [verb] _____________________ . He grew [adj.] ____________________. In the dark of the night, he [verb] _____________________ [noun] _____________________ in the cemetery and wolves in the woods. 11. (page 7) Then, luckily, Al began to [verb] _____________________ . He felt strong again. 12. (page 7) But he was left [adj.] ____________________ . Some doctors believe the deafness was caused by the high fever of his illness. 13. (page 8) Soon he started asking when he could go to school. Al was [adj.] ____________________ to learn. Ma Edison worried that Al might become ill again. So she kept him home all year. Noun - spirits of dead people Verb - get well - go up higher - saw in his mind Adjective - hard-of-hearing - sicker - very motivated; very interested 8 Vocabulary practice for chapter 2 Directions: Write the meaning for each word in the blank. Use your work from Activity 2. base __________________________________ cemetery __________________________________ fail __________________________________ goods __________________________________ headed __________________________________ recover __________________________________ treat __________________________________ 9 Vocabulary list for chapter 3 backward – He called Al a backward boy. (adj.) blinked – Al blinked and slid down in his seat. (verb I) cane – The schoolmaster carried a heavy cane. (noun C) currents – Al asked about batteries and electric currents. (noun C) flew into a rage – The schoolmaster flew into a rage. (verb expression) hardly – At last, Al was allowed to start school; he could hardly wait. (adv) recite – Everyone in class had to recite the alphabet. (verb T) smacked – He smacked him cane on Al’s desk. (verb T) trembled – Al’s voice trembled. (verb I) My Study Notes 10 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 3: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 3, pages 9-11) Directions: Read these sentences in your book and read the words that are missing. Then, use the other words in the sentence to figure out the correct meanings of the missing words. Next, select the correct meaning from the word bank at the bottom of the page. If you can’t figure out the meaning, you can use a dictionary. [The part-of-speech will help you use your dictionary.] 1. (page 9) At last, Al was allowed to start school. He could [adv.] _____________________ wait. He ran to the one-room schoolhouse. He sat down with the other pupils. 2. (page 9) The schoolmaster was Mr. Crawford. He wore a long coat and carried a heavy [noun] _____________________ . 3. (page 9) Al started to ask questions. "What is electricity ... ? What ... ?" "Silence!" the schoolmaster cried. Whack! He [verb] _____________________ his cane on Al's desk. 4. (page 9) Al [verb] _____________________ and slid down in his seat. 5. (page 9) "Do not speak until I give permission," the schoolmaster said [adv.] _____________________ . 6. (page 9) "Yes, sir," said Al. His voice [verb] _____________________ . 7. (page 10) The schoolmaster made the class sit still. Then he made everyone [verb] _____________________ the alphabet. After that, the pupils recited their arithmetic sums. 8. (page 10) Once, when a boy made a mistake, the schoolmaster smacked his cane on the boy's [noun] _____________________ . 9. (page 10) One day Al raised his hand. "Please, sir," he asked. "Can you tell me: What is electricity? What are electric [noun] _____________________? How do batteries work?" 10. (page 10) The schoolmaster [verb exp.] _____________________ . "Questions! Questions! I have no time to answer such questions!" he shouted at Al. 11. (page 10) He called Al a(n) [adj.] _____________________ boy with a(n) "[adj.] _____________________" mind. "Thomas Alva Edison will never learn anything," he said. 12. (page 10) He ran home and told his ma what had happened. When she heard, she went [adv.] _____________________ to the school. Noun - finger joints (where the fingers bend) - movements of electricity - stick for walking Verb - got very angry and yelled - hit - closed and opened his eyes quickly - tell from memory - shook from fear Adjective - confused - not able to learn successfully 11 Adverb - immediately - almost not; only with difficulty - strictly Vocabulary practice for chapter 3 Directions: Write the meaning for each word in the blank. Use your work from Activity 3. backward __________________________________ blinked __________________________________ cane __________________________________ currents __________________________________ flew into a rage __________________________________ hardly __________________________________ recite __________________________________ smacked __________________________________ trembled __________________________________ 12 Thomas Alva Edison was about 5 years old when this picture was taken. His family called him Al. 13 Vocabulary list for chapter 4 awkward -- Al was awkward at sports and games. (adj.) cellar – He had to move the laboratory to the cellar. (noun C) convinced – Al’s mother convinced his father to let Al keep the laboratory. (verb T) device - The receiving operator used a device with an electromagnet and an iron bar. (noun C) experiments – He got a science book and did experiments at home. (noun U) infection -- He had just suffered a bad ear infection. (noun C) installed – Workers installed a new machine in railroad stations. (verb T) laboratory – He set up a laboratory in his bedroom. (noun C) literature – Al liked to study history and literature. (noun U) magnetism – He learned about magnetism and optics. (noun U) materials – He needed many different materials for his experiments. (noun C) operator – The telegraph operator pressed a key to send an electrical signal. (noun C) optics – He learned about magnetism and optics. (noun U) pharmacy – He bought some materials at the pharmacy. (noun C) strung – They strung wires through the woods. (verb T) telegraph – The telegraph sent and received messages through wires. (noun C) My Study Notes 14 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 4: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 4, pages 12-15) Directions: Read these sentences in your book and read the words that are missing. Then, use the other words in the sentence to figure out the correct meanings of the missing words. Next, select the correct meaning from the word bank at the bottom of the page. If you can’t figure out the meaning, you can use a dictionary. [The part-of-speech will help you use your dictionary.] 1. (page 12) Al’s ma decided to give him [noun] _____________________ at home. She had been a schoolteacher before she got married. 2. (page 12) He became a good reader. He didn’t [verb] _____________________ arithmetic or spelling. But he liked history and [noun] _________________________ . 3. (page 12) One day his ma gave him a new book. The book was full of information about science. All kinds of science – such as [noun] _____________________ , [noun]_____________________ , [noun]_____________________ , and [noun]_____________________ . It also explained how to make science [noun] _____________________ at home. 4. (page 13) He set up a [noun] _____________________ in his bedroom and collected materials – wires, batteries, magnets, [noun]_____________________ of metal, [noun]_____________________ , beeswax, feathers, chemicals, and [noun]_____________________ . 5. (page 13) When he couldn't find [noun]_____________________ , he spent his pennies to buy them at the [noun]_____________________ . 6. (page 13) Al earned money by weeding and [noun]_____________________ the vegetable garden in the backyard. Sometimes his pa made him [verb]_____________________ onions, corn, [noun]_____________________ , and [noun]_____________________ 7. around town to sell them. (page 13) His laboratory grew. Materials [verb] _____________________ everywhere. Chemicals [verb]_____________________ on the furniture and the floor. Sometimes an experiment [verb]_____________________ . "He will blow us all up!" Al's pa cried. 8. (page 13) Ma Edison [verb] _____________________ Pa to let Al keep the laboratory. "Let him be," she [verb] _____________________ . "The boy knows what he wants to do." Noun (single) - books, plays, poems, etc. - energy (power from electrons) - energy (power from magnets) - heavy silvery metal - place to buy medicines - place to do science work - science of light and vision - science of things in space - turning over soil for growing Noun (plural) - bitter red & white vegetables - round red vegetables - school work - soft dry bits of crushed stuff - tests to learn new things - things - very small pieces 15 Verb - blew up into many parts - collected together - enjoy and do well at - persuaded (got someone to agree) - poured over - carry in a wagon - said with strong emotion 9. (page 13) But she ordered Al to move the laboratory to the [noun]_____________________ . There, Al [verb]_____________________ his bottles and jars again. He didn't want anyone to touch them. So he put a [noun]_____________________ marked Poison on each one. 10. (page 13) Al spent many hours a day reading and [noun]_____________________ . Soon he became interested in a new machine that was being [adj.]