Table S1: Sequences of the three PCR primer pairs A, B
advertisement

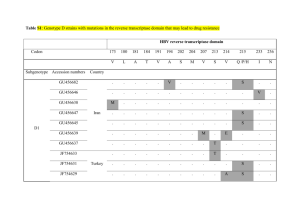
Table S1: Sequences of the three PCR primer pairs A, B, and C applied to determine the CEBPA mutational status. Gene Nucleotide sequence CEBPA-A-F CEBPA-A-R CEBPA-B-F CEBPA-B-R CEBPA-C-F CEBPA-C-R 5'-TCG CCA TGC CGG GAG AAC TCT AAC-3' 5'-AGC TGC TTG GCT TCA TCC TCC T-3' 5'-CCG CTG GTG ATC AAG CAG GA-3' 5'-CCG GTA CTC GTT GCT GTT CT-3' 5'-CAA GGC CAA GAA GTC GGT GGA CA-3' 5'-CAC GGT CTG GGC AAG CCT CGA GAT-3' Table S2A: Molecular characterization of CEBPA mutations. # pat. age FAB N-mutation Single CEBPA mutations: 1 38 M2 236-237insGC 2 51 M2 392-393insT 3 55 M2 245delG 4 49 M1 216-217insCG 5 22 M1 6* 33 M2 7” 53 M1 C-mutation 1079-1080insTCT Double CEBPA mutations: 1 40 M2 563-564insCG 1094-1095insCTG 2 57 M2 327-328insC 3 52 M2 395delC 4 47 M1 213delC 1098-1099insGTC 1076-1077insAAG 1088-1089insTCT 5 44 M2 327-328insC 1098-1099insGTC 6 27 M2 319insT 7 40 M1 291delC 940insAAG 937insCAG 8 52 M2 286-287insTC 1076-1077insCCG 9 51 M2 327insT 1094-1095insCTG 10 53 M1 291insGC 11 39 M1 213insAG 1076-1077insACG 1088-1089insCCG 12 29 M1 395insCG 937insCAG others AA change A29fsX160 A91fsX107 G32fsX159 P23fsX160 S310-311ins 692C>G Y181X 1083C>T Q312X Y138fsX160 L315-316ins E59fsX107 V316-317ins F82fsX159 K309-310ins P22fsX159 S313-314ins E59fsX107 V316-317ins D106X 314insK A47fsX159 313insQ P46fsX160 K309-310ins E59fsX107 L315-316ins A47fsX160 K309-310ins P22fsX160 S313-314ins F82fsX160 313insQ One patient had the following two point mutations of unknown significance and was not considered in this analysis: 1167G>A (inducing G340S) and 744745GC>TT (inducing A199L). *This patient also had the following point mutations: 672C>G, 676C>T, 678-679GG>TT, and 683C>T; they were all located on the same allele also carrying the 692C>G (encoding a novel stop codon) as identified by allele specific cloning of PCR products. * and “: These two patients had point mutations encoding a novel stop codon downstream of the ATG located at amino acid position 120. Thus, formation of the wild-type 42kDa and of the 30ka peptides is both affected. Table S2B: Clinical course of AML patients with CEBPA mutations. # pat. Age FAB DFS (months) OS (months) Single CEBPA mutations: 1 38 M2 6 2 51 M2 32 3 55 M2 12 4 49 M1 1 5 22 M1 22 6* 33 M2 42 7” 53 M1 3 8 33 15 3 23 43 5 Double CEBPA mutations: 1 40 M2 40 41 follow-up (months) relapse (months) AA change yes no yes yes no no yes A29fsX160 A91fsX107 G32fsX159 P23fsX160 S310-311ins Y181X Q312X 41 no 28 no Y138fsX160 L315-316ins E59fsX107 V316-317ins F82fsX159 K309-310ins P22fsX159 S313-314ins E59fsX107 V316-317ins D106X 314insK A47fsX159 313insQ P46fsX160 K309-310ins E59fsX107 L315-316ins A47fsX160 K309-310ins P22fsX160 S313-314ins F82fsX160 313insQ 33 23 43 2 57 M2 23 28 3 52 M2 2 3 4 47 M1 33 34 34 no 5 44 M2 35 36 36 no 6 27 M2 15 16 16 no 7 40 M1 33 34 34 no 8 52 M2 28 32 32 no 9 51 M2 11 12 10 53 M1 41 42 11 39 M1 20 24 12 29 M1 37 38 yes yes 42 no yes 38 no DFS: disease-free survival; OS: overall survival; Follow-up in months is indicated for patients alive and disease-free from time of diagnosis censored at their last follow-up visit. Table S3: Clinical characteristics of AML patients according to CEBPA