Nutrient Cycles Quiz 2015
advertisement

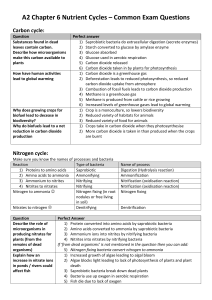
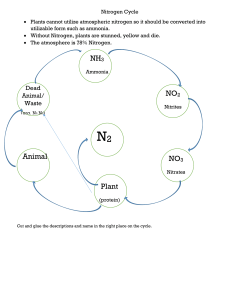
Unit 2: Ecosystems and Cycles (1pt each) Water Cycle: Match the process with its description 1. ______ Breaking down biomass (glucose) into water (and CO2) 2. ______ Forming water droplets from water vapor 3. ______ Water filtering down through soil and rock to underground streams 4. ______ Water being converted from water to water vapor by the sun’s energy from a plant 5. ______ Water produced as a result of condensation (1pt each) Carbon cycle: True of False (T/F) 6. ______Combustion of fossil fuels or forest fires releases carbon dioxide (CO2) back into the atmosphere. 7. ______Photosynthesis takes oxygen from the atmosphere and converts it to glucose by carbon fixation. 8. ______Organic compounds like glucose can be produced by volcanic outgassing or by the weathering of limestone. 9. ______Eating plants or animals that have eaten plants is how carbon is assimilated into an animal 10. ______The carbon sink (limestone, oil, coal) is too large to be unaffected by human activity. (1pt each) Nitrogen cycle: Multiple Choice 11. _____ Nitrogen fixation converts nitrogen gas (N2) to nitrates, ammonia, and nitrites by A. special bacteria C. fertilizer factories B. photosynthesis D. combustion 12______Bacteria in the nitrogen cycle convert waste and dead biomass into nitrites, ammonia, and nitrates by: A. nitrogen fixation C. leaching B. decomposition D. respiration 13.______ Nitrogen gas can be produced by ______ A. Special bacteria C. volcanos B. combustion of fossil fuels D. decomposition 14.______ Plants assimilate nitrates from the Earth into their biomass as A. Proteins and DNA C. carbon dioxide and oxygen B. Glucose and water D. nitrates, nitrites and ammonia 15. Write out a nodes and edge path for how the nitrogen in the proteins (yes there are some!) in an apple that falls off a tree, gets into the atmosphere. 16. Write the chemical equation for photosynthesis: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Respiration Condensation Percolation Transpiration Precipitation 6. T 7. F 8. F 9. T 10. F 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. A B A D Apple Nitrates, nitrites, ammonia decomposition 16. CO2 + H2O Nitrogen Gas special bacteria C6H12O6 + O2