_____________________ in railroad stations – a telegraph. 11. (page 14) The [noun] _______________________ sent and received messages through wires by [noun]_____________________ of electricity. 12. (page 14) The sending [noun]_____________________ pressed a key that moved up and down to send a(n) [noun]_____________________ . A short press made a "dot." A longer press made a "dash." Dots and dashes were [noun]_____________________ for letters and numbers. 13. (page 14) The receiving operator used a [noun]_____________________ called a "sounder," which caused an electromagnet to [verb]_____________________ an iron bar. When the bar [verb]_____________________ the electromagnet, it caused a sharp [noun]_____________________ to click the dots and dashes onto a [noun]_____________________ of paper. The receiver could then decode, or "read," the message. 14. (page 15) The boys [verb]_____________________ the materials into two small boxes. One box went into each boy's house. Then they [verb]_____________________ wires to the boxes. 15. (page 15) Next they [verb]_____________________ the wires through the woods from house to house. They [verb]_____________________ the wires along nails [adj.]_____________________ into trees to hold the wires off the ground. 16. (page 15) They [verb]_____________________ a few code signals back and forth to each other. Their telegraph set [verb]_____________________ ! 17. (page 15) Al continued reading and experimenting at home. But when he [verb]_____________________ eleven, the family decided to [verb]_____________________ Al in another school. 18. (page 15) He had just suffered a bad ear [noun]_____________________ . That made his poor hearing worse. [adv.]_____________________ , Al couldn't hear very well inside the classroom. Also, there weren't enough books for everyone. 19. (page 15) Outside, Al was [adj.]_____________________ at sports and games. Children [verb]_____________________ him and made him feel awful. Noun - communication device (before the telephone) - doing science tests - energy burst - illness - small long piece - small machine - systems of writing - tool - unheated basement - very short energy bits - word; name - worker Verb (T) - enter - fastened; tied - fastened; tied - hit softly - hung - made fun of ; annoyed - pull - put - put in a row - touched; hit against Verb (I) or (Linking) - became - was successful 16 Adjective or Adverb - because of that; therefore - clumsy - hammered - set up by people Vocabulary practice for chapter 4 Directions: Write the meaning for each word in the blank. Use your work from Activity 4. awkward __________________________________ cellar __________________________________ convinced __________________________________ device __________________________________ experiments __________________________________ infection __________________________________ installed __________________________________ laboratory __________________________________ literature __________________________________ magnetism __________________________________ materials __________________________________ operator __________________________________ optics __________________________________ pharmacy __________________________________ strung __________________________________ telegraph __________________________________ 17 Every day after Al worked as a newsboy on the Grand Trunk Railroad, he went to the Detroit Public Library where he attempted to read every book. 18 Unit 2 – More context clues for vocabulary In this unit, you will continue to learn how to figure out meanings of new words by using the context. You already know that the context is the sentences and words around the new word. You will also continue to practice using your dictionary to check your opinions about word meanings. Unit 2 objectives In this unit, you will learn to: 1. use context to make logical guesses about new words 2. use parts-of-speech to select dictionary definitions 3. use dictionary definitions to check your logical guesses 19 Vocabulary list for chapter 5 baggage car – The baggage car was empty. The conductor let Al put his things there. (noun C) boarded – He boarded the train again in the afternoon. (verb T) conductor – The train conductor tried to help Al. (noun C) customers – New customers got on at every station. (noun C) dull – He started to read every book in order, but some were dull. (adj.) engineer – The train engineer let him ride the locomotive. (noun C) evaporated – Phosphorus was supposed to be in water, but the water evaporated. (verb I) exposed – The phosphorus got exposed to air. (adj.) notice – The railroad company put out a public notice: BOYS FOR HIRE. (noun C) passengers – The passengers were good customers. (noun C) phosphorus – There was a stick of phosphorus in a bottle. (noun U) rage – The conductor turned red with rage. (noun U) roamed – Thieves and rough men roamed in a big city. (verb I) scraps – Al moved bottles, test tubes, scraps, and chemicals onto the train. (noun C) wares – Tom sold candy, nuts, and fruit. He carried his wares in a basket. (noun plural) My Study Notes 20 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 5: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 5, pages 16-20) Directions: Read these sentences in your book and read the words that are missing. Then, use the other words in the sentence to figure out the correct meanings of the missing words. Next, select the correct meaning from the word bank at the bottom of the page. If you can’t figure out the meaning, you can use a dictionary. [The part-of-speech will help you use your dictionary.] 1. (page 16) The year was 1859. Pa Edison's dream of becoming rich did not come true. He [verb] ____________________ one business problem after another. 2. (page 16) Port Huron had a new [noun] ____________________– the Grand Trunk line. It connected the town to the busy city of Detroit, sixty-three miles away. 3. (page 16) The railroad company put out a(n) [noun] ____________________________: BOYS FOR HIRE. The company wanted boys to work as news and candy butchers. They would sell newspapers, cigars, [noun] ________________________, and fruit to the [noun] _______________________ in the railway cars. 4. (page 17) "A job would be good for Al," said Pa. "It might keep him out of trouble." Al's ma didn't like the idea. She worried about train [noun] _______________________. She worried about her son alone in a big city, where thieves and rough men [verb] _______________________. 5. (page 17) "Lots of children work to help their families, Al [verb] ________________________. "I'll give you and Pa some of my [noun] _______________________ every week." 6. (page 17) "What about your [noun] _______________________?" she asked. 7. (page 17) "I'll go to a free reading room every afternoon before [noun exp.] _________________________," Al said. At last, his ma agreed. 8. (page 17) Al went to work for the Grand Trunk railroad. Each morning he [verb] ____________________ the train at seven o'clock. 9. (page 17) He carried [noun] ____________________ in a basket. Up and down the [noun] ____________________ of the cars he went, calling out, "Candy for sale! Peanuts, popped-corn balls, berries, and [noun] ____________________!" 10. (page 17) The train moved along at thirty miles per hour. New [noun] ____________________ got on at every station. 11. (page 17) Al did well selling his wares. His pocket [verb] ____________________ with coins. 12. (page 17, 19) Al kept his promise and went to the free reading room at the Young Men's [noun] _________________________ . There were shelves and shelves of books! Noun (single) - announcement (message) for people - getting on the train to go home - organization; group - train Noun (plural) - brown/green sweet fruit - candies - crashes (accidents) - money from working - people who buy things - riders (people who travel) - school assignments (school work) - things to sell - walkways between rows of seats 21 Verb - gave reasons - got on - had - shook and made noise - wandered (walked) around 13. (page 19) Al tried to read the whole library. He started to read every book in order. But some were [adj.] _________________________ . Finally he [verb] _________________________ only the ones he liked. 14. (page 19) In the late afternoons, Al boarded the train again. On the way home he sold [noun] _________________________ of newspapers. He had bought them at the office of the Detroit Free Press. 