Nutrition
advertisement

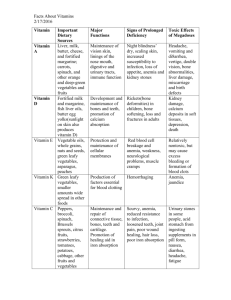
Iron Calcium Phosphorus Sodium Iodine • Saturated • Unsaturated MINERALS • • • • • • Sugars • Starches • Fiber • Amino acids • Complete • Incomplete CARBOHYDRATES A chemical compound that serves as a building block of proteins PROTEIN • Calorie FATS • Fat soluble • Water soluble VITAMINS VOCABULARY UNIT 2 The unit used to measure the energy value of foods. • Nutrient A chemical substance that helps maintain the body. • Malnutrition A deficient state of the body, caused by a lack of nutrition • Nutrition The study of how the body uses the nutrients in foods. NUTRIENT PROTEIN CARBS FAT VITAMIN A FUNCTION SOURCES Build & repair body cells Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dried beans, nuts, peas Carry nutrients, energy, keep warm Sugars – fruit, cakes, pies, candy Fiber – potatoes Starches – pasta, breads, cereals Energy, stores fat soluble vitamins, cushion organs, insulate, add flavor Keep eyes in good condition, helps eyes adjust to light, health skin Butter, margarine, salad oil, shortening, fat in meats Dark green & deep yellow veg., pumpkin, liver, potatoes, spinach, broccoli, carrot, sweet pot., red/orange peppers THIAMIN appetite, digestion, waste elimination, memory NIACIN digestion, healthy nervous system; prevent pellagra Liver, pork, milk, egg yolk, dry beans, whole grain breads, cereals, yeast, p. butter, potatoes, peas, bread skin, hair, eyes, repro. system, helps body use p,f,c for energy Milk, cheese, liver, kidneys, heart, eggs, green leafy veg, enriched grains, yeast RIBOFLAVIN VITAMIN C Normal growth, develop bones, teeth, gums, prevent infection & scurvy Pork, lean meats, fish, liver, bread Citrus, tomatoes, cantaloupe, strawberries, brussel sprouts, broccoli, cabbage, peppers NUTRIENT FUNCTION SOURCES VITAMIN D Strong bones & teeth, prevent rickets, helps body use calcium & phosphorus VITAMIN E Slows aging process, digests fat, healing Green leafy vegetables, nuts, whole grain, oils, cereals, milk, liver Promotes normal clotting of blood Liver, green leafy veg., cauliflower, oil, tomatoes, wh.grain, egg yolk, soybeans VITAMIN K IRON Builds hemoglobin (carry O2) CALCIUM PHOSPHORUS IODINE Strong bones & teeth, works with phosphorus Helps calcium build bones & teeth Helps thyroid gland to function properly Fortified milk, Sun, fish liver oils, egg yolk, liver, salmon, tuna Liver, variety meats, egg yolk, lean meats, yeast, raisins, molasses, green leafy, dried fruit & beans, peas, nuts Milk, milk products, green leafy, molasses, legumes Milk, ice cream, cheese, meat, poultry, wh. grain cereals, beans, peas, nuts, fish Salt water fish, iodized salt NUTRIENT PROTEIN CARBS FAT VITAMIN A THIAMIN NIACIN RIBOFLAVIN VITAMIN C FUNCTION SOURCES NUTRIENT VITAMIN D VITAMIN E VITAMIN K IRON CALCIUM PHOSPHORUS IODINE FUNCTION SOURCES NUTRIENT PROTEIN CARBS FAT VITAMIN A FUNCTION Build & repair body cells Carry nutrients, energy, keep warm Energy, stores fat soluble vitamins, cushion organs, insulate, add flavor Keep eyes in good condition, helps eyes adjust to light, health skin SOURCES Meat, fish, poultry, eggs, dried beans, nuts, peas Sugars – cakes, pies, candy Fiber – potatoes Starches – pasta, breads, cereals Butter, margarine, salad oil, shortening, fat in meats Dark green & deep yellow veg., pumpkin, liver, potatoes, spinach, broccoli, carrot, sweet pot. THIAMIN, appetite, digestion, waste elimination, memory NIACIN digestion, healthy nervous system; prevent pellagra RIBOFLAVIN skin, hair, eyes, repro. system, helps body use p,f,c for energy Milk, cheese, liver, kidneys, heart, eggs, green leafy veg, enriched grains, yeast VITAMIN C Normal growth, develop bones, teeth, gums, prevent infection & scurvy VITAMIN D Strong bones & teeth, prevent rickets, helps body use calcium & phosphorus Citrus, tomatoes, cantaloupe, strawberries, brussel sprouts, broccoli, cabbage, peppers Fortified milk, Sun, fish liver oils, egg yolk, liver, salmon, tuna VITAMIN E Slows aging process, digests fat, healing VITAMIN K Promotes normal clotting of blood IRON CALCIUM PHOSPHORUS IODINE Builds hemoglobin (carry O2) Strong bones & teeth, works with phosphorus Helps calcium build bones & teeth Helps thyroid gland to function properly Pork, lean meats, fish, liver, bread Liver, pork, milk, egg yolk, dry beans, whole grain breads, cereals, yeast, p. butter, potatoes, peas, bread Green leafy vegetables, nuts, whole grain, oils, cereals, milk, liver Liver, green leafy veg., cauliflower, oil, tomatoes, wh.grain, egg yolk, soybeans Liver, variety meats, egg yolk, lean meats, yeast, raisins, molasses, green leafy, dried fruit & beans, peas, nuts Milk, milk products, green leafy, molasses, legumes Milk, ice cream, cheese, meat, poultry, whole grain cereals, beans, peas, nuts, fish Salt water fish, iodized salt • Pellagra is a niacin deficiency disease. Italian word meaning ‘sour skin.’ Pellagra is classically described by "the four D's": diarrhea, dermatitis, dementia and death. A more [14] comprehensive list of symptoms includes: High sensitivity to sunlight Aggression Dermatitis, alopecia, oedema Smooth, beefy red glossitis Red skin lesions Insomnia Weakness Mental confusion Ataxia, paralysis of extremities, peripheral neuritis Diarrhea Dilated cardiomyopathy Eventually dementia Frostig and Spies (acc. to Cleary and Cleary) described more specific psychological symptoms of pellagra as:[15] Psycho-sensory disturbances (impressions as being painful, annoying bright lights, odours intolerance causing nausea and vomiting, dizziness after sudden movements) Psycho-motor disturbances (restlessness, tense and a desire to quarrel, increased preparedness for motor action) Emotional disturbances Extreme Goiter (Thyroid gland is located in the neck.) RICKETS Rickets is the softening of the bones in children, potentially leading to fractures and deformity. Rickets is among the most frequent childhood diseases in many developing countries. The predominant cause is Vitamin D deficiency, but lack of adequate calcium in the diet may also lead to rickets. Although it can occur in adults, the majority of cases occur in children suffering from severe malnutrition, usually resulting from famine or starvation during the early stages of childhood. Osteomalacia is the term used to describe a similar condition occurring in adults, generally due to a deficiency of Vitamin D. The origin of the word "rickets" is unknown. The Greek-derived word "rachitis" (meaning "inflammation of the spine") was later adopted as the scientific term for rickets, due chiefly to the words' similarity in sound. There are few dietary sources of Vitamin D. The best ones are fatty fish such as salmon and sardines and margarines supplemented with Vitamin D. Milk contains added Vitamin D, but for people who don't drink milk regularly, they get most of their Vitamin D from exposure of the skin to sunlight. The average person has enough Vitamin D stored in their body to last for two or three years. People who get little exposure to sunlight and don't drink lots of milk and eat foods rich in Vitamin D are most likely to suffer from rickets or osteomalacia. In particular, elderly people or latchkey children who're housebound or confined to residential or nursing homes are at most risk. Scurvy…. The pirate’s disease What Vitamin prevents C scurvy? Handout: “Nutrition: The Individual” 1. List the six basic nutrients. protein 2. Write the sentence that provides reminders of the first letter of each nutrient. 3. The energy required to carry on your life processes when your body is at rest is called ______ __________. What are the four functions that fats serve? 4. a. b. 5. 6. 7. 8. fats c. d. _______________ are a major source of energy. The body uses carbohydrates to manufacture ________, a sugar used by our cells. ________ is composed of amino acids that are used build and repair muscle tissue. There are 22 amino acids, but only ___ are essential for an adult’s diet. Handout: “Nutrition: The Individual” – (cont.) 9. __________ is used to aid digestion, carry off wastes, and regulate body temperature and chemical processes. 10. ____% of the human body is composed of water. 11. Most humans require at least ___ glasses of water per day. 12. The word ‘vitamin is derived from the term “ _______,” which means life. 13. Vitamins help the body to convert food into ________. 14. Inorganic elements which are scratched from the earth’s surface are called ______________. 15. List five examples of the answer for number 14 above. a. b. c. d. e. 16. _______ is a mineral which helps the blood carry oxygen. 17. Without _________your bones could not grow and heal. 18. R.D.A. stands for _________________________________. Handout: “Nutrition: The Individual” – (cont.) 19. What are the six groups of food represented in the USDA Food Pyramid? a. grains b. c. d. e. f. 1 5 ½ c. - 6 oz. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 20. How many servings should the average teen-ager have of each group? 21. The measurement of the heat or energy produced when food is burned in your body is called a ______________. 22. T or F People who are overweight often encourage their children to overeat or to eat too much sugar & starch. 23. T or F Diets based on eating one kind of food are very appealing and perfectly safe. 24. T or F It’s perfectly possible to lose weight on a well balanced diet which includes all of the foods in the food pyramid. 25. List three examples of carbohydrates: a. b. c. 3 -2 - 1 • 3 major nutrients that provide energy (have calories) • 2 fat soluble vitamins & sources where you can obtain them • 1 food group & the recommended serving size. WWW.CHOOSEMYPLATE.GOV Healthy Nutrition Guidelines Be sure to write the quantities & details Food Journal ~ Day 1 Breakfast Lunch Dinner Snacks Drinks Activities lasting more than 10 min. Food Journal ~ Day 2 Food Journal ~ Day 3 BELL RINGER The most concentrated source of energy is found in ______. Our biggest source of energy is from ________________.