POPULATIONS AND ECOSYSTEMS
advertisement

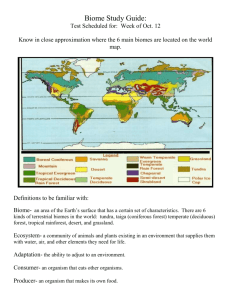
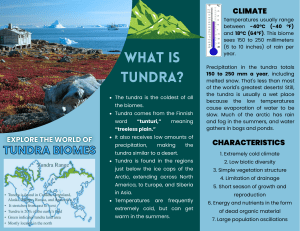
POPULATIONS AND ECOSYSTEMS ECOSYSTEM • Any group of living and nonliving things interacting with each other. 2 types: §Terrestrial Ecosystemland based §Aquatic Ecosystemwater based TERRESTRIAL (LAND) • Grassland- big open spaces with only a few bushes and trees found by rivers and streams. Soil is fertile, so crops grow well. • Deserts- land of extreme heat and dryness. • Forests- Tall trees/wooded areas AQUATIC (WATER) • Ponds- body of water shallow enough to allow plant roots to reach the bottom. • Lakes- too deep to support plant root except near the shore. Water temperature is different between the bottom layer and upper layer of the water. • Oceans- covers 3/4ths of the Earth’s surface ESTUARIES • Enclosed body of water where fresh water and salt water meet and mix. SALT MARSHES • Barrier where the land meets the sea, such as barrier islands or coastal areas. BIOMES Similar ecosystems throughout the world grouped together based on climate factors. • Tundra • Taiga • Deciduous • Tropical forest rainforest DECIDUOUS FORESTS • Area of high amounts of trees that change with the seasons. RAIN FOREST • Near the equator and receives rain all year long. Covers only 6% of Earth’s land, but produces 40% of Earth’s oxygen. TUNDRA • Located at the top of the world near the North Pole. Permafrost, permanent frozen layer of ground that briefly thaws during the short summer. TAIGA • Below (South of) the Tundra contains thick evergreen forests. Temperatures are below freezing in winter and summers are short, warm/humid, and rainy. Most animals in this area are predators. TRANSFER OF ENERGY • Producers- plants, bacteria, and alga, which use photosynthesis • Consumers- animals that rely on other organisms for food. • Decomposers- organisms that break down dead organic matter. Creates materials that are used by producers. CONSUMERS • Primary(herbivores)plant eaters. • Secondary(carnivor es)- flesh eaters. • Tertiary (omnivores)eat both plants and animals SYMBIOSIS • Relationship in which two species live closely together and depend on each other. FOOD CHAIN • Steps energy is passed from producer to consumer. FOOD WEB • Shows the relationship between many organisms. ENERGY PYRAMID • Ratio of an ecosystem between producers, consumers, and decomposers. Largest amount of energy comes from the sun. https://www.brainpop.com/sci ence/energy/energypyramid/ preview.weml CARRYING CAPACITY • Number of individuals in a population that the resources of a habitat can support. (Balance) • Example FERTILE • Capable life. of supporting a large population of FAUNA • Animal life of a particular region, period, or special environment.