15. (page 19) "Read the [adj.] _________________________ news!" he called out. The passengers were good customers. 16. (page 19) Al worked every day [prep.] _________________________ Sunday. Week after week. Month after month. He didn't get back to Port Huron until dark each night. Then from the train station he had to ride a [noun] _________________________ through a scary cemetery [adv. exp.] _________________________ get home. 17. (page 19) He liked working. He liked earning money. (And it was fun when the [noun] __________________________ let him ride the [noun] __________________________ .) But Al often felt tired and lonely. 18. (page 19) The [noun] __________________________, Mr. Stevenson, was kind to Al. He listened to the boy when he had time. When Al told him that he [verb] __________________________working on his experiments, the conductor tried to help. 19. (page 19) "Half of the [noun] __________________________ is empty," he said. "Why not keep the [noun] __________________________ there?" 20. (page 19) Little by little, Al moved his bottles, jars, [noun] __________________________________, [noun] __________________________, and chemicals onto the train. He had a traveling laboratory! 21. (page 20) On one shelf there was a stick of [noun] ___________________________________in a bottle. This chemical was supposed to be kept safe in water all the time. But the water had [verb] __________________________, and Al forgot to add more water. 22. (page 20) The phosphorus got [adj.] _________________________ to the air. That meant danger. Sure enough, all of a sudden it caught fire. 23. (page 20) The conductor appeared just in time. He [verb] _________________________to put out the fire before there was a(n) [noun] ____________________________ . 24. (page 20) The conductor turned red with [noun] ____________________________. At the next station, he threw Al's whole laboratory off the train. Noun (single) - a chemical (makes fire when mixes with air) - accident that causes lots of damage - person driving the train - strong anger - ticket collector on the train - train car for suitcases and packages - train engine - wagon pulled by horses Noun (plural) - small bits of things - small packs - tall narrow glass bottles for mixing chemicals - things Verb - changed into air - felt sad because he wasn’t - selected; picked - was able 22 Others - but not - most current (newest) - not interesting; boring - open; uncovered - so that he could Vocabulary practice for chapter 5 Directions: Write the meaning for each word in the blank. Use your work from Activity 5. baggage car __________________________________ boarded __________________________________ conductor __________________________________ customers __________________________________ dull __________________________________ engineer __________________________________ evaporated __________________________________ exposed __________________________________ notice __________________________________ passengers __________________________________ phosphorus __________________________________ rage __________________________________ roamed __________________________________ scraps __________________________________ wares __________________________________ 23 Vocabulary list for chapter 6 agreed – The telegraph operator agreed to send the announcement. (verb I) announcement – Al asked the telegraph operator to send a news announcement. (noun C) bundles – He picked up his bundles of newspapers. (noun C) clever – People said that Al was a clever fellow. (adj.) depot – People bought newspapers at the train depot. (noun C) engraved – Letters are engraved on the small blocks of type. (adj.) local – Al’s newspaper was full of local news. (adj.) lug – Al and his friends had to lug the papers to the train depot. (verb T) press – He bought a small printing press. (noun C) realized – He realized that people wanted to know about the Civil War battles. (verb + that) replace – Al needed something to replace his laboratory. (verb T) type – He also bought some type, small metal blocks with letters on them. (noun U) venture – At age fifteen, Al began a new venture. (noun C) My Study Notes 24 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 6: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 6, pages 21-25) Directions: Read these sentences in your book and read the words that are missing. Then, use the other words in the sentence to figure out the correct meanings of the missing words. Next, select the correct meaning from the word bank at the bottom of the page. If you can’t figure out the meaning, you can use a dictionary. [The part-of-speech will help you use your dictionary.] 1. (page 21) Al was lucky. He did not lose his job. Mr. Stevenson was truly a kind friend. But Al needed something to [verb] _________________________ his laboratory. He was fifteen now, and he wanted more to do during his hours [prep.] _________________________ the train. 2. (page 21) Finally, he had an idea. When he went to pick up his [noun] _________________________ of newspapers at the office of the Detroit Free Press, he often watched the printers set type and print the newspaper. 3. (page 21) Why not print a little newspaper of his own, he thought. With money he had saved, he bought a small, used [noun] _________________________ . 4. (page 21) He also bought some old type - small metal blocks with letters and numbers [adj.] _________________________ on them. 5. (page 22) Al taught himself to set [noun] _________________________ – letter by letter, line by line. He learned how to ink it and press paper over the wet type. 6. (page 22) It was slow work, and it took lots of [noun] _________________________ . But Al did it! He wrote and published a one-page newspaper. He called it the Weekly Herald. It was full of [adj.] _________________________ news. 7. (page 23) Al printed four hundred copies of the Weekly Herald and sold them all for two cents a piece. How [adj.] _________________________ he felt! 8. (page 23) "Al Edison is a [adj.] _________________________ [noun] _________________________ ," passengers said. "Are you going to become a newspaperman?" they asked him. 9. (page 23) [adv.] _________________________ , he found a way to make more money than his Weekly Herald was earning. 10. (page 23) The year was 1862. The United States was in the [adj.] _________________________ of the Civil War. The North and the South were fighting bloody battles against each other. 11. (page 23) One April day a huge battle was fought in the [noun] _________________________ at Shiloh, Tennessee. Thousands of soldiers were killed. Noun (single) - ability to wait without becoming angry - machine for printing - person; guy - small metal blocks with letters/numbers - southern states of the U.S. Noun (plural) - small packs Verb - use instead of 25 Adjective - cut (into) - middle - near the area (where Al lived) - smart; sharp - wonderful Adverb / Prep. - during this time - on 12. (page 23) Al saw how interested the office people were when they heard the news. He [verb] _________________________ that people everywhere wanted to know about the [adj.] _________________________ battle. [adv.] _________________________ Al saw the [noun] _________________________ to sell more newspapers than ever that day. 13. (page 23) He hurried to a man [adj. exp.] _________________________ giving Al newspapers to sell. 14. (page 24) "Would you trust me with a thousand copies?" Al asked. "I promise to pay back every cent." "A thousand copies!" the man said. "What a crazy idea!" But he let Al take the newspapers on loan. Then Al got three friends to help him [verb] _________________________ the newspapers to the train [noun] _________________________ . 15. (page 24) Suddenly Al had another idea. Why not get the news about the battle sent to the railroad stations right away? The [noun] _________________________ could then [verb] _________________________ the news to the waiting [noun] _________________________ . That way they would be excited and curious to read about Shiloh [adv.] _________________________ their train – and Al, the news butcher – arrived. 16. (page 24) Al asked the Detroit station [noun] _________________________ to send out the Shiloh news [noun] _________________________ to all the railroad stations. The Detroit telegrapher [verb] _________________________ . 17. (page 24) By the time Al reached each station, a big crowd was waiting to buy newspapers. At the first station, he sold each copy for ten cents. At the next station he [verb] _________________________ the price to fifteen cents. By the time the train [verb] _________________________ Port Huron, he sold the last copies for thirty-five cents each! 18. (page 24-25) Al was a clever fellow all right! That night, after great success in [noun] _________________________ , a thought came to Al. "The telegraph notice [verb exp.] _________________________ ," he said to himself. "The telegraph is just about the best thing [adj. exp.] _________________________ . I want to become a telegraph operator." 