Red - Raleigh Charter High School
advertisement

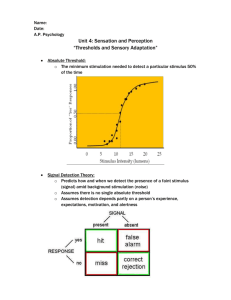
Red Ace – What is the difference between sensation and perception? 2 – What do we call the minimum threshold required to detect a stimulus 50% of the time? 3 – What is signal detection theory? 4 – What is Weber’s Law? 5 – What is gate-control theory? 6 – What theory explains why you see a red afterimage after staring at a green circle? 7 – What do we call a stimulus that is below the absolute threshold? 8 – All of our senses are subject to sensory adaptation. Why, then, do images not disappear when we stare at them for a long time? 9 – What is sensory adaptation? 10 – What part of the eye lets light in? Jack – What part of the eye regulates the amount of light coming in? Queen – What do we call the central part of the retina? King – Name two differences between rods and cones (beside their shapes)? Black Ace – What causes the blind spot? 2 – What is audition? 3 – What aspect of a sound wave determines the pitch? 4 – Name the three bones in the middle ear. 5 – What is the name of the snail-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound waves to neural messages? 6 – What is the difference between place theory and frequency theory? 7 – How do we locate sounds? 8 – What is the name of the neurotransmitters that block pain? 9 – What is sensory interaction? 10 –What is gustation? Jack – What is kinesthesis? Queen – What organ regulates your vestibular sense? King – What are proprioceptors and where are the located? Red Ace – What is the difference between sensation and perception? 2 – What do we call the minimum threshold required to detect a stimulus 50% of the time? 3 – What is signal detection theory? 4 – What is Weber’s Law? 5 – What is gate-control theory? 6 – What theory explains why you see a red afterimage after staring at a green circle? 7 – What do we call a stimulus that is below the absolute threshold? 8 – All of our senses are subject to sensory adaptation. Why, then, do images not disappear when we stare at them for a long time? 9 – What is sensory adaptation? 10 – What part of the eye lets light in? Jack – What part of the eye regulates the amount of light coming in? Queen – What do we call the central part of the retina? King – Name two differences between rods and cones (beside their shapes)? Black Ace – What causes the blind spot? 2 – What is audition? 3 – What aspect of a sound wave determines the pitch? 4 – Name the three bones in the middle ear. 5 – What is the name of the snail-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound waves to neural messages? 6 – What is the difference between place theory and frequency theory? 7 – How do we locate sounds? 8 – What is the name of the neurotransmitters that block pain? 9 – What is sensory interaction? 10 –What is gustation? Jack – What is kinesthesis? Queen – What organ regulates your vestibular sense? King – What are proprioceptors and where are the located? Red Ace – Sensation is DETECTION of a stimulus, perception is ORGANIZATION and INTERPRETATION 2 – absolute threshold 3 –experience and motivation can affect your ability to detect a stimulus; absolute threshold changes depending on situation 4 –two stimuli must differ by a certain PERCENTAGE as opposed to a constant amount in order to perceive a difference 5 – The theory stating that psychological factors can block pain messages from traveling to our brain 6 – opponent process theory of color vision 7 – subliminal 8 – because our eyes jiggle 9 – diminished sensitivity to a constant stimulus 10 – pupil Jack – iris Queen – fovea King – 1) more rods than cones, 2) cones detect color, rods don’t; 3) cones concentrated in fovea, rods on periphery, 4) rods more sensitive to light, 5) cones more detail sensitive Black Ace – hole in the retina where the optic nerve leaves the eye 2 – hearing 3 – frequency 4 – hammer, anvil, and stirrup (collectively, they are called ossicles) 5 – cochlea 6 – Frequency theory describes how we distinguish low-pitched sounds – the frequency at which the basilar membrane vibrates; Place theory describes how we distinguish high-pitched sounds – what located of the basilar membrane vibrates the most 7 – time lag between when the sound reaches the left and right ear. 8 – endorphins 9 – one sense can influence another (example – food tastes different if your can’t smell it) 10 – taste Jack – sense of location of body parts Queen – semicircular canals Kings – cells that detect tension in your muscles for your kinesthetic sense; they are located in muscles, tendons, and joints. Red Ace – Sensation is DETECTION of a stimulus, perception is ORGANIZATION and INTERPRETATION 2 – absolute threshold 3 –experience and motivation can affect your ability to detect a stimulus; absolute threshold changes depending on situation 4 – two stimuli must differ by a certain PERCENTAGE as opposed to a constant amount in order to detect a difference 5 – The theory stating that psychological factors can block pain messages from traveling to our brain 6 – opponent process theory of color vision 7 – subliminal 8 – because our eyes jiggle 9 – diminished sensitivity to a constant stimulus 10 – pupil Jack – iris Queen – fovea King – 1) more rods than cones, 2) cones detect color, rods don’t; 3) cones concentrated in fovea, rods on periphery, 4) rods more sensitive to light, 5) cones more detail sensitive Black Ace – hole in the retina where the optic nerve leaves the eye 2 – hearing 3 – frequency 4 – hammer, anvil, and stirrup (collectively, they are called ossicles) 5 – cochlea 6 – Frequency theory describes how we distinguish low-pitched sounds – the frequency at which the basilar membrane vibrates; Place theory describes how we distinguish high-pitched sounds – what located of the basilar membrane vibrates the most 7 – time lag between when the sound reaches the left and right ear. 8 – endorphins 9 – one sense can influence another (example – food tastes different if your can’t smell it) 10 – taste Jack – sense of location of body parts Queen – semicircular canals Kings – cells that detect tension in your muscles for your kinesthetic sense; they are located in muscles, tendons, and joints.