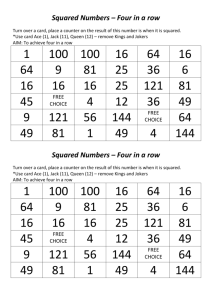
Redblack with evolution

Questions
Hearts
Ace –Define evolution.
2 – What was the name of Charles Darwin’s book that described natural selection?
3 – Who proposed the idea that characteristics acquired during an individual’s life are passed on to their offspring?
4 – A fossil is found to contain 2 micrograms of carbon-14. Judging by its mass, it is thought to have contained 16 micrograms of carbon-14 originally. If the half-life of carbon-14 is 6000 years (I rounded off), how old in the fossil?
5 – Who was the first guy to study fossils? He did his work in the Paris basin.
6 – What do we call a change brought about by natural selection that helps an organism survive in its environment. (NOT a change that occurs during an organism’s lifetime)
7 – Define species.
8 – What was the name of Darwin’s boat?
9 – What is differential success in the reproduction of different phenotypes resulting from the interaction of organisms with their environment?
10 – What is the loss or gain of alleles from a population due to the emigration or immigration of fertile individuals, or the transfer of gametes, between populations?
Jack – What do we call the total aggregate of genes in a population at any one time?
Queen – To what country do the Galapagos Islands belong?
King – In what type of rock are fossils typically found?
Diamonds
Ace – Name one way that Lamarck’s and Darwin’s theories are alike and name one way they are different.
2 – Who condensed Darwin’s work into 5 observations and 3 inferences?
3 – What are the changes in the gene pool of a small population due to chance?
4 – Define homologous structures.
5 – Define vestigial structures.
6 – Contrast gradualism and punctuated equilibrium.
7 – List the five conditions that must be met for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
8 – What does it mean for a population to be in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (also called genetic equilibrium)?
9 – What are the two cases that usually lead to dramatic genetic drift?
10 – In what type of nonrandom mating do individuals choose mates that are similar to themselves?
Jack – Name 3 prezygotic barriers to hybridization.
Queen –Give 2 specific examples of postzygotic barriers to hybridization.
King – Define speciation.
Spades
Ace – What do we know about organisms that are close together on a phylogenetic tree?
2 – What is the best way to determine evolutionary relationships between organisms?
3 – What type of speciation occurs due to geographic isolation?
4 – What do we call selective breeding, such as that often seen with plants and domestic animals?
5 – Why are species on islands most similar to species on the nearest mainland?
6 – What type of evolution leads to analogous structures?
7 – What was Hackel’s proposed hypothesis that an organism’s ebrological development is a replay or its evolutionary history?
8 – What is always at the bottom of a phylogenetic tree?
9 – What are the 2 Hardy Weinberg equations?
10 – What do we call a change in the DNA sequence?
Jack – Name different types of mutations.
Queen –What is the coexistence of two or more distinct forms of individuals in the same population?
King – What is a graded change in some trait along a geographical axis?
Clubs
Ace – What is the emergence of numerous species from a common ancestor introduced into an environment, presenting a diversity of new opportunities and problems?
2 – What type of selection eliminates the extremes?
3 – What type of selection favors opposite extremes?
4 – What is it called when the males and females of a species have different secondary sex characteristics, such as bird plumage?
5 – What species concept defines species based on reproductive isolation?
6 – The geologic time scale divides eras into __________________ and divides those into __________________.
7 – What are two types of dating used to determine the ages of rocks and fossils?
8 – What supercontinent was created when all of the earth’s land masses converged?
9 – What usually delineates the boundaries between geologic eras?
10 – Name the 8 levels of classification of living things.
Jack – What couple is famous for finding the remains of Australopithecus?
Queen – What method is used to replicate small samples of DNA?
King – What do we call an evolutionary branch of a phylogenetic tree?
Answers
Hearts
Ace – The changes in species over time
2 – The Origin of Species
3 – Lamarck
4 – 18,000
5 – Cuvier
6 – adaptation
7 – Group of organisms with similar characteristics that mate to produce viable offspring
8 – HMS Beagle
9 – natural selection
10 – gene flow
Jack – gene pool
Queen – Ecuador
King – Sedimentary
Diamonds
Ace – ALIKE: both described how traits are passed on from parents to offspring; DIFFERENT: Lamarck – inheritance of acquired characteristics, Darwin: persistence of traits that increase fitness.
2 – Earnst Mayr
3 – genetic drift
4 – Structures in different species that may have different functions but that are similar in structure because of common ancestry.
5 – Structure that is reduced in size and/or function but is homologous to useful structures on evolutionary ancestors.
6 – Gradualism: small changes over long time periods; Punctuated equilibrium: Rapid changes that occur after sudden extreme changes in environment – leads to gaps in fossil record.
7 – 1. Large population size 2. No immigration/emigration 3. Random mating 4. No mutation 5. No natural selection.
8 – Frequency of alleles in population remains constant over generations.
9 – Founder effect and bottleneck
10 – assortative mating
Jack – mechanical isolation, habitat isolation, behavioral isolation, temporal isolation, gametic isolation
Queen – Sheep/Goat, Mule, Liger
King – The origin of new species in evolution.
Spades
Ace – They are closely related
2 – DNA analysis
3 – allopatrick
4 – artificial selection
5 – Island biogeography – species from mainland migrate to islands
6 – convergent evolution
7 – ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny
8 – common anscestor
9 – p + q = 1, p 2 + 2pq + q 2 = 1
10 – mutation
Jack – point, frameshift (insertion, deletion), inversion, duplication
Queen – polymorphism
King – cline
Clubs
Ace – adaptive radiation
2 – stabilizing selection
3 – diversifying selection
4 – sexual dimorphism
5 – biological species concept
6 – periods; epochs
7 – radiometric dating, racemization
8 – Pangaea
9 – mass extinctions
10 – domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species
Jack – Mary and Louis Leakey
Queen – Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
King – clade