19. (page 25) At age fifteen, with this exciting new [noun] _________________________ , Al also decided to change his name. He now preferred to call himself Tom. Noun (single) - business - notice of new information - opportunity; possibility - person operating a message machine - station Noun (plural) - things being sold - travelers - workers Verb - arrived at - carry - increased - knew and understood - said yes - tell - was successful (worked) 26 Adjective / Adverb - happening - immediately - newest - responsible for - when Vocabulary practice for chapter 6 Directions: Write the meaning for each word in the blank. Use your work from Activity 6. agreed __________________________________ announcement __________________________________ bundles __________________________________ clever __________________________________ depot __________________________________ engraved __________________________________ local __________________________________ lug __________________________________ press __________________________________ realized __________________________________ replace __________________________________ type __________________________________ venture __________________________________ 27 Now called Tom, Edison worked as a Western Union telegraph operator. He was soon to become a full-time inventor. 28 Unit 3 – Adverb phrases and clauses In this unit, you will learn the grammatical differences between when and while adverb clauses, and between while adverb clauses and during adverb phrases. You will also begin to study how to sequence events in before and after adverb clauses and phrases. Unit 3 objectives In this unit, you will learn to: 1. use grammatical information to distinguish between phrases and clauses 2. use verb morphology to correctly identify while and when clauses 3. understand how before and after are used to indicate sequence of events in English 29 Vocabulary list for chapter 7 boxcar – Suddenly, a loaded boxcar rolled off a side track. (noun C) collision – Luckily, both trains stopped before there was a collision. (noun C) device - It was a bother to wake up every hour. So Tom made a device to solve the problem. (noun C) dispatching – Tom had to send a signal to the train dispatching office every hour. (adj.) freight train – One night Tom was supposed to signal a freight train that another train was coming in the opposite direction. (noun C) grateful – Mr. MacKenzie was grateful that Tom had rescued his son. (adj.) gravel – They fell onto the gravel. (noun U) operate – Tom operated a small telegraph station in Port Huron. (verb T) platform – Tom stood waiting on the station platform. (noun C) share – Tom paid for his share of the food. (noun single) shelter – Tom saved little money for food, clothing, or shelter. (noun U) tinkered – Tom tinkered with Mr. Walker’s watch repair instruments. This made Mr. Walker angry. (verb I) trousers – He wore a shirt, wrinkled trousers, and a pair of old shoes. (noun plural) My Study Notes 30 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 7: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 7, pages 26-31) Directions: First read Chapter 7 in your book. Then complete the sentences with: before, after, when, while, or during. Part I: Directions: Underline the first event, but do not underline the second event. Then, use before or after in these sentences. The rules are: after + first event; before + second event. Example: Thomas Alva Edison was hard-of-hearing after he had scarlet fever. 1. (page 26) ____________ a boxcar rolled off a side track, it rolled onto the main track and moved faster and faster. 2. (page 26) Tom grabbed Jimmy off the track ____________ the boxcar sped past them. 3. (page 27-28) ____________ Tom rescued Jimmy, Jimmy’s father, Mr. MacKenzie, gave Tom telegraph lessons every afternoon. Soon, Tom was living in Mount Clemens with the MacKenzie family. 4. (page 28) ____________ several months, Tom had learned the Morse Code and how to operate the telegraph machine. 5. (page 28) ____________ he could leave the MacKenzie’s, Tom had to find another job. 6. (page 28) ____________ Tom found a job in Port Huron, he worked as a telegraph operator in Mr. Walker’s jewelry and variety shop. 7. (page 29) ____________ Tom made a device to send the signal automatically, he did not need to wake up every hour anymore. 8. (page 29) Luckily, the trains stopped ____________ they hit each other. 9. (page 29-30) ____________ this experience, Tom was very upset, and he decided to leave Ontario. He never stayed very long at one job because it was hard for him to stay out of trouble. 10. (page 31) ____________ several years, Tom decided that he did not want to be a telegraph operator for the rest of his life. He wanted to be free, and he liked using his imagination better than following rules. 11. (page 31) ____________ Tom became bored with sending and receiving messages, he began experimenting with a new system to allow two messages to travel at the same time. 12. (page 31) It was not a long time ____________ Tom realized that he could be an inventor. 31 Part II: Directions: Underline the verb in the first clause/phrase of these sentences. NOTE: Sometimes there is no verb. Then, use while or when or during in these sentences. The rules are: when, while, and during are about events happening at the same time. The grammar is different: when + a full sentence with a simple present or past verb; while + a full sentence with a progressive (…ing) verb; during + noun phrase. Example: When Thomas Alva Edison had scarlet fever, he lost some of his hearing. 13. (page 26) ____________ Tom was waiting on the station platform, a freight train was switching boxcars in the railroad yard. 14. (page 26) ____________ Tom looked up, he saw the stationmaster’s little son, Jimmy, playing on the track. 15. (page 28) There were no telegraph messages, ____________ Tom was reading copies of a magazine called Scientific American and fooling around with Mr. Walker’s watch repair instruments 16. (page 28) __________ Tom fooled around with Mr. Walker’s watch repair tools, Mr. Walker became angry. 17. (page 28) __________ the Civil War, it was easy for Tom to find a new job because many men were away fighting battles. 18. (page 28) ____________ Tom found a new job, he moved to the Stratford Junction station in Ontario, Canada. 19. (page 29) He was sixteen years old ____________ he became the night time telegraph operator. 20. (page 29) Tom had to send a signal to the train every hour ____________ the night. It was a bother to wake up every hour. Tom made a device (small machine) to solve the problem. 21. (page 29) Tom was not fired ____________ his boss learned about the automatic signals. 22. (page 29) One night ____________ two trains were coming toward each other, Tom was unable to send a message out in time. 23. (page 30) Tom spent his money on books and materials for experiments. One time he only had 50 cents in his pocket ____________ he arrived in a city. 24. page 30) ____________ Tom was traveling, Tom and his friends kept in touch by sending each other telegraph messages. 25. (page 31) At that time, people could send only one message at a time through a telegraph wire. The second message had to wait, ____________ someone was sending the first message. 32 Vocabulary practice for chapter 7 Directions: Write the Chapter 7 words for these parts-of-speech and definitions. ____________________ (adj.) sending ____________________ (adj.) thankful ____________________ (noun C) piece of equipment; small machine ____________________ (noun C) crash ____________________ (noun C) raised area in front of a train stop ____________________ (noun C) train car with sides and roof for carrying freight (things people buy and sell) ____________________ (noun C) train that carries things people buy and sell ____________________ (noun plural) pants ____________________ (noun single) portion; part ____________________ (noun U) a place to live ____________________ (noun U) small pieces of rock ____________________ (verb I) tried to figure out something; make small changes ____________________ (verb T) used and controlled 33 Vocabulary list for chapter 8 boasted – He boasted that he didn’t change his clothes until he finished a project. (verb + that) budgets – Tom spent most of his money. He didn’t like bookkeeping or making budgets. (noun C) councilmen – Tom worked on an electric voting machine for city councilmen in Washington, D.C. (noun C) fired up – Tom was fired up with excitement about inventions. (adj. expression) investment – In Boston, he went to work for an investment business. (noun C) manufacturing – Tom was thinking about manufacturing his new invention. (noun U) patent – Tom received a patent for his electric voting machine. The patent protected his invention so no one else could steal his idea and make money from it (noun C) plenty – He ran into plenty of problems. (pronoun) projects – One of Tom’s first projects was the duplex telegraph. (noun C) stock – The investment company used different machines to print the prices of stocks. Tom invented a new stock printer telegraph. (noun C) surrounded – People surrounded Tom, and these people were tinkering with things like optic glass materials, fire alarms, and telegraphs. (Verb T) My Study Notes 34 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 8: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 8, pages 32-38) Directions: First read Chapter 8 in your book. Then complete the sentences with: before, after, when, while, or during. Part I: Directions: Underline the first event, but do not underline the second event. Then, use before or after in these sentences. The rules are: after + first event; before + second event. Example: Thomas Alva Edison was hard-of-hearing after he had scarlet fever. 