Click to view - Kb`s Day Nursery Sticky Logo
advertisement

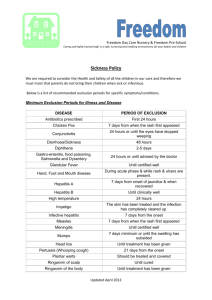
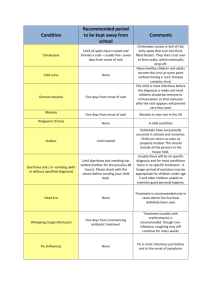
CHILDREN WITH ALLERGIES, SICK OR INFECTIOUS When a child enrols at Kb’s the parents/carers are required to provide information regarding any allergies or intolerances. This information is recorded on the child’s registration form. If a child has an allergy or intolerance this information is then posted on the allergy form in the downstairs kitchen & upstairs craft room with the severity of allergy. All staff are made aware of the child’s allergy and the information will be transferred to the child’s contact card. If medication is required parents will train staff on the administration of the medicine and required forms will be completed. (see Administration of Medicine policy) The child’s key person or friend will administer the medicine. A medicine form is to be completed each day for the child and parents to sign before and after it is administered or each 6 months when it is a chronic ongoing allergy or condition. SICKNESS POLICY The following advice is taken from the Kent Health Protection Unit (document publication 2008) and applies to all staff and children. Any staff absent from work due to ill health must notify the nursery by phone as soon as you are aware of their sickness, the duration of the sickness or sick note and when returning to work. They MUST phone the nursery by 4pm the day before they intend to return to work. Exclusion from Nursery Infectious diseases are common among young children and nursery settings often present an ideal situation for diseases to spread. Some diseases may present a risk to others such as pregnant women, and children may need to be excluded. Many diseases are so trivial that excluding them from education cannot be justified. There are some general rules about the exclusion of children from school and other childcare settings. Children who are unwell should be in the comfort of their home, even if they are not infectious. This is up to the key person’s discretion. If parents are unavailable to collect the child the alternative named person will be called. Children who are contagious may be excluded from Nursery. It is at the discretion of the nursery to decide who and when they will exclude, eg conjunctivitis noticed in one child is contagious bacteria and very easily transmitted between young children and in such circumstances the manager will make a decision to exclude the infected child. Please see attached Common communicable diseases document. Children and staff with diarrhoea should be excluded for 24hours from last bout, unless the diarrhoea is known to be due to a non-infectious cause (e.g celiac disease, ulcerative colitis) Children and staff who have vomited, whether at home or nursery shall be excluded from the setting until 48 hours after the last episode of vomiting. If the vomiting is due to a medical condition the manager must be consulted and exclusion will be at their discretion. Children who have been prescribed antibiotics or any other medicine can usually return to nursery before they have completed the course, providing they are well. The child will need to be at home for the first 24hrs of receiving the medication if they haven’t had that specific drug before. Common Communicable Diseases Chickenpox Chickenpox and Shingles are caused by the same virus (varicella-zoster virus). Chickenpox may start with a headache and a temperature, but the rash itself may be the first sign of the illness. The rash appears as small red ‘pimples’, usually starting on the back, chest and stomach and spreading to the face, scalp, arms and elsewhere. Within a few hours the ‘pimples’ become blisters which begin to dry and crust within about 2 days. The rash appears in a succession of crops over 3-5 days. Chickenpox is spread from person to person by contact with the blisters or by airborne droplets. It is highly infectious for one or two days before the rash appears and for not more than five days after the appearance of the first spots. The incubation period is 14 to 21 days. Staff or children with chickenpox or shingles must stay away from the nursery for at least five days from the onset of the rash. There is no need to stay away until the lesions are healed. Conjunctivitis This is an infection of the outer structures of the eye and the inside of the eyelid which may be caused by several different organisms, including bacteria and viruses. The first signs of infection are excessive watering and irritation of the eye, followed by swelling and possible discharge of pus from the eye. The infection can be spread between people by direct contact and in circumstances where spread with the nursery is evident, it will be necessary to recommend exclusion of affected children until they recover. Slapped Cheek Syndrome This is a mild viral disease due to parvovirus B19, spread by respiratory droplets. By the time the ‘slapped cheek’ rash appears most patients are no longer infectious and excluding children with the rash serves no useful purpose. German Measles (Rubella) Rubella is now very rare in school age children. It spreads by contact with droplets from the respiratory system of infected individuals. The incubation period is 14 to 23 days, the child is infectious for one week before the rash appears until one week after its onset. Children or staff with rubella should be excluded for five days from when the rash first appeared. Glandular Fever Although it can occur in younger children, this viral disease is much more common in adolescents. There is no treatment. This is not a very infectious disease and the child should only be kept away if feeling unwell. Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease This is a mild disease caused by the Coxsackie’s virus. A fever is common, with ulcers in the mouth and a red, raised rash on the hands and feet, which then develops into small blisters. The incubation period is three to seven days. As this is a mild disease and is most infectious before the blisters appear, it is not necessary for children to be excluded from school. Measles Measles is an acute and highly infectious condition which can be a serious disease. The illness starts with what appears at first to be an ordinary cold, sore eyes, sneezing, coughing and a runny nose. These symptoms are accompanied by a fever. They are usually present for about four days before the rash appeals and during this period the child is very infectious. So, if measles is suspected it is wise to keep the child away from nursery. Scarlet Fever Scarlet Fever illness is caused by certain strains of streptococcal bacteria. This is usually a mild diseases, starting with fever a sore throat, followed by a rash which does not affect the face, but there is a blushing of the cheeks. The infection can be treated with antibiotics. An infected child should stay away for 24 hours from the start of antibiotics. Impetigo A skin infection usually caused by the staphylococcus or streptococcus bacteria. The infection usually affects the face, particularly around the nose and mouth and is spread by direct contact. The incubation period is usually 4 to ten days and the child can return to nursery once the scabs are completely crusted and healed. Whooping Cough The disease is most infectious in the early weeks before the typical ‘whoop’ develops and is spread by droplets. Children should stay away from nursery until five days from commencing antibiotic treatment. Vomiting and Diarrhoea Children and staff who have symptoms of vomiting should be excluded from nursery until that person has been symptom free for 48 hours. If the vomiting is due to a medical condition, pregnancy or travel sickness this will be at the discretion of the manager. Children and staff who have symptoms of diarrhoea should be excluded from nursery until that person has been symptom free for 24 hours. (Not 24 from the first bout of diarrhoea but 24 hours from the last bout of diarrhoea.) Kb’s Day Nursery Jan 2016 Kb’s Review Date: January 2017