BC Science 8 Chapter 2

BC Science 8 Chapter 2
2.1
Body Systems http://www.smm.org/tissues/
Systems:
A system is made of individual parts that work together as a whole.
A system is usually connected to one or more systems.
If one part of a system is missing or damaged, the system will not function well or not at all.
If Grade 8 we will be dealing with only the circulatory, digestive, respiratory, excretory, and
immune system.
Organ Systems:
Cell Tissue Organ Organ system Organism
Gland Muscle Tissue Heart Circulatory
Hormone Nerve Tissue
Nervous Connective
Lung blood Epithelial Tissue
2.2
Digestive http://www.argosymedical.com/Digestive/samples/animations/Digestion/index.html
(Digestion) http://www.argosymedical.com/Digestive/samples/animations/Dual%20Roles%20of%20the%20P ancreas/index.html
(Pancreas) http://www.argosymedical.com/Digestive/samples/animations/Sherwood%20Swallowing/index.
html
(Swallowing) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tat0QYxlCbo&feature=related
(Liver) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TWUZx738OZM&feature=related
(Liver & Pancreas)
Excretory http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XF_lF3J4ZKs
Nutrients: substances the body requires for energy, growth, development, repair and maintenance
-Carbohydrates: source of energy. Simple (glucose) and complex (chain of simple carbs – pasta, brown rice, and whole grains).
-Protiens: build parts of body muscle, skin, hair and nails.
Fish, meat, poultry, nuts soy and diary.
-Fats: build cell membranes. Butter oil, meat, milk.
Unsaturated fats are liquid at room temperature (corn oil, olive oil.) saturated fat are solid at room temperature (butter). Eating too much saturated fat can lead to plaque build up in arteries.
Sodium (Na) – nerve activity – (bacon, salt, butter)
Magnesium (Mg) – muscle and nerve activity, bone formation –
(fruit, veggies, grains)
Calcium (Ca) - muscle and nerve activity, teeth and bone formation, - (milk, grains, calcium fortified o.j.)
Phosphorus (P) - muscle and nerve activity, teeth and bone formation -(Milk, grains, veggies)
Copper (Cu) – development of red blood cells (grains, liver)
Potassium (K) - muscle and nerve activity, veggies and bananas
Sulfur (S) – hair, nails, and skin builder (Grains, cheese, eggs fruits)
Water – not a nutrient but transports nutrients and wastes, cools body through sweat. You need 3-5 L daily
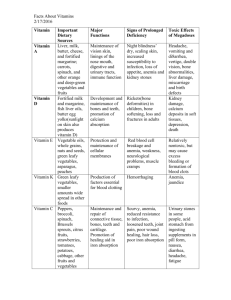
Vitamin A
This vitamin plays a really big part in eyesight: night vision and color. It helps your body fight infections by boosting your immune system.
Source
-milk fortified with vitamin A
-liver
-orange fruits and vegetables (like cantaloupe, carrots, sweet potatoes)
-dark green leafy vegetables (like kale, collards, spinach)
The B Vitamins
The B vitamins are important in metabolic activity — help make energy.
They also involved in making red blood cells , which carry oxygen throughout your body.
Source:
-whole grains
-fish
-poultry and meats
-eggs
-dairy products
-leafy green vegetables
Vitamin C
This vitamin is important for keeping body tissues in good shape. C helps you heal. (i.e. a cut)
This vitamin also helps your body resist infection .
Sources: citrus fruits - oranges sweet red peppers
Vitamin D
Need for strong bones and teeth. It also helps your body absorb calcium.
Sources: made in the skin when exposed to milk fortified with vitamin D fish egg yolks liver
Vitamin E
Protects your cells and tissues from damage. It is also important for the health of red blood cells.
Sources: whole grains leafy green vegetables vegetable oils like sunflower, canola, and olive egg yolks nuts and seeds
Vitamin K
Clotting of blood
Sources: leafy green vegetables dairy products, like milk and yogurt broccoli soybean oil
Four Stages: Ingesting, digesting, absorbing and eliminating
Enzymes: protien that helps speed up reations.
3 Enzymes you need to know about in gr 8: amaylase (mouth
– carbs), pepsin (stomach – protein) and bile (duodenum – fats)
Stage 1: Ingestion – when food enters mouth
Stage 2: Digestion-
-begins in mouth. Mechanical - teeth and tongue creating bolus
(small pieces of food). Chemical – amylase breaks down bolus ( complex to simple carbs)
-food then moves to the pharynx (area where air tube meets esophagus). Epiglottis covers airway tube when you swallow.
Food moves down the esophagus by peristalsis – muscle contractions.
-food then moves to the stomach. Inside the stomach is gastric
juice - HCL, mucus (protects the stomach walls), and the enzyme
pepsin. Pepsin breaks down protein. 2 sphincters in the stomach – one separates the esophagus from the stomach and the other separates the small intestine from the stomach.
Digestion
Small Intestine chime from the stomach enters the small intestine. It is 6m long and 2.5cm in diameter. The first meter of it is called the Duodenum. The pancreas, liver, gall bladder secrete into the duodenum. The liver produces Bile which contains enzymes to break down fats.
Stage 3: Absorbing
This occurs in the small intestine. It has villi to increase absorption of nutrients. It expands the surface area of the small intestine to 250 sq meters – size of a tennis court!!!!
The large intestine is 5cm by 1.5m. Its job is to absorb water
Bacteria: many live in the digestive system.
Ex: bacteria in the lg intestine produce
Vitamin K – blood clotting.
Stage 4: Eliminating
Undigested solid waste exits body via the anus as feces.
Excretory system – removes liquids and gases through the urinary tract.
Main organs – 2 kidneys, ureters,
bladder and urethra. Kidneys filter blood and form urine