Meiosis & Fertilization Flashcards There are 7 errors in the
advertisement
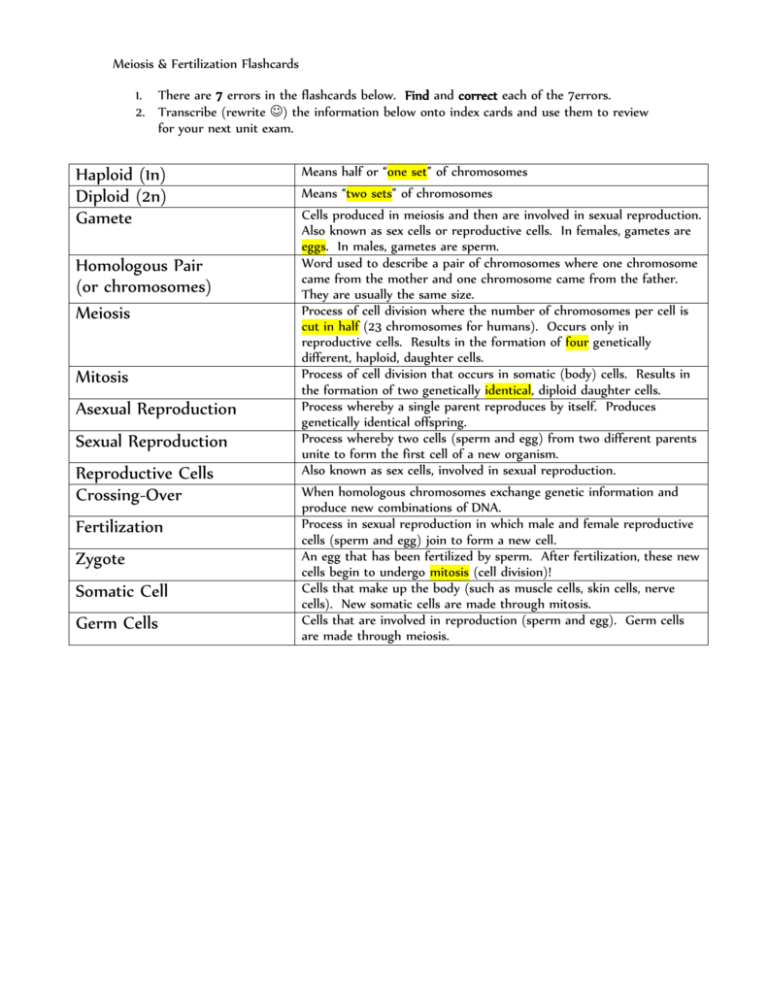
Meiosis & Fertilization Flashcards 1. There are 7 errors in the flashcards below. Find and correct each of the 7errors. 2. Transcribe (rewrite ) the information below onto index cards and use them to review for your next unit exam. Haploid (1n) Diploid (2n) Gamete Homologous Pair (or chromosomes) Meiosis Mitosis Asexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Reproductive Cells Crossing-Over Fertilization Zygote Somatic Cell Germ Cells Means half or “one set” of chromosomes Means “two sets” of chromosomes Cells produced in meiosis and then are involved in sexual reproduction. Also known as sex cells or reproductive cells. In females, gametes are eggs. In males, gametes are sperm. Word used to describe a pair of chromosomes where one chromosome came from the mother and one chromosome came from the father. They are usually the same size. Process of cell division where the number of chromosomes per cell is cut in half (23 chromosomes for humans). Occurs only in reproductive cells. Results in the formation of four genetically different, haploid, daughter cells. Process of cell division that occurs in somatic (body) cells. Results in the formation of two genetically identical, diploid daughter cells. Process whereby a single parent reproduces by itself. Produces genetically identical offspring. Process whereby two cells (sperm and egg) from two different parents unite to form the first cell of a new organism. Also known as sex cells, involved in sexual reproduction. When homologous chromosomes exchange genetic information and produce new combinations of DNA. Process in sexual reproduction in which male and female reproductive cells (sperm and egg) join to form a new cell. An egg that has been fertilized by sperm. After fertilization, these new cells begin to undergo mitosis (cell division)! Cells that make up the body (such as muscle cells, skin cells, nerve cells). New somatic cells are made through mitosis. Cells that are involved in reproduction (sperm and egg). Germ cells are made through meiosis.