Guided Notes 13.4
advertisement

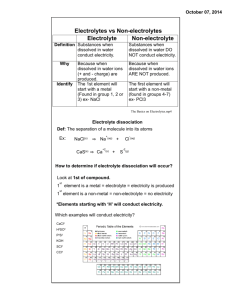
Sec. 13.4: “Physical Properties of Solutions” 1. Conductivity: the ability to conduct an ____________ ___________. a. Conductivity of a substance depends on 2 things: i. Does it contain ______________ particles? ii. Are the particles free to _____________ around? 2. ____________ move freely within a _________, thus allowing it to conduct electricity. a. Solid NaCl contains ________, but they can’t move, so solid NaCl is ________ a conductor. b. An aqueous solution of ________ compounds, such as NaCl, contains charged _______, which _______move around. Solutions of ioninc compounds _________ electricity. c. __________ water does ________ conduct electricity. 3. Electrolyte: a substance that ____________ in water to give a solution that conducts an _____________ _____________. a. Strong electrolytes ____________ dissociate into __________ and conduct electricity well. b. __________ compounds are usually __________ electrolytes. c. Weak electrolytes provide __________ ions in solution. d. Even in high ______________, solutions of ____________ electrolytes conduct electricity ____________. e. Covalent compounds may be __________ electrolytes, __________ electrolytes, or ____________________. 4. The extent to which ____________ dissociate into ions is indicated by the _______________ of their solutions. a. The sugar sucrose _________ __________ ionize at all in solution. b. It is a _______________ and __________ __________ conduct electricity. c. Non-electrolyte: a liquid or solid substance that __________ _________ allow the flow of an electric current, either in solution or in its pure state, such as __________ or sucrose. 5. Acids react with water to form the hydronium ion, _____________. a. Hydronium ion: an __________ consisting of a __________ combined with a molecule of water; ___________. b. Acetic acid is a __________ electrolyte. In water, only about ________ of acetic acid molecules ____________ into hydronium ions and acetate ions: H3O+ (aq) + CH3COO- (aq) H2O (l) + CH3COOH (aq) 6. Hydrogen chloride dissolves in water to form a strongly conducting solution called _______________ __________. a. Hydrogen chloride is a __________ electrolyte because it ionizes _______________, as shown by the following equation: HCl (g) + H2O (l) H3O+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) 7. The terms strong and weak have nothing to do with __________________. a. The term strong means that the substance provides a __________ proportion of __________ in solution. 8. Rainwater in a relatively unpolluted area, is a ____________________ of electricity. a. Water from wells, lakes, or rivers has been in contact with soil and rocks, which contain __________ compounds that _______________ in water. b. The more _________ dissolved in water, the __________ it conducts electricity. 9. The __________ properties of water are changed when substances ___________ in it. a. __________ can be added to icy sidewalks to melt the ice. b. The salt actually ___________ the freezing point of water. c. Ice is able to melt at a ___________ temperature than it normally would. d. This change is called: ____________________________________________. 10. Non-volatile ____________ such as salt also increase the _____________ point of a solvent. a. This change is called: _____________________________________________. b. Glycol in a car’s radiator _____________ the boiling point of water in the radiator, which prevents _____________. c. It also ____________ the freezing point, preventing _____________ in cold weather. 11. Any physical effect of the _____________ on the _____________ is a colligative property. a. Colligative property: a property of a substance or system that is determined by the number of particles present in the system but independent of the properties of the particles themselves. b. What does this mean in plain English? ______________________________________________________________ 12. Any ____________, whether an electrolyte or non-electrolyte, contributes to the colligative properties of the _____________. a. The ____________ the particle concentration, the ____________ the boilingpoint _______________ or the freezing-point _______________. 13. 1 mole of NaCl is expected to give _______ the amount of change as 1 mole of sucrose, C12H22O11: NaCl (s) Na+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) C12H22O11 (s) C12H22O11 (aq) _____ dissolved particles _____ dissolved particle CaCl2 has about _______ the effect as 1 mole of sucrose: CaCl2 (s) Ca 2+ (aq) + 2 Cl- (aq) _____ dissolved particles 14. Dissolved solutes __________ the __________ ____________ of the solvent. a. Colligative properties are all caused by a __________ in the __________ pressure of the solvent. b. A solution has ____________ solvent particles per volume than the pure solvent has, so ____________ solvent particles are available to _____________. c. Vapor pressure will be ____________ in proportion to the number of ___________ particles. 15. Soap molecules contain long, ________________ hydrocarbon chains, which are ____________ in the non-polar dirt and oils on your skin. a. Soap molecules also have _____________ charged ends, which are __________ in the water you use to wash your hands. b. Soap: a substance that is used as a cleaner and __________________in water. 16. Soap is a __________________. a. Surfactant: a compound that concentrates at the _______________ surface between two _________________ phases. b. A ________________ is a surfactant that is used for cleaning purposes. c. Detergent: a water-soluble cleaner that can ______________ dirt and oil. Usually these products are ____________ and not natural products d. A __________ is a particular type of _____________ and is a natural product. 17. __________ is an emulsifying agent. a. Emulsion: any mixture of two or more _______________ liquids in which one liquid is dispersed in the other. b. An emulsifying agent links the ___________ and _____________ phases. c. Without an ______________ agent, the polar and nonpolar molecules remain _________________. d. Lecithin is an emulsifying agent that is used in salad dressing to keep the oil and vinegar mixed. 18. Soaps are actually ___________. a. When dissolved, soaps form _________. The polyatomic anion of soap contains a long, ___________________ part. b. It is this non-polar hydrocarbon chain that is soluble with _______ and _______. 19. Soaps are _______ ideal cleansing agents because the salts of some of their anions are ____________ in water, especially salts of calcium, magnesium, and iron(III). a. __________ water has high concentrations of these cations, which react with anions such as the palmitate anion to form _______________ salts. b. This is where bathtub ________ comes from. 20. Synthetic _______________ can be used in hard water ___________ forming precipitates and scum a. Today, almost all laundry products and shampoos contain synthetic detergents. b. The basic structure of a synthetic detergent is the same as the structure of a ___________. c. The long non-polar tail of the detergent is connected to the salt of a sulfonic acid which does _________ form insoluble precipitates with magnesium or calcium, which are found in ___________ water. 21. Whew…that’s it for this chapter!