1. (page 32) ____________ Tom arrived in Montreal, he got a message about a job opening from his friend, Milt Adams. 2. (page 32-33) Tom got the message from Milt Adams ____________ he moved to Boston. 3. (page 33) Tom worked on the telegraph duplex ____________ work hours. 4. (page 34) ____________ one year, Tom decided to become a full-time inventor. 5. (page 33-34) ____________ Tom worked for the Western Union Telegraph Co, he worked for Charles Williams. 6. (page 34) Tom received money ____________ he arranged for a business loan from a few rich men in Boston. 7. (page 35) ____________ Tom invented his electric voting machine, the Washington lawmakers did not want to buy his machine. 8. (page 35-36) Tom decided to make only inventions that people wanted ____________ his negative experience with his electric voting machine. 9. (page 36) Tom lived in Boston ____________ he moved to New York City. 10. (page 36) ____________ Tom began his job with the investment company in New York City, he invented a new machine for printing stock prices. 11. (page 36) The investment company gave Tom a lot of money ____________ he invented the new machine for printing stock prices. 12. (page 36) Tom rented a building, installed equipment, and hired two helpers ____________ he moved to Newark, New Jersey, 13. (page 36) Tom had almost no money left ____________ he rented a building, installed equipment, and hired two helpers. 14. (page 37) ____________ Tom improved the telegraph machine, four messages could not be sent at the same time on one wire. 35 15. (page 37) Tom was happy that he had not given up ____________ he invented the quadraplex telegraph, 16. (page 37) Soon ____________ Tom met Mary Stilwell, they fell in love and got married. Part II: Directions: Underline the verb in the clause/phrase after the blank in these sentences. NOTE: Sometimes there is no verb. Then, use while or when or during in these sentences. The rules are: when, while, and during are about events happening at the same time. The grammar is different: when + a full sentence with a simple present or past verb; while + a full sentence with a progressive (…ing) verb; during + noun phrase. Example: When Thomas Alva Edison had scarlet fever, he lost some of his hearing. 17. (page 32) ____________ Tom arrived in Montreal, he had only a little money in his pocket. 18. (page 33) ____________ his free time, Tom read new books about electricity. 19. (page 34) At first, ____________ he was working for Charles Williams, Tom earned no money. 20. (page 34) ____________ Tom was living in Boston, he invented an electric voting machine. 21. (page 34) ____________ law makers in Washington, D.C. voted, they had to speak their votes. 22. (page 35) ____________ 1968, Tom got his first patent for his electric voting machine. 23. (page 35) ____________ a person has a patent, another person cannot copy the same invention and make money from it. 24. (page 36) ____________ Tom was living in New York City, he worked for an investment company. This company used machines to show stock prices. 25. (page 36) ____________ Tom had enough money, he could start his own company and have a laboratory of his own. 26. (page 36-37) ____________ Tom was working, he often ate poorly or nothing at all. 27. (page 37) Sometimes, ____________ Tom was working, he fell asleep at his worktable. 28. (page 37) ____________ he was working on a project, he often did not change his clothes or comb his hair for days. 29. (page 37) ____________ Tom had problems inventing something, he did not give up. 30. (page 37) ____________ this part of his life, Tom worked on many inventions at the same time. 31. (page 37) ____________ Tom and Mary were dating, they went for a ride in Tom’s carriage. 32. (page 37) ____________ their marriage, Tom and Mary had three children. 36 Vocabulary practice for chapter 8 Directions: Write the Chapter 8 words for these parts-of-speech and definitions. ____________________ (verb T) were around nearby ____________________ (adj.) lots; many ____________________ (adj.) ready to do something ____________________ (noun C) assignments; jobs ____________________ (noun C) people managing the government ____________________ (noun C) formal registered agreement that someone has the right to make and sell a product (Another person can’t make and sell this product; only the patent holder can make and sell it.) ____________________ (noun C) plans for saving and spending money ____________________ (noun C) small part of a business (Ex: When you buy stock in Google, you are buying part of the Google Corporation.) ____________________ (noun U) using money to make more money (for example: buying and selling stocks) ____________________ (noun U) making (something) in a factory ____________________ (verb T) bragged; exaggerated about himself 37 Edison’s Phonograph: The phonograph was Edison's first major invention. Edison’s Telephone: Thomas Edison made improvements to the telephone, which was invented by Alexander Graham Bell in 1876. 38 Unit 4 – More about before and after In this unit, you will continue to learn about before and after clauses of English. You will also study how to determine the sequence events in before and after clauses and phrases. You will use this information to answer questions with correct verb forms. Unit 4 objectives In this unit, you will learn to: 1. use reading comprehension and logic to determine the order of events 2. select the correct adverb (before or after) to introduce clauses to show time sequence. 3. write the correct verb form following a question 39 Vocabulary list for chapter 9 acres – Tom bought several acres of land in Menlo Park, New Jersey. (noun C) assistants – Tom hired many assistants – chemists, mathematicians, machinists, and draftsmen. (noun C) convert – Alexander Graham Bell invented a machine to convert human voice sounds into electrical current. (verb T) cylinder – A cylinder soaked in ink was rolled over the punctured waxed paper. (noun C) duplicate – This made a duplicate copy of the wax paper original. (adj.) flashed – An idea flashed through Edison’s mind. (verb I) original – This made a duplicate copy of the wax paper original. (noun C) pastures – The cows roamed in nearby pastures. (noun C) picket fence - The picket fence kept cows away from the building. (noun C) punctured – A cylinder soaked in ink was rolled over the punctured waxed paper. (adj.) record – Why not record those vibrations? (verb T) seeped – The ink seeped through the holes onto another sheet of paper underneath. (verb I) stencil – The waxed paper became a stencil, and many copies could be made. (noun C) story – He built a two-story wood building. (noun C) struck a deal – They struck a deal. (verb expression) surrounded – The building was surrounded by a picket fence to keep away cows. (adj.) transmitter - Thomas Edison made improvements to Alexander Graham Bell’s telephone. He made a better transmitter. (noun C) underneath – The ink seeped through the holes onto another sheet of paper underneath. (adv.) vibrations – They conducted tests to learn about vibrations and sound waves. (noun C) My Study Notes 40 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 9: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 9, pages 39-45) Directions: First read Chapter 9 in your book. Then answer these questions with correct verbs and with before or after clauses/phrases. Remember: after + first event; before + second event. Example: When did Thomas Alva Edison become hard-of-hearing? ANSWER: Thomas Alva Edison became hard-of-hearing after he had scarlet fever. 