Topic 3.3 DNA Structure
advertisement
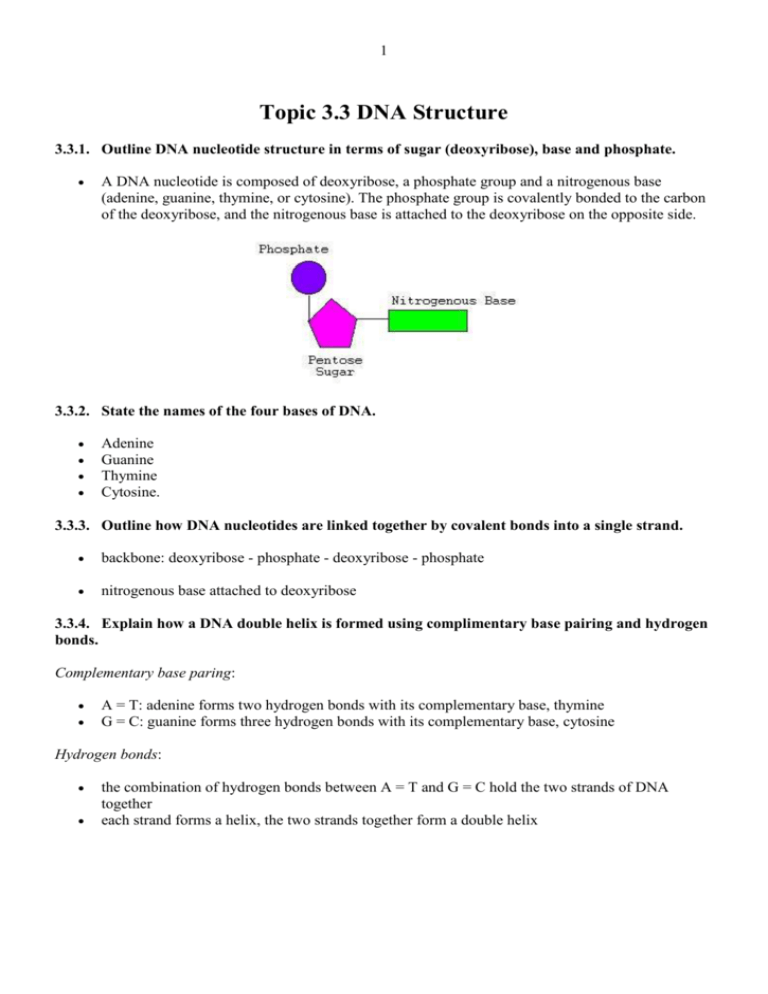
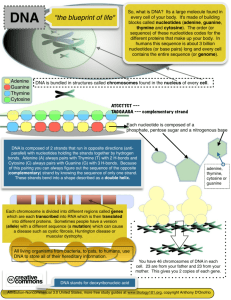
1 Topic 3.3 DNA Structure 3.3.1. Outline DNA nucleotide structure in terms of sugar (deoxyribose), base and phosphate. A DNA nucleotide is composed of deoxyribose, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, thymine, or cytosine). The phosphate group is covalently bonded to the carbon of the deoxyribose, and the nitrogenous base is attached to the deoxyribose on the opposite side. 3.3.2. State the names of the four bases of DNA. Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine. 3.3.3. Outline how DNA nucleotides are linked together by covalent bonds into a single strand. backbone: deoxyribose - phosphate - deoxyribose - phosphate nitrogenous base attached to deoxyribose 3.3.4. Explain how a DNA double helix is formed using complimentary base pairing and hydrogen bonds. Complementary base paring: A = T: adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with its complementary base, thymine G = C: guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with its complementary base, cytosine Hydrogen bonds: the combination of hydrogen bonds between A = T and G = C hold the two strands of DNA together each strand forms a helix, the two strands together form a double helix 2 3.3.5. Draw and label a simple diagram of the molecular structure of DNA.