Nucleic Acids – Organic/Macromolecule #4
advertisement

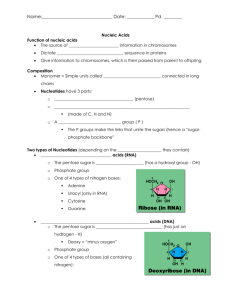
Nucleic Acids – Organic/Macromolecule #4 Name:_______________________________________Date:_____________Per:___________ To understand the importance of nucleic acids, you must first understand the importance of proteins. Proteins have to have a special shape in order to do their job. That shape is determined by the order of the amino acids. A cell has to be able to make all of its proteins in just the right amino acid arrangement, in order for proteins to do their job. Without the proper shape the proteins can’t do their job. This amino acid arrangement comes from nucleic acids, aka DNA. Nucleic acids store the code that tells how the amino acids should be arranged so the proper shape of the protein can be made. There are two types of nucleic acids DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). The building blocks of DNA and RNA are nucleotides. Nucleotides get linked together to make DNA and RNA like the amino acids get linked together to make proteins. A nucleotide is made of three parts, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogen base. So the elements that make up the nucleotide are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, and nitrogen. In DNA, there are four different types of nitrogen bases. They are called adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. DNA is made up of two strands of nucleotides, hooked together in a