mutational status. all CEBPA CEBPA wt CEBPA CEBPA mut single double (n=224) (n=205) (n=19) (n=7) (n=12) ______________________________________________________________________ _ sex 102f/112m 93f/102 9f/10m 3f/4m 6f/6m median age* 53 54 51 53 49 median WBC G/L 19.8 27.8 12.1 14.1 11.2 (range) (0.6-360) (0.6-360) (2.8-36) (3.2-36) (2.828) median % blasts in blood 68 72 60 65 58 (range) (0-99) (0-99) (12-90) (22-90) (12-88) median LDH units/L° 808 848 515 535 492 extramedullary manifestations (n) 51 48 3 1 2 de novo AML, n 204 194 19 7 12 secondary AML, n 20 20 0 0 0 MDS (n) 17 17 0 0 0 therapy-related (n) 3 0 0 0 0 consolidation in CR1+ chemotherapy (n) autologous transplant (n) allogenous transplant (n) FAB classification: M0 M1 M2 M4 M5 M6 M7 72 54 33 54 34 33 9 10 0 3 4 0 6 6 0 20 61 56 48 31 5 3 20 53 47 48 31 5 3 0 8 11 0 0 0 0 0 3 4 0 0 0 0 0 5 7 0 0 0 0 *All patients were younger than 61 years at diagnosis. °LDH normal <480 units/L. +159 of 224 patients achieved a first complete remission after two cycles of induction chemotherapy and thus underwent consolidation therapy. P-values were calculated with the Mann-Whitney test. No significance of p<0.05 was achieved for any comparison between single versus double CEBPA mutation groups. Significant differences were observed between CEBPA mutant and CEBPA wild-type patients for WBC at diagnosis (p=0.012), for LDH at diagnosis (p=0.032), and for allogenous transplant as consolidation treatment in CR1 (p=0.003). Abbreviations: FAB, French American British classification; WBC, white blood cell count; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase. MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome. Table S4: Molecular and karyotype abnormalities of AML patients according to CEBPA mutational status. all (n=224) CEBPA CEBPA wt (n=205) CEBPA CEBPA mut (n=19) single (n=7) double (n=12) ______________________________________________________________________ _ FLT3-ITD n(%) NPM1 mutation n(%) 63(28) 102(46) 62 101 good-risk* n(%) intermediate-risk” n(%) bad-risk+ n(%) 38(17) 121(54) 65(29) 38 104 63 1 1 1 1 0 17 2 0 0 0 6 1° 0 11 1# *Good-risk patients comprised t(8;21) and inv(16) with n=20, and n=18 patients, respectively. “Intermediate-risk patients showed a normal karyotype (n=111), +8 (n=8), and -Y (n=2). +Bad-risk patients comprised all other karyotype results. °This patient had monosomy 7. #This patient had del6q24. AML patients with CEBPA mutations had significantly less FLT3-ITD (p=0.023) and NPM1 mutations (p=0.008). Table S5: Clinical outcome of AML patients according to CEBPA mutational status. all (n=224) CEBPA CEBPA wt (n=205) CEBPA CEBPA mut (n=19) single (n=7) double (n=12) ______________________________________________________________________ _ CR1 achieved, n(%) Death in CR1, n Relapse, n(%) of patients with CR1 OS at two years (%) DFS at two years (%) Patients disease-free in follow-up, n(%) median, months 159(71) 10 140 10 19 0 137(61) 48 46 130(63) 46 44 7(37) 69 63 4(54) 43 43 12 31 3 33 83(37) 37 76 38 7 0 12 0 3(25) 83 75 9 34 Abbreviations: first complete remission, CR1; overall survival, OS; disease-free survival, DFS. At two years, OS and DFS were significantly shorter in AML with single versus double CEBPA mutations (p=0.005, and p=0.011, respectively).