POPULATIONS AND ECOSYSTEMS
advertisement

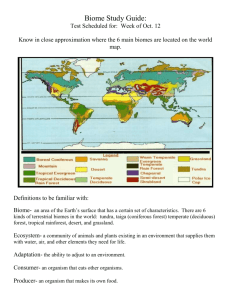
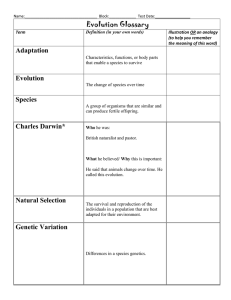
POPULATIONS AND ECOSYSTEMS ECOSYSTEM • Any group of living and nonliving things interacting with each other. 2 types: Terrestrial Ecosystemland based Aquatic Ecosystemwater based TERRESTRIAL (LAND) • Grassland- big open spaces with only a few bushes and trees found by rivers and streams. Soil is fertile, so crops grow well. • Deserts- land of extreme heat and dryness. • Forests- Tall trees/wooded areas AQUATIC (WATER) • Ponds- body of water shallow enough to allow plant roots to reach the bottom. • Lakes- too deep to support plant root except near the shore. Water temperature is different between the bottom layer and upper layer of the water. • Oceans- covers 3/4ths of the Earth’s surface ESTUARIES • Enclosed body of water where fresh water and salt water meet and mix. SALT MARSHES • Barrier where the land meets the sea, such as barrier islands or coastal areas. CONTINENTAL SHELF • Where most life lives. • Land under the ocean that gently slopes to a point which there is a steep drop off. • Shoreline/coastlineEdge of a body of water. PLANKTON • microscopic organisms that drift on the oceans' currents and are the beginning of the food chain for most of the planet. Found close to the surface because they need the sun’s energy. BIOMES Similar ecosystems throughout the world grouped together based on climate factors. • Tundra • Taiga • Deciduous • Tropical forest rainforest DECIDUOUS FORESTS • Area of high amounts of trees that change with the seasons. RAIN FOREST • Near the equator and receives rain all year long. Covers only 6% of Earth’s land, but produces 40% of Earth’s oxygen. TUNDRA • Located at the top of the world near the North Pole. Permafrost, permanent frozen layer of ground that briefly thaws during the short summer. TAIGA • Below (South of) the Tundra contains thick evergreen forests. Temperatures are below freezing in winter and summers are short, warm/humid, and rainy. Most animals in this area are predators. TRANSFER OF ENERGY • Producers- plants, bacteria, and alga, which use photosynthesis • Consumers- animals that rely on other organisms for food. • Decomposers- organisms that break down dead organic matter. Creates materials that are used by producers. CONSUMERS • Primary(herbivores)plant eaters. • Secondary(carnivor es)- flesh eaters. • Tertiary (omnivores)eat both plants and animals SYMBIOSIS • Relationship in which two species live closely together and depend on each other. FOOD CHAIN • Steps energy is passed from producer to consumer. FOOD WEB • Shows the relationship between many organisms. ENERGY PYRAMID • Ratio of an ecosystem between producers, consumers, and decomposers. Largest amount of energy comes from the sun. https://www.brainpop.com/sci ence/energy/energypyramid/ preview.weml CARRYING CAPACITY • Number of individuals in a population that the resources of a habitat can support. (Balance) • Example FERTILE • Capable life. of supporting a large population of FAUNA • Animal life of a particular region, period, or special environment.