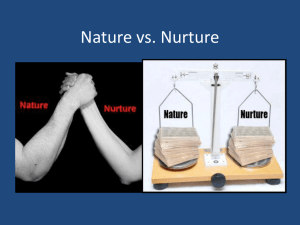
Chapter 3 Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity What are some
advertisement

Chapter 3 Nature, Nurture, and Human Diversity I. II. III. IV. V. What are some examples demonstrating the similarities and differences among humans? a. Differencesb. SimilaritiesWhat are several questions that interest behavior geneticists? a. Behavior geneticist’s studyb. Question 1: c. Questions 2: What are the main components of our genes? a. Define Chromosomes. How many do humans have? b. Define DNA: c. Define Genes: d. What do human genome researchers do/discovered? e. How are human traits influenced by gene complexes? What are the differences between identical and fraternal twins and how do twin studies help us understand the effects of environment and heredity? a. Define Identical twins: 1. Supporting detailb. Define Fraternal twins: 1. Supporting detailc. What did Bouchard (2004) find in terms of identical twins? d. What did John Loehlin and Robert Nichols (1976) find about genetic influences? e. Provide a brief summary of separated twins Jim and Jim f. Provide a brief summary of separated twin Oskar Stohr and Jack Yufe How can adoption studies help geneticists understand the effects of environment and heredity a. What have researchers found in terms of members of adoptive families? 1. 2. 3. b. Steven Pinker (2002) explains thatc. Is adoptive parenting a fruitless venture? Why not? 1. VI. Benefits of adoptive home life? How does the relative stability of our temperament illustrate the influence of heredity on development? a. Define Temperament: b. VII. Provide examples on temperamental differences found in children 1. Example 2. Example 3. Example What is heritability? a. Define Heritability: b. What percentage of our individual personality or intelligence is inherited? Why? c. Group differences. Provide a brief summary on group differences and heritability d. VIII. IX. Nature and Nurture. What is the analogy that is provided to help explain nature and nurture? How can genetically influenced traits evoke responses from others? a. Why are genes and experience both important? b. Define Interactions: What is molecular genetics? a. b. c. d. e. X. Define Molecular genetics: What is the goal of molecular behavior? How can genetic tests be useful? What are some benefits of DNA scanning techniques? What are “designer babies”? Pros and cons of this? 1. 2. 3. What do evolutionary psychologists a. Define Evolutionary psychologists: b. Describe the research of Dmitry Belyaev c. d. e. f. Define Natural Selection: Define Mutation: What does “Genes and experience together wire the brain.” (p.108) Why are all humans so much alike? g. XI. XII. Natural Selection and Mating Preferences (111) 1. What are traits men and women find attractive in the opposite sex? a. Men b. Women 2. How do genes play a part with these preferences? What are some criticisms of the evolutionary perspective? a. b. c. What are some of the conditions that can affect human development? a. How does nurture in the womb play a role in development? (eg. Identical twins) b. How can experience modify the brain? 1. What did research by Rosenzweig and Krech find about rats? 2. How does touch and massage benefit baby rats (Fields, 2001)? 3. How does this relate to humans? c. XIII. How much credit (or blame) do your parents deserve in terms of your development? 1. Provide examples on why parents do matter in child development (nurture) a. b. 2. Provide examples on why shared environmental influence matter a. b. 3. How is parent nurture like nutrition? 4. Summarize Howard Gardner’s position on parents and peers What is culture? a. Define Culture: 1. Describe the importance of the following a. Language b. Preservation of innovation c. Division of labor 2. Our capacity for culture/similarities is important because? 3. 4. How do cultures differ? a. Define Norm: 1. Example b. Define Personal Space: 1. Example Provide two examples demonstrating why changes in the human gene pool cannot account for culture over time? a. Example b. Example XIV. What are the differences between an individualist culture from a collectivist culture? a. Define Individualism: b. Define Collectivism: c. Describe life in an individualist culture d. Describe life in a collectivist culture e. XV. How does child rearing differ in individualist and collectivist cultures? 1. Individualist: 2. Collectivist: What are some biological and psychological differences between males and females? a. In terms of aggression: b. In terms of social power: c. In terms of social connectedness: d. e. XVI. 1. Men – Side by side 2. Women – Tend and Befriend How is biological sex determined? 1. Define/Explain X Chromosomes: 2. Define/Explain Y Chromosomes: 3. Define/Explain Testosterone: What are gender roles and what are the two theories of gender-typing? 1. Define Role: 2. Define/Explain Gender roles: 3. Do gender roles reflect what is biologically natural for men and woman? 4. 5. 6. 7. How doe gender roles vary over time? a. Example b. Example Define Gender identity: Define Gender-typed: Summarize the concept of social learning theory 8. Summarize the concept of gender schema theory Reflections on Nature and Nurture a. What is the biopsychosocial approach to development?