Nitrogen Fixation Lab: Rhizobium & Plant Growth
advertisement

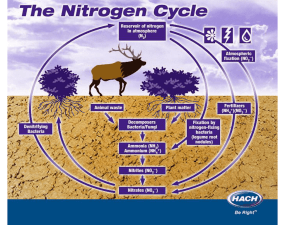
NITROGEN FIXATION LAB WARNING: DO NOT BEGIN ANY LAB WORK UNTIL YOU HAVE READ AND ANSWERED THE PRE LAB QUESTIONS AND I HAVE CHECKED YOUR ANSWERS Plants need nitrate (NO3) to create the amino acids that they need to grow. Unfortunatel y Nitrate is not always available so it must be created using nitrogen gas (N2) from the atmosphere. The process of converting N2 to NO3 is called nitrogen fixation. Nitrogen fixation occurs when specialized bacteria attach themselves to the roots of plants. The bacteria form a symbiotic relationship with the plants. The plants give the bacteria sugars which the bacteria need for food, while the bacteria make nitrates for the plants. There is however one problem. Only certain types of plants called legumes can form a relationship with the bacteria. Beans are legumes while radishes are not. In this lab, you will determine how the presence of a nitrogen fixing bacteria called Rhizobium effects the level of nitrogen found in radish and bean plants. You will also determine how the presence of bacteria effects plant growth. PRE LAB QUESTIONS ( answer these questions on your individual lab sheet) 1. How will the presence of Rhizobium affect the amount of nitrate in your group's radishes? Explain in detail why? 2. How will the presence of Rhizobium affect the amount of nitrate in your group's beans? Explain in detail why? 3. Out of all four plants which one should have grown the most? Explain why you chose your answer in detail? 4. What is nitrogen Fixation? DETAILS 5. What are the independent and dependent variables in this experiment? 6. How will you measure and compare the growth of your plants? Add the following tables to your sheet to keep track of your results BEANS Test Rhizobium Sample Control Sample Plant Growth Nitrogen Content mg/L RADI SHES Measuring Nitrates In order to measure the amount of nitrate in your plant roots you will need to use the nitrates chemical test kit. Follow the procedure below for each of the 4 plant samples. Remember to fully clean your materials and your hands between samples or you will contaminate your results. You should work on more then 1 sample at a time. Step 1 - After removing your plants from their containers and removing the dirt, cut off a small ( 1cm) section of the plants root Step 2 - Obtain a small beaker of distilled water and a pipette from the side of the room. Fill a small test cylinder to the 3mL line with the distilled water (it is the 2nd small line from the bottom) Step 3 - Obtain the Nitrate Test Solution #1 bottle from the kit and use it to fill the test cylinder the rest of the way up to the 5 mL mark. Place your root section into the container, cap, and shake vigorously for 1 minute. Step 4 - Remove the cap from the cylinder and add 2 spatulas full of the Nitrate Indicating powder #2. Recap and shake vigorously for 1 minute. Place the cylinder aside and wait at least 10 minutes before reading. Measuring Plant Growth You will determine your own method for measuring plant growth. Options include measuring total height, total mass, number of leaves, size of leaves etc. Make sure you select the most successful plant in each container before you compare them. Clean UP Before moving on, make sure all dirt goes in the container, all materials get put back and you clean your desk surface and if needed the floor. This can cost you points. POST LAB QUESTIONS( answer these questions on your individual lab sheet) 1. Do your experimental results match your prediction from PRE LAB Question #1? If not, explain at least two possible errors in your experiment. 2. Do your experimental results match your prediction from PRE LAB Question #2? If not, explain at least two possible errors in your experiment. 3. Do your experimental results match your prediction from PRE LAB Question #3? If not, explain at least two possible errors in your experiment. 4. What did you learn from this experiment?