Eastern Intermediate High School
advertisement
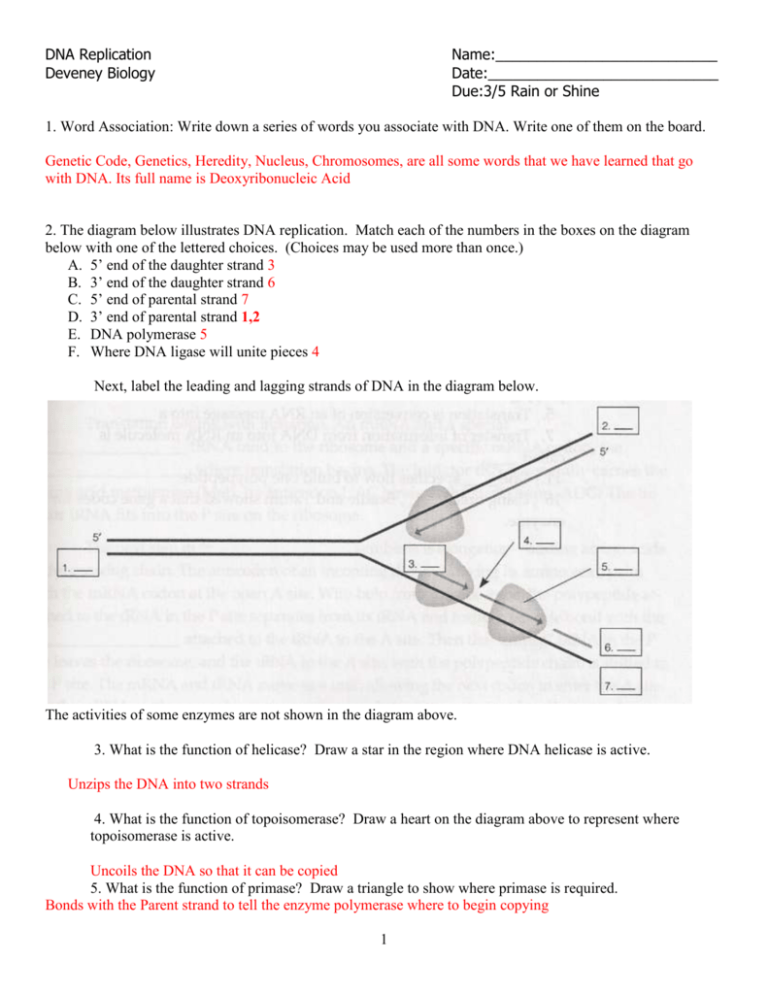
DNA Replication Deveney Biology Name:___________________________ Date:____________________________ Due:3/5 Rain or Shine 1. Word Association: Write down a series of words you associate with DNA. Write one of them on the board. Genetic Code, Genetics, Heredity, Nucleus, Chromosomes, are all some words that we have learned that go with DNA. Its full name is Deoxyribonucleic Acid 2. The diagram below illustrates DNA replication. Match each of the numbers in the boxes on the diagram below with one of the lettered choices. (Choices may be used more than once.) A. 5’ end of the daughter strand 3 B. 3’ end of the daughter strand 6 C. 5’ end of parental strand 7 D. 3’ end of parental strand 1,2 E. DNA polymerase 5 F. Where DNA ligase will unite pieces 4 Next, label the leading and lagging strands of DNA in the diagram below. The activities of some enzymes are not shown in the diagram above. 3. What is the function of helicase? Draw a star in the region where DNA helicase is active. Unzips the DNA into two strands 4. What is the function of topoisomerase? Draw a heart on the diagram above to represent where topoisomerase is active. Uncoils the DNA so that it can be copied 5. What is the function of primase? Draw a triangle to show where primase is required. Bonds with the Parent strand to tell the enzyme polymerase where to begin copying 1 6. The basic steps of DNA replication: a. DNA topoisomerase untangles the coils while DNA Helicase unzips the DNA. The DNA is separated into two strands. b. DNA primase bonds at the replication fork. DNA polymerase pairs the bases A-T and G-C. DNA Polymerase checks work and corrects mistakes Nucleotides are paired c. DNA ligase follows behind and bond the nucleotides together. Two strands of DNA are created. Directions: Complete each sentence. 8. Guanine, cytosine, thymine, and ____adenine______________ are the four ____nitrogenous bases______________ in DNA. 9. In DNA, guanine always forms hydrogen bonds with ___cytosine_______________. 10. The process of ______replication____________ produces a new copy of an organism’s genetic information, which is passed on to a new cell. 11. The double coiled, “staircase” shape of DNA is called a _______double Helix___________. Directions: Answer each question in complete sentences. 12. What do the letters DNA stand for? ____Deoxyribonuclic acid__________________________________________________ 13. Where is DNA found? Nucleus Label the nucleotides (A, T, G, C) in the DNA molecule below: 2 14. What is the orginal strand of DNA called? What is the new strand of DNA called? The orginal Strand in the parental strand. The new strand is the the daughter strand 15. What is the first step in the process of DNA replication? From 6a DNA topoisomerase untangles the coils while DNA Helicase unzips the DNA. The DNA is separated into two strands. 16. Which enzyme is responsible for “unzipping” the DNA double helix? Helicase__________________ 17. Which enzyme is responsible for facilitating the hydrogen bonding between nucleotides in a new DNA molecule? Polymerase 18. Which enzyme is responsible for creating the covalent bonds that connect the sugarphosphate backbone of the new DNA molecules? Ligase_ 19. If the sequence of one single strand of DNA is C-A-A-G-T-A-G-G-C-T, what is the sequence of the complementary strand? GTTCATCCGA 20. Describe the origin of each strand of the new double helices created after DNA replication. Half of the strand is the parental strand Half of it is made from nucleotides floating around in the nucleus 21. Why is DNA replication important to the growth and development of a multi-cellular organism? Every cell must have a copy of its DNa 22. Place the following terms in the correct order from smallest to largest: Nucleosome, supercoils, coils, chromosome, Nucleotide Nucleotide, Nucleosome, coil, supercoil, chromosome 3 Original 23. The model of DNA below is ready to be copied. Compared to the original double helix, evaluate the copies made during three attempts of DNA replication. List any errors with the replication if they occurred: A T C C G T G Replication #1 T A G G AND C A C Replication #2 A T T A C G C G G C T A G C AND A T C A G T G T A G G C A C A T C C G T G T A G G C A C A T C C G T G List problems if any: _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ T A G G C A C List problems if any: _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ 24. Complete the diagram on the left. Then circle the areas in the diagram on the right that show a genetic mutation. DNA Correctly Copied DNA Incorrectly Copied A G C T A T A A G C T A T A A G C T A T A T C G A T G T 25. Explain how the mutations might have been caused in the diagram above. Toxic chemicals or radiation cause DNA to not be properly copied this can lead to mutations 4 G G C T A C A T C G A T A T








