Slug Mating Game
advertisement

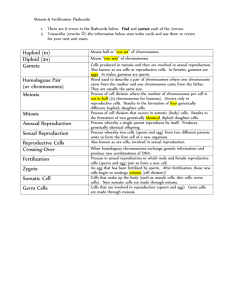
Name________________________ Genetics of the Baxter Slug Learning Targets Learn and apply vocabulary: gene, allele, dominant, recessive, genotype, phenotype. I can relate genotypes to phenotypes. I can show how Meiosis selects alleles for sperm and egg cells. I can explain how genes and traits are passed from parents to offspring. Introduction Baxter Slugs reproduce sexually, just like humans. These traits are controlled by their genes (found on chromosomes) and have two different alleles each: Trait Eye Shape Body Pattern Teeth Gender Phenotype Round Eyes Star Eyes Polka-Dotted Body Striped Body Buck-Teeth Fangs for Teeth Male (no eyelashes) Female (long eyelashes) Symbol for Allele R r D d B b Y X In this activity, you will analyze the genotypes and phenotypes of two parent slugs. You will then simulate Meiosis in both parents to produce sperm and egg cells. Finally, you will produce an offspring slug and analyze its genotypes and phenotypes. Procedure & Results Part One – Daddy Slug and his Sperm 1. Obtain a set of chromosomes for Daddy Slug. 2. Record the genotypes and phenotypes of Daddy Slug in your table. 3. Make a sketch of Daddy Slug based on his phenotypes (NOTE: give males no eyelashes). 4. Cut out Daddy Slug’s chromosomes. 5. Simulate Meiosis (you will need to replicate all of the chromosomes, perform Meiosis I, then perform Meiosis II). The end result should be 4 sperm cells. Check your sperm cells with your teacher. 6. Randomly pick one sperm cell to work with and discard the other ones. Enter the alleles of the chosen sperm cell into the table (NOTE: the sperm cell should only have ONE copy of each gene!). Table 1: Daddy Slug Genotypes and Phenotypes Sketch of Daddy: Trait Genotype Phenotype Eye Shape Body Pattern Teeth Gender Sperm Cell Allele Part Two – Mama Slug and her Eggs 1. Obtain a set of chromosomes for Mama Slug. 2. Record the genotypes and phenotypes of Mama Slug in your table. 3. Make a sketch of Mama Slug based on her phenotypes (NOTE: give females eyelashes). 4. Cut out Mama Slug’s chromosomes. 5. Simulate Meiosis (you will need to replicate all of the chromosomes, perform Meiosis I, then perform Meiosis II). The end result should be 4 egg cells. Check your egg cells with your teacher. 6. Randomly pick one egg cell to work with and discard the other ones. Enter the alleles of the chosen egg cell into the table (NOTE: the egg cell should only have ONE copy of each gene!). Table 2: Mama Slug Genotypes and Phenotypes Sketch of Mama: Trait Genotype Phenotype Eye Shape Egg Cell Allele Body Pattern Teeth Gender Part Three – Slug Reproduction! 1. Have the sperm cell fertilize the egg cell by combining the chromosomes from the sperm and egg cells to form an embryo. 2. Pair the homologous chromosomes in the new embryo. Check your embryo with your teacher. 3. For each trait, record the allele from Daddy, the allele from Mama, the genotype and the phenotype in the Baby Slug table. 4. Make a sketch of Baby Slug based on his/her phenotypes. Table 3: Baby Slug Genotypes and Phenotypes Allele Allele Trait from from Genotype Daddy Mama Eye Shape Sketch of Baby: Phenotype Body Pattern Teeth Gender Analysis Questions Please answer these questions fully and thoughtfully after completing the activity. 1. How many copies of each chromosomes does Daddy Slug have?_____ 2. How many copies of each chromosome are in a sperm cell?_____ 3. How it is possible for two Round-Eyed parent slugs to have a Star-Eyed baby. Explain this, and show the Daddy genotype and Mama genotype that could lead to this. 4. Compare your Baby Slug to those of other groups. Most of the Baby Slugs should look different from each other even though you all used the same parents for this activity. Explain why this is.