Essential Questions, vocab, and practice quiz
advertisement

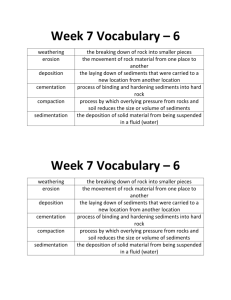
STANDARD 3 REVIEW MODULE 3 LEARNING GOAL Objective 2 Describe the nature of the changes that rocks undergo over long periods of time. A. Diagram and explain the rock cycle. B. Describe the role of energy in the processes that change rock materials over time. Vocabulary: Rock cycle: The many processes that change rocks into different rocks. Erosion: The process of moving sediments from one location to another. Deposition: The process of leaving sediments behind. Creates layers of rock Weathering: The process of breaking rocks down into smaller and smaller pieces Compaction: The squishing of sediments so they form a sedimentary rock. Cementation: “Gluing” sediments together into a rock with minerals in ground water. Crystallization: The process of turning lava or magma to igneous rock. Learning Activities: Rock Cycle SMARTNotes differentiated reading multimedia STANDARD 3 MODULE 3 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK Compaction and cementing to rock Heat and melting #3 MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition Heat and melting #1 IGNEOUS ROCK Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition Heat and melting Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK Crystallizing and solidifying #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 1.) What processes leads to sedimentary rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, compaction. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava USE THE ROCK CYCLE 2.) What processes lead to metamorphic rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava USE THE ROCK CYCLE 3.) What processes lead to igneous rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava 4.) Describe the rock cycle and as many processes as possible using examples. STANDARD 3 MODULE 3 CONTENT PRACTICE QUIZ ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Heat Crystallizing and solidifying and melting Weathering, erosion, deposition #1 Heat and melting Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK IGNEOUS ROCK Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 1. What processes leads to sedimentary rock? a.) Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, compaction. b.) High temperature and pressure c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Heat #1 and melting Weathering, erosion, deposition Crystallizing and solidifying Heat and melting Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK Heat and pressure IGNEOUS ROCK Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 2. What processes lead to metamorphic rock? a.) Magma and lava b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) High temperature and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition #1 Compaction and cementing to rock ROCK CYCLE IN SEDIMENTARY ROCK EARTH’S CRUST Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Heat and melting Weathering, erosion, deposition Crystallizing and solidifying Heat and melting Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK Heat and pressure #2 IGNEOUS ROCK Weathering, erosion, deposition USE THE ROCK CYCLE 3. What processes lead to igneous rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.) Melting, cooling and hardening. c.) Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. d.) Magma and lava Weathering, erosion, deposition SEDIMENTARY ROCK Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Heat Crystallizing and solidifying and melting Weathering, erosion, deposition #1 Heat and melting Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK Heat and pressure IGNEOUS ROCK Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 4. What is the source of energy that drives plate tectonics and the rock cycle? A. The Sun B. Thermal Energy C. Radioactive Decay in the core D. Mechanical Energy 5. The creation of lava and magma involve what form of energy directly? A. The Sun B. Thermal Energy C. Radioactive Decay in the core D. Mechanical Energy 6. Tectonic plates move around and help shape the surface of the Earth. This creates melting of rock material, heat and pressure is applied to rock material, and rock material is also weathered, eroded, and deposited. These processes change rock material from one type of rock to another. One step on the rock cycle is when mountains are built and gravity acts on the rock material and then pulls it down in a landslide. As the landslide moves down slope. This an example of what type of energy? A. The Sun B. Thermal Energy C. Radioactive Decay in the core D. Mechanical/kinetic Energy STANDARD 3 MODULE 3 VOCAB PRACTICE QUIZ 1. “Gluing” sediments together into a rock with minerals in ground water. A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 2. The process of turning lava or magma to igneous rock. A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 3. The process of leaving sediments behind. Creates layers of rock A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 4. The squishing of sediments so they