Biology 12
advertisement

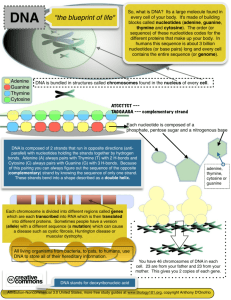
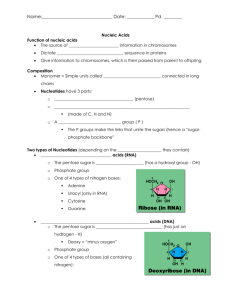
Biology 12 Mr. Ciardullo Name: ________________________ Date: __________ Period: ____ 2.7 - Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides 1. What are the two types of 1. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) nucleic acids? 2. RNA (ribonucleic acid) 2. What are two functions of 1. stores genetic information in the cell DNA? 2. replicates and transmits this information when a cell reproduces and when an organism reproduces 3. What is the science of altering the genes in living organisms biotechnology about? 4. What does DNA code for? the order in which amino acids are to be joined to form a protein 5. What does RNA convey? DNA's instructions regarding the amino acid sequence 6. What are the monomers nucleotides that make up nucleic acid polymers? 7. What are the 3 subunits 1. phosphate of a nucleotide? 2. pentose sugar 3. nitrogen-containing base 8. Label the 3 subunits in the diagram of a nucleotide at right 9. What are the names of 1. adenine (A) the 4 bases found in 2. thymne (T) nucleotides of DNA? 3. guanine (G) 4. cytosine (C) 10. Which bases have 2 rings adenine and guanine (called purines) 11. Which bases have 1 ring thymine and cytosine (called pyramidines) 12. Which base replaces uracil (U) thymine in RNA? 13. Predict whether it is a pyrimadine - 1 ring pyramidine or purine See Figure 2.28 page 40 to answer the following questions: 14. What is a linear molecule a strand of nucleotides called? 15. What is the backbone of alternating molecules of sugar - phosphate the DNA strand made of? 16. How many strands does a DNA has 2 DNA molecule have? How RNA has 1 many does an RNA have? 17. The 2 strands of DNA are double helix twisted into shape called a ...? 18. In DNA, adenine always adenine - thymine bonds with ...? and guanine guanine - cytosine always bonds with...? 19. What kind of bonds hold hydrogen bonds the complementary bases together? 20. How many hydrogen bonds adenine - thymine have 3 are there between adenine guanine - cytosine have 2 and thymine? Between guanine and cytosine? 21. What does ATP stand for, Adenosine triphosphate and where does the name Adenosine = adenine plus ribose come from? triphosphate because it has three phosphate groups 22. What are 2 functions of 1. monomers of nucleic acids nucleotides in cells? 2. energy carriers in cells 23. What is the difference it has 3 phosphate groups instead of 1 between ATP and the nucleotide it is based on? 24. Draw an ATP molecule 25. Where is the energy In the bonds between the phosphate groups stored in an ATP molecule? 26. What is ATP called when it ADP (adenosine diphosphate) loses a phosphate group? 27. List 3 ways in which the 1. used to synthesize macromolecules such as energy from ATP carbohydrates and proteins breakdown is used in cells 2. in muscle cells it is used to stimulate muscle contractions 3. in nerve cells it is used for the conduction of nerve impulses 28. From your knowledge of in the mitochondria cell structures, where in the cell is ATP broken down to produce energy? 29. In what kinds of cells muscle cells and nerve cells would you expect to see a lot of mitochondria?