1. (page 39) When did Tom buy several acres of land in Menlo Park, New Jersey? ANSWER: Tom __________________ several acres of land in Menlo Park ____________ he decided to leave Newark. 2. (page 39) When did Tom build a two-story building on this land? ANSWER: Tom __________________ a two-story building on this land ____________ people called the building an “Invention Factory.” 3. (page 39) When were there no research laboratories like Tom’s? ANSWER: There __________________ no research laboratories like Tom’s ____________ Tom started his research laboratory. 4. (page 41) When did Tom hire many assistants? ANSWER: Tom __________________ many assistants soon ____________ the building was finished. 5. (page 41) When did Tom invent an electric pen? ANSWER: Tom __________________ an electric pen ____________ he made stencils for a copy press. 6. (page 41) When were people able to make many copies of a document? ANSWER: People __________________able to make many copies of a document _____________ Tom’s electric pen made stencils for the copy press. 7. (page 41) When were Tom and his assistants very happy? ANSWER: Tom and his assistants __________________ very happy _____________ they had developed and manufactured several products. 8. (page 42) When did Alexander Graham Bell begin working on an instrument to change human voice sounds into electrical current? ANSWER: Alexander Graham Bell __________________ working on this instrument _____________ he married a deaf woman. 41 9. (page 42) When did Thomas Edison work at the Charles Williams workshop? ANSWER: He __________________ at the Charles Williams workshop _____________ Alexander Graham Bell. 10. (page 42) When did Alexander Graham Bell’s telephone transmit and receive actual words? ANSWER: His telephone __________________ real words one year _____________ June, 1875. 11. (page 43) When did Alexander Graham Bell get a patent on his telephone? ANSWER: He __________________ a patent on his telephone _____________ he started the Bell Telephone Company. 12. (page 43) When did Western Union hire Thomas Edison? ANSWER: Western Union __________________ him _____________ Bell started the Bell Telephone Company. 13. (page 43) When did Thomas Edison notice a lot of carbon black inside his kerosene lamp? ANSWER: He __________________ a lot of carbon black inside his lamp _____________ it went out. 14. (page 43-44) When did Thomas Edison make a better telephone than Alexander Graham Bell? ANSWER: He __________________ a better telephone _____________ he used carbon on the transmitter. 15. (page 45) When were Western Union and the Bell Telephone Company in a business “war?” ANSWER: They __________________ in a business “war” _____________ they made an agreement. 16. (page 45) When did Western Union stop working on telephones? ANSWER: Western Union __________________ working on telephones _____________ it made an agreement with the Bell Telephone Company. 17. (page 45) When did Tom get the idea to begin recording sound vibrations? ANSWER: Tom __________________ this idea _____________ he experimented again and again with sound wave vibrations. 42 Vocabulary practice for chapter 9 Directions: Write the correct word for the blank in these new sentences. Use the words from chapter 9. 1. A good idea ________________________ (verb I) through my mind while I was eating lunch. 2. A hearing aid will ________________________ (verb T) speech sounds into electricity and makes them louder. 3. A large company will need to hire many ________________________ (noun C). 4. Cattle eat grass in ________________________ (noun C). 5. Deaf people can feel sound ________________________ (noun C). 6. Edison could ________________________ (verb T) different noises on his new machine. 7. He had a ________________________ (adj.) arm because he was careless with a knife. 8. In geometry, students learn to calculate the area of a ________________________ (noun C). 9. She can make many copies from a ________________________ (noun C). 10. Some people build a ________________________ (noun C) around their house. 11. The house was ________________________ (adj.) by trees. 12. The TV station needs a more powerful ________________________ (noun C) to send out a stronger signal 13. The water leaked through the roof into the room ________________________ (adv). 14. They live in a ten________________________ (noun C) building. 15. Today, we make ________________________ (adj.) copies of work with a machine. 16. Tom bought several ________________________ (noun C) of land in the country. 17. Water ________________________ (verb I) through the roof because of the holes. 18. We ________________________ (verb expression) and started a new business. 19. We studied a copy of the painting, but we had no ________________________ (noun C). 43 Vocabulary list for chapter 10 applauded – After the demonstration, people applauded. (verb I) brass – He used a brass cylinder on the model. He covered the cylinder with tinfoil. (noun U) charming – Some people thought the phonograph was only a charming toy. (adj.) cylinder – The cylinder turned, and a needle tip scratched grooves into the tinfoil. (noun C) demonstration – Tom gave a demonstration in many cities. (noun C) gathered – Everyone gathered around the model. (verb I) granted – The U.S. government granted Edison a patent for the phonograph. (verb T) model – Tom’s assistants worked on the first model of the “talking machine.” (noun C) NOTE: Find the cylinder, shaft, and crank on the illustration on page 47. NOTE: Find the patent numbers on the back of a piece of equipment that you own. patent - Two months later, he received a patent. (noun C) preserve – The phonograph could preserve important speeches. (verb T) recited – He recited a poem. (verb T) rotate – Tom turned the crank to rotate the cylinder. (verb T) sketches – He drew hundreds of sketches. (noun C) thrilled – The president was thrilled at the demonstration. (adj.) wonder – December 6, 1877, was a time of wonder in the factory. (noun U) My Study Notes 44 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 10: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 10, pages 46-50) Directions: First read Chapter 10 in your book. Then answer these questions with correct verbs and with before or after clauses/phrases. Remember: after + first event; before + second event. Example: When did Thomas Alva Edison become hard-of-hearing? ANSWER: Thomas Alva Edison became hard-of-hearing after fever he had scarlet 1. (page 46) When did Tom’s assistants think he was crazy? ANSWER: They __________________ he was crazy ______________ he decided to make a machine to record and play back voices. 2. (page 46) When did Tom draw hundreds of sketches for a recording machine? ANSWER: Tom __________________ hundreds of sketches ____________ his assistants worked on the first model. 3. (page 47) When did everyone gather around? ANSWER: Everyone __________________ around ____________ the model for the machine was finished. 4. (page 47-48) When did Tom shout “Mary had a little lamb” into the mouthpiece? ANSWER: He __________________ “Mary had a little lamb” ____________ he could play it back on the phonograph. 5. (page 48) When was Tom very excited? ANSWER: He __________________ very excited ____________ the recording machine worked. 6. (page 48) When did Thomas Edison receive a patent for his phonograph? ANSWER: He __________________ a patent for it ____________ two months. 7. (page 48) When did Thomas Edison invent the phonograph? ANSWER: He __________________ the phonograph ____________ newspaper reporters, magazine writers, and tourists came to Menlo Park, New Jersey. 8. (page 48-49) When did Thomas Edison go to many cities to demonstrate his recording machine? ANSWER: He __________________ to many cities ____________ he invented the recording machine. 45 9. (page 48) When did people call Thomas Edison the “Wizard of Menlo Park?” ANSWER: They __________________ him the “Wizard of Menlo Park” ____________ he invented his recording machine. 10. (page 49) When was Thomas Edison invited to Washington, D.C.” ANSWER: He __________________ invited to Washington, D.C. ____________ he had already visited many other cities. 11. (page 49) When did the scientists see the recording machine? ANSWER: The scientists __________________ the machine ____________ President Hayes saw it. 12. (page 49) When did President Hayes learn about the recoding machine? ANSWER: President Hayes __________________ about the machine ____________ scientists saw it. 13. (page 49) When did Edison arrive at the White House? ANSWER: He __________________ at the White House ____________ Mrs. Hayes awoke. 14. (page 49) When did Mrs. Hayes wake up? ANSWER: She __________________ up ____________ Thomas Edison demonstrated the machine. 46 Vocabulary practice for chapter 10 Directions: Write correct word for the blank in these new sentences. Use the words from chapter 10. 