Carbohydrates- monomers are monosaccharides (= simple sugars)
advertisement

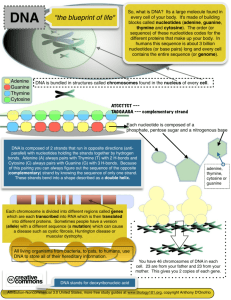
Carbohydratesmonomers are monosaccharides (= simple sugars) Contain C,H,O Short-term energy storage Categorized into simple & complex types Come from plants & glycogen from meat products Short-term energy storage in organs Ex’s: starch, glucose, glycogen, cellulose, fructose, sucrose Lipids: glycerol group and fatty acid chains Non-polar- don’t dissolve in H2O Release energy for use in cells (highest amt. of energy compared to any other MM) Provide protection for organs & cells (cell membrane) Aid in the absorption of vitamins Come in saturated (beef, animal oils, butter) or unsaturated form (veggie oils, fish oils). Regulates tissue inflammation and repair Maintains body heat Meats, dairy products, oils, steroids, hormones Proteins: amino acids Come in several different shapes; more than 100,000 kinds in the body Enzymes help regulate chemical reactions Structural material helps in repair of body (hair, skin, nails) Made through protein synthesis (central dogma of biology) Help protect body from pathogens (antibodies) Transport CO2 and O2 throughout bloodstream Allows muscle contraction Ex’s: enzymes, meat products, dairy, nuts, hemoglobin (blood), myosin & actin (muscle fibers) Nucleic Acids: nucleotides (nitrogen base, phosphorous group, sugar) - DNA bases Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine - RNA Uracil, Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine. Comes in either 1 (RNA) or 2 strands (DNA) Replication—process by which DNA copies itself. Contain hereditary info. And instructions for making proteins. Responsible for increasing genetic diversity through reproduction Ex’s: RNA, DNA