Handy Dandy Grammar
advertisement

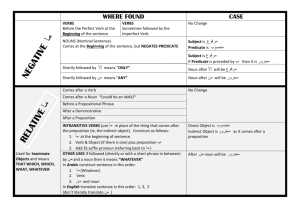
Handy Dandy Grammar Reference Sheet 1) Noun – word used to name a person, place, thing, or idea. (In a sentence, nouns (and pronouns) can be used in various ways. S – subject, DO – direct object (RECEIVES THE ACTION FROM THE VERB), IO – indirect object, OP – object of the preposition, PN – predicate nominative (renames the subject)). Proper – particular person, place, or thing Ex. James, White House, Red River Common – not a particular person, place, or thing Ex. woman, city, building Abstract – a quality, characteristic or idea Ex. beauty, love, courage Collective – names a group Ex. crowd, team, class 2) Articles (A)– a, an, the 3) Pronoun – a word used in place of a noun. (Pro) Ex. Fishermen complained about the weather forecast. They said it had not warned them of the storm. Personal Pronouns – I, me, you, he, she, it, we, us, they, them Possessive Forms – my, mine, your, his, her, its, our, their Relative/Interrogative – who, whom, which, whose, that Demonstrative – this, these, that, those Indefinite – all, any, anybody, anyone, both, each, either, everybody (one), few, many, most, neither, nobody, no one, other, several, some, somebody (one), such 4) Adjective (ADJ)– word used to modify a noun or a pronoun. What kind? – blue eyes, large city, brilliant student Which one- this woman, that suggestion How many? – several reasons, ten players Predicate Adjective (PA) – separated from the word it modifies by a linking verb. Ex. Debra is beautiful. Ex. The stew tasted delicious. 5) Verb – word that expresses action or otherwise helps make a statement. (V) Action physical – hit, play, move, run Mental – think, know, imagine, believe Linking – expresses a state or condition – links subject to the word that describes it (PA) or renames it (PN). Ex. The author is our guest (author and guest are the same person). Jeffrey is talented. (talented describes Jeffrey) Helping – helps the main verb express action or make a statement. Ex. has played should have played 6) Adverb (ADV) – a word used to modify a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. How – She drives carefully. To what extent – She can almost drive How often - She drives daily. When – She drives early in the morning. Where – She drives everywhere. 7)Preposition(Prep) – shows relationship of a noun to some other word in the sentence. Prepositions must take an object (a noun or pronoun). Ex. in the hall (in – preposition, hall – object of the preposition under the trees (under – preposition, tree – object of the preposition) Common Prepositions: about above across after against along among around at before behind below beneath beside between down during except for from in into like of off on over past since through to toward under until up upon with within without 8) Conjunction (Conj) – a word that joins words or groups of words. Ex. Bring your lunch and one dollar. You must pass every subject and maintain a good average. Coordinating Conjunctions (FANBOYS): for and nor but or yet so Subordinating Conjunctions (common): after provided since though unless although until because when before where if while 9) Interjection – word that expresses emotion and has no grammatical relation to other words in the sentence. (Usually used with an exclamation point). Ex. Oh! My goodness! Ouch! Hurry! VERBALS – verbals are forms of verbs that are used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs. A verbal with modifiers or a complement is a verbal phrase. Participle – form of a verb that can act as an adjective. Can be past or present. EX. Irma’s shining eyes betrayed her excitement. (Present) The shattered window needs replacement. (Past) Gerund – a form of a verb (ending in –ing) that is used as a noun. EX. Reading is my favorite hobby. Infinitive – form of a verb that appears with the word to and acts as a noun, adjective, or an adverb EX. To explore an underground cave required experience and the right equipment. BASIC SENTENCE PATTERNS 1) Subject, verb. Ex. The audience wept. 2) Subject, verb, direct object. Ex. The judge dismissed the jury. 3) Subject, verb, indirect object, direct object. Ex. The man gave his sweetheart a necklace. 4) Subject, verb, predicate adjective. Ex. The doctor was tired. 5) Subject, verb, predicate nominative. Ex. Pablo Picasso was a great painter. SENTENCE TYPES – There are four basic types of sentence structure: Simple - Contains one independent clause and no subordinate clauses. Ex. The wind chilled the tundra. Compound - Contains two or more independent clauses but no subordinate clauses. Ex.. The wind chilled the tundra, and the snow battered my face. Complex - Contains one independent clause and at least one subordinate clause. Ex. Because we thought there might be an avalanche, we decided to leave the mountain. Compound/Complex - .Contains two or more independent clauses and at least one subordinate clause. Ex. Because it is the coldest continent on Earth, Antarctica has no native population, and it holds the record for the lowest temperature ever recorded -128.6 F. Sentences Classified by Purpose 1) A declarative sentence is a sentence that makes a statement. Ex. In 1945, the United Nations had fifty-one members. 2) An imperative sentence is a sentence that gives a command or makes a request. Ex. Stop talking and open your books. 3) An interrogative sentence is a sentence that asks a question. Ex. Which book did you like most? 4) An exclamatory sentence is a sentence that expresses strong feeling. Ex. How beautiful it is!!