1. ________________________ (noun U) is a shinny gold-colored metal. 2. A ________________________ (noun C) has round sides and can roll down a hill. 3. A painter might make many ________________________ (noun C) before the final painting. 4. An inventor can get a ________________________ (noun C) from the government for a new product. 5. First, an inventor will usually make a ________________________ (noun C) of a new invention. 6. Mr. Collins is a ________________________ (adj.) young man. Many people like him. 7. The actors were ________________________ (adj.) because the show was very successful. 8. The government ________________________ (verb T) her a patent for her new invention. 9. The play was good and the people ________________________ (verb I). 10. The professor gave a ________________________ (noun C) so students would learn to use the machine. 11. The student memorized a poem and ________________________ (verb T) it from memory. 12. The students________________________ (verb I) around the machine so they could see the demonstration. 13. Today, video cameras can ________________________ (verb T) important events. 14. We had to ________________________ (verb T) the board to paint the other side. 15. Will the 21st century be a time of ________________________ (noun U)? 47 An artist shows Tom and his helpers at work in the lab. Many long, hard hours of experimenting with different materials led to one of the greatest inventions of all time. 48 Unit 5 – Difficult question forms In this unit, you will work on question forms that often are difficult for English language learners. You will learn to tell which words signal yes/no answers and which words indicate information answers. You will study yes/no questions with have, has, had, and should. You will also study information questions with which, how did, and what happened. Unit 5 objectives In this unit, you will learn to: 1. tell which questions require yes/no answers and which require specific information 2. give short English answers to which … or questions 3. write complete short sentences to what happened questions 4. write complete short phrases to how did questions 49 Vocabulary list for chapter 11 causes – Oxygen causes a filament to burn out quickly. (verb T) coated – Tom coated a cotton thread with carbon. (verb T) crew – Tom hired a crew of 2000 people. (noun C) discouraged – Tom never became discouraged. (adj.) district – The power station generated and controlled electricity throughout the district. (noun C) ditches – They dug ditches, installed pipes, and connected wires. (noun C) filament – An electric current would pass through a filament (a thin fiber or wire) and heat the filament. (noun C) flickered – Some filaments flickered on and off. (verb I) formed – He formed an electric company. (verb T) generate – Tom developed a system to generate and send out electricity. (verb T) glow – The glow of an arc light was blinding. Tom’s goal was to control incandescence (the bright glow from heat). (noun single) installed – They dug ditches, installed pipes, and connected wires. (verb T) invested – Many people invested money in the electric company. (verb T) lasted – Arc light lasted only a few hours. (verb I) NOTE: Find the filaments in the pictures of Edison’s sketches on page 54 and in the picture on page 56. obtained – Tom obtained money from his inventions. (verb T) plenty of – There were plenty of breakdowns and delays. (pronoun exp.) practical – Tom was always practical. Now he wanted to bring light to cities. (adj.) show-off – Some magazines called Tom a “show-off.” (noun C) sparks – In the arc lamp, sparks of electricity jumped across pieces of carbon. (noun C) split – Some filaments split apart. (verb I) substance – Carbon is the substance at the end of a burned matchstick. (noun C) the globe – Soon cities across the globe had light from electricity. (noun specific) vacuum pump – They developed a special mercury vacuum pump to get all of the air out of the glass. (noun C) weary – Tom’s assistants became weary. (adj.) My Study Notes 50 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 11: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 11, pages 51-58) Directions: First read Chapter 11 in your book. Next, circle each Yes/No question word. Then write a very short answer to each question. Do not copy sentences or phrases from the text. Some of the questions are partly finished; use these as models for the others. NOTE: Have, Has, Had, Should are YES/NO question words. Which – … or …, How did …, What happened …are not YES/No questions. Example: Had Thomas Alva Edison become hard-of-hearing from scarlet fever? Yes 1. (page 51) How did people make light in 1878? ANSWER: with ________________________________________________________ 2. (page 51) Had scientists been working for a long time to make light? 3. (page 51) What happened to the sparks of electricity in an arc lamp? ANSWER: They _______________________________________________________. 4. (page 51) Should arc lamps be used inside? 5. (page 51) Should people look into an arc lamp? 6. (page 53) Had Tom made many sketches and filled many notebooks before he invented the electric lamp? 7. (page 53) Which kind of lamp was Tom working on – an arc lamp or an electric lamp? 8. (page 53) What would happen after current passed through a wire and heated the wire? ANSWER: It would _____________________________________________________. 9. (page 53) How did Tom find the right materials to use for the filament? ANSWER: by trying _____________________________________________________ 10. (page 53) What happened to a piece of Mr. MacKenzie’s beard? ANSWER: Tom _________________________________________________________. 11. (page 54) Had one magazine given Tom some money? 12. (page 54) Which element causes a light bulb to burn out quickly – mercury or oxygen? 51 13. (page 54) Have Tom’s assistants become tired after working for many months on the electric light? 14. (page 54) How did they finally get the air out of the glass? ANSWER: with _______________________________________________________ 15. (page 55) Had Tom tried a cotton thread filament before October 22, 1879? 16. (page 55) Which substance did they use to cover the cotton thread – filament or carbon? 17. (page 55) Should the filament in a light bulb last a long time? 18. (page 55) What happened when Tom turned on his new light bulb? 19. (page 55) Had Tom used gas, flame, or oil in his lamp? 20. (page 55) Which kind of power did Tom use in his lamp – gas, candles, oil, or electricity? 21. (page 55) How did people travel to Menlo Park to see the “light of the future?” ANSWER: by _________________________________________________________ 22. (page 57) What happened at night after the people arrived at the station? 23. (page 57) How would Tom bring light to cities? ANSWER: by __________ing ____________________________________________ 24. (page 57) Had Tom invented many machines before he had a successful power station? 25. (page 57) What happened while the workers were making the power station? 26. (page 57-58) Had Tom hired many people to dig ditches, install pipes, and connect wires after the power station started in 1882? 52 27. (page 58) What happened after Tom pulled the main power switch on Pearl Street in New York City in 1882? 28. (page 58) Had Tom become a rich man after he invented the electric light bulb? 29. (page 57-58) How did other cities get light soon after New York City had light? ANSWER: by _________ing power stations 30. Which kind of power do we mostly use for lights in buildings today – gas, oil, electricity, or kerosene? 53 Vocabulary practice for chapter 11 Directions: Write the word and the part-of-speech for each definition. Use words from chapter 11. Word Part-ofSpeech Definition ___________________________ _________ covered ___________________________ _________ earth ___________________________ _________ got; received ___________________________ _________ long narrow hole in the ground ___________________________ _________ machine that removes air from a closed space ___________________________ _________ many ___________________________ _________ part of a city ___________________________ _________ produce; make ___________________________ _________ put in ___________________________ _________ started ___________________________ _________ use money to make more money in the future ___________________________ _________ useful ___________________________ _________ workers ___________________________ _________ bright light ___________________________ _________ broke ___________________________ _________ continued to stay on ___________________________ _________ made a light that went on and off ___________________________ _________ makes ___________________________ _________ person who tries to impress others ___________________________ _________ ready to give up ___________________________ _________ small bits of bright electrical light ___________________________ _________ stuff ___________________________ _________ thin wire ___________________________ _________ tired 54 Mina Miller was the second wife of Thomas Edison. 