form a sedimentary rock. A. Cementation B. Compaction C. Weathering D. Crystallization 5. The process of breaking rocks down into smaller and smaller pieces A. Cementation B. Compaction C. Weathering D. Crystallization 6. The process of moving sediments from one location to another. A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 7. The many processes that change rocks into different rocks. A. Cementation B. Rock Cycle C. Weathering D. Crystallization STANDARD 3 MODULE 3 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS KEY ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK #1 Heat and melting Crystallizing and solidifying Heat and melting Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK IGNEOUS ROCK Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 1.) What processes leads to sedimentary rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, compaction. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava USE THE ROCK CYCLE 2.) What processes lead to metamorphic rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava USE THE ROCK CYCLE 3.) What processes lead to igneous rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava 4.) Describe the rock cycle and as many processes as possible using examples. The rock cycle shows the many ways matter can be changed from one rock type to another. However, all matter is conserved and recycled. It never disappears, rather it can only be changed into another form or rock. For instance when a rock is melted, cooled, and crystallized it becomes an igneous rock. If any rock is under great pressure and heat (but not melted) it will change into a metamorphic rock. And finally, if a rock is weathered into small pieces, eroded, deposited, and cemented and/or compacted it becomes a sedimentary rock. STANDARD 3 MODULE 3 CONTENT PRACTICE QUIZ KEY ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK #1 Heat and melting Crystallizing and solidifying Heat and melting Heat and pressure IGNEOUS ROCK METAMORPHIC ROCK Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 1. What processes leads to sedimentary rock? a.) Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, compaction. b.) High temperature and pressure c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) Magma and lava ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK #1 Heat and melting Crystallizing and solidifying Heat and melting Heat and pressure IGNEOUS ROCK METAMORPHIC ROCK Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 2. What processes lead to metamorphic rock? a.) Magma and lava b.)Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. c.) Melting, cooling and hardening. d.) High temperature and pressure ROCK CYCLE IN Weathering, erosion, deposition Compaction and cementing to rock Heat #3 Heat and pressure METAMORPHIC ROCK and melting MAGMA/LAVA SEDIMENTS Weathering, erosion, deposition EARTH’S CRUST SEDIMENTARY ROCK #1 Heat and melting Crystallizing and solidifying Heat and melting Heat and pressure IGNEOUS ROCK Heat and pressure Weathering, erosion, deposition #2 USE THE ROCK CYCLE 3. What processes lead to igneous rock? a.) High temperature and pressure b.) Melting, cooling and hardening. c.) Weathering, erosion, deposition, cementing, pressure. d.) Magma and lava 4. What is the source of energy that drives plate tectonics and the rock cycle? A. The Sun B. Thermal Energy C. Radioactive Decay in the core D. Mechanical Energy 5. The creation of lava and magma involve what form of energy directly? A. The Sun B. Thermal Energy C. Radioactive Decay in the core D. Mechanical Energy 6. Tectonic plates move around and help shape the surface of the Earth. This creates melting of rock material, heat and pressure is applied to rock material, and rock material is also weathered, eroded, and deposited. These processes change rock material from one type of rock to another. One step on the rock cycle is when mountains are built and gravity acts on the rock material and then pulls it down in a landslide. As the landslide moves down slope this an example of what type of energy? A. The Sun B. Thermal Energy C. Radioactive Decay in the core D. Mechanical/kinetic Energy STANDARD 3 MODULE 3 VOCAB PRACTICE QUIZ KEY 1. “Gluing” sediments together into a rock with minerals in ground water. A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 2. The process of turning lava or magma to igneous rock. A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 3. The process of leaving sediments behind. Creates layers of rock A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 4. The squishing of sediments so they form a sedimentary rock. A. Cementation B. Compaction C. Weathering D. Crystallization 5. The process of breaking rocks down into smaller and smaller pieces A. Cementation B. Compaction C. Weathering D. Crystallization 6. The process of moving sediments from one location to another. A. Cementation B. Erosion C. Deposition D. Crystallization 7. The many processes that change rocks into different rocks. A. Cementation B. Rock Cycle C. Weathering D. Crystallization