Spring 2008 Exam 1 answers
advertisement

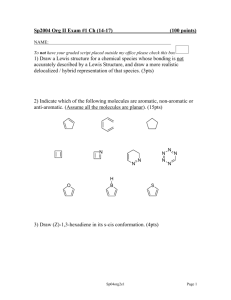
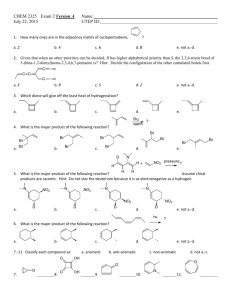
Chemistry 320, Spring 2008 Exam 1 1. Label these compounds aromatic, antiaromatic, or neither. (10 pts) Antiaromatic a. neither aromatic b. O c. e. d. Aromatic antiaromatic 2. Ultraviolet spectroscopy is used to determine the amount of protein in a sample. In this method, absorbance is measured at 280 nm. Which of the following amino acids would you expect to absorb at that wavelength? [note: the carbonyl group does NOT absorb at that wavelength] (10 pts) Absorbs at 280 nm doesn’t Doesn’t Absorbs at 280 nm 3. An unknown compound has the formula C7H12. a. What is the DU for this compound? (2 pts) DU = 2 [2*7+2-12]/2 = 4/2 b. The unknown reacts with H2 in the presence of Pd to give C7H16. What information does this provide about the structure of the unknown? (4 pts) There are no rings in the compound. The degrees of unsaturation are either due to two double bonds or one triple bond. c. The unknown reacts with H2 in the presence of Lindlar catalyst to give C7H14. What information does this provide about the structure of the unknown? (4 pts) There must be a triple bond in the molecule. H2/Lindlar reacts with alkynes, but not alkenes. d. The product from part c, C7H14, gives these two aldehydes upon ozonolysis. Show the structure of the original unknown. (5 pts) 4. Show syntheses of these compounds from the indicated starting materials. (10 pts) a. 2-chloro-4-nitrotoluene from benzene b. p-nitrobenzoic acid from benzene 5. Provide a step-by-step mechanism for one of the following reactions. (10 pts) 6. Show the products for five of these reactions. Don’t forget to show stereochemistry where appropriate. (15 pts) Multiple Choice: (3 pts each) Choose the one best answer. 7. In the first step of the following reaction, nucleophile. H H C C + H-Br H H + a. H , Br b. H+, CH2=CH2 c. +CH2CH3, Brd. HBr, Bre. CH2=CH2, Br- is the electrophile and is the CH3CH2Br 8. The definition of an aromatic compound includes which of the following: a. It is fully conjugated. b. It is cyclic. c. Has 4n+2π electrons. d. All of the above. e. None of the above. 9. Which statement below does not describe an antiaromatic compound? a. The HOMOs are half filled. b. Each atom has a p-orbital that participates in conjugation. c. The compound exhibits high reactivity. d. There are 4n + 2 electrons in conjugation. e. c and d 10. Which compound has the longest wavelength max? O a. O b. O c. O d. e. d. e. 11. Which alkene would react fastest with Br2 in CH2Cl2l? a. b. c. 12. In the reaction of toluene with nitric acid and sulfuric acid which structure below is an appropriate resonance structure for the intermediate? CH3 H NO2 H I a. b. c. d. e. CH3 CH3 H NO2 II NO2 III I only II only III only I and II none of the above 13. Which set of reagents is used for the purpose of adding water to an alkene in a Markovnikov addition without rearrangement? a. BH3, THF followed by H2O2, NaOH b. H2O, H2SO4 c. disiamylborane followed by H2O2, NaOH d. Hg(O2CCH3)2, H2O followed by NaBH4, NaOH e. none of these 14. Which of the following is a correct statement regarding electrophilic aromatic substitution? a. The arenium ion intermediate will lose a hydrogen to regain aromaticity, usually from a position other than the site of electrophilic attack. b. Formation of the arenium ion intermediate has a high activation barrier due to loss of aromaticity. c. The arenium ion intermediate has several resonance structures and is negatively charged. d. Reformation of the aromatic ring has a low activation barrier and therefore occurs slowly. e. Many suitable electrophiles are unreactive and can be stored for long periods of time prior to use. 15. Place the following in order of reactivity towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. O OH Cl NO 2 I II III a. I > II > III > IV b. I > II > IV > III c. II > I > III > IV d. II > I > IV > III e. III > IV > II > I CH 3 IV 16. What would be the best series of synthetic reactions to accomplish the following transformation? NO 2 CN Br a. 1. Fe, HCl; 2. Br2, FeBr3; 3. NaNO2, HCl; 4. CuCN b. 1. Br2, FeBr3; 2. Fe, HCl; 3. NaNO2, HCl; 4. CuCN c. 1. Fe, HCl; 2. NaNO2, HCl; 3. Br2, FeBr3; 4. CuCN d. 1. Fe, HCl; 2. NaNO2, HCl; 3. CuCN; 4. Br2, FeBr3 e. 1. Br2, FeBr3; 2. NaNO2. HCl; 3. Fe, HCl; 4. CuCN