55 Vocabulary list for chapter 12 boarding school – Tom’s daughter, Marion, went to boarding school. (noun C) broke out – One winter, a fire broke out in one of his factory buildings. (verb expression) cared about – Tom had cared about Mary. (verb expression) competition – He worried about competition from other inventors. (noun U) exploded – Once a pot of hot wax exploded in his face and burned him. (verb I) fame – Tom didn’t care much about fame. (noun U) images – One man made a machine to project large images on a screen. (noun C) peephole – Tom and an assistant made a machine to see movies through a peephole. (noun C) project – Later, one man made a machine to project large images on a screen. (verb T) proposed – Tom proposed marriage to Mina Miller. (verb T) spared – Everything was destroyed; only the laboratory was spared. (adj.) studio – Tom built the first movie studio. (noun C) version – Tom improved another inventor’s version of an electric battery. (noun C) X-rays – Tom designed a screen to show X-rays. (noun C) My Study Notes 56 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 12: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 12, pages 59-65) Directions: First read Chapter 12 in your book. Next, circle each Yes/No question word. Then write a very short answer to each question. Do not copy sentences or phrases from the text. Some of the questions are partly finished; use these as models for the others. NOTE: Have, Has, Had, Should are YES/NO question words. Which – … or …, How did …, What happened …are not YES/No questions. Example: Had Thomas Alva Edison become famous all over the world? Yes 1. (page 59) Has Tom stopped working after he becomes famous? 2. (page 59) Have inventors been jealous of each other? 3. (page 59) What happened to Tom’s wife, Mary? ANSWER: She _______________________________________________________. 4. (page 59) Had Tom spent a lot of time with his wife before she became ill? 5. (page 60) Which of Tom’s children went to boarding school – Tom’s daughter or Tom’s sons? 6. (page 59-60) Which woman was Tom’s second wife – Mary or Mina? 7. (page 61) What happened after Tom moved to West Orange? ANSWER: He ________________________________________________________. 8. (page 61) Had Tom invented an electric battery? 9. (page 61) How did people study X-ray pictures? ANSWER: with _______________________________________________________ 10. (page 61) Which part of the world had the best material for making rubber – the United States or South America? 11. Should people be near X-ray machines for a long time? 57 12. (page 61) What happened before Tom’s face got burned? ANSWER: A ___________________________________________________________. 13. (page 62) People liked taking pictures. How did they take pictures? ANSWER: with _________________________________________ 14. (page 62) How did people see moving pictures with a kinetoscope? ANSWER: by looking into __________________________________________________ 15. (page 63) What happened after Tom invented a moving-picture projector? ANSWER: Many people could _____________________________ at the same time. 16. (page 63) What happened when the roof of the movie studio opened? ANSWER: Sunlight ______________________________________________________. 17. (page 63) Which environment is best for taking pictures – a dark room or a light room? 58 Vocabulary practice for chapter 12 Directions: Write the word and the part-of-speech for each definition. Use words from chapter 12 Word Part-ofSpeech Definition ___________________________ _________ being well-known and famous ___________________________ _________ blew up ___________________________ _________ electromagnetic waves that can go through solid things [Doctors use them to take pictures of the inside of a person’s body.] ___________________________ _________ loved ___________________________ _________ not destroyed ___________________________ _________ pictures of things ___________________________ _________ place where people make movies ___________________________ _________ residential school; school where students stay day and night ___________________________ _________ shine; show with a bright light ___________________________ _________ small hole to look through ___________________________ _________ started ___________________________ _________ suggested ___________________________ _________ two or more people in a contest to see who has the best product ___________________________ _________ way of doing something 59 Vocabulary list for chapter 13 created – Tom, who was seventy years old, created a research department for the U.S. Navy. (verb T) devices – He also worked on parts for submarines and devices to find enemy submarines. (noun C) documents – A handwritten note from Thomas Alva Edison to General John J. Carty is one of the many Edison documents that were saved for all to see and learn from. (noun C) emblem – A special “Golden Jubilee” emblem was created for the 50th anniversary of Edison’s lightbulb. (noun C) failed – Tom’s health failed rapidly. (verb I) Golden Jubilee – A special “Golden Jubilee” emblem was created for the 50th anniversary of Edison’s lightbulb. (noun proper) hailed – People hailed him as the “man of the century.” (verb T) honored – People often praised and honored Tom. (verb T) praised – People often praised and honored Tom. (verb T) submarines – He also worked on parts for submarines and devices to find enemy submarines. (noun C) My Study Notes 60 Student's Name _____________________ Date _____________________ Did you work with a tutor? ______ Tutor's Name _____________________ Activity 13: Thomas Alva Edition (Chapter 13, pages 66-70) Directions: First read Chapter 13, the last chapter in the book. Next, circle each Yes/No question word. Then write a very short answer to each question. Do not copy sentences or phrases from the text. Some of the questions are partly finished; use these as models for the others. NOTE: Have, Has, Had, Should are YES/NO question words. Which – … or …, How did …, What happened …are not YES/No questions. Example: Had Thomas Alva Edison become famous all over the world? Yes 1. (page 66) Has Tom lost more of his hearing? 2. (page 66) Had Tom stopped reading and learning after he grew old? 3. (page 66) How did Tom help the U.S. during World War I? ANSWER: by ___________________________________________________________. 4. (page 66) Which things did Tom research for the U.S. Navy – tools for finding submarines or light bulbs? 5. (page 66) What happened in October 1929? ANSWER: There was _____________________________________________________. 6. (page 67) Had Thomas Edison and Henry Ford become friends? 7. (page 68) Which kind of technology did Thomas Edison improve – atomic power or communication? 8. (page 68) What happened to homes and work places because of Edison’s inventions? ANSWER: Homes and work places had ______________________________________. 9. (page 68) What happened on October 18, 1931? ANSWER: Thomas Alva Edison __________________________. 61 10. (page 68) Had Edison lived a long life? 11. (page 68) Which phrase best describes Edison – “man of the century” or “citizen of the U.S.?” 12. (page 69) Should we remember Edison because of his inventions? 13. (page 70) How did Thomas Edison write letters? ANSWER: with _________________________________ 14. (page 70) Which words did Edison say into the first phonograph – “the original model” or “Mary had a little lamb?” 15. (page 70) Have many of Edison’s documents been saved for us to see today? 16. Which of Thomas Edison’s inventions have you used? 62 Vocabulary practice for chapter 13 Directions: Write the word and the part-of-speech for each definition. Use words from chapter 12 Word Part-ofSpeech Definition ___________________________ _________ started ___________________________ _________ boats that can move underwater ___________________________ _________ equipment and machines ___________________________ _________ said good things about him ___________________________ _________ respected, admired, and looked up to ___________________________ _________ 50th anniversary celebration ___________________________ _________ symbol with a special design ___________________________ _________ got bad; became very weak and ill ___________________________ _________ said with great respect ___________________________ _________ written papers, letters, notes 63 Edison’s Light Bulb: Edison lit up the world with his invention of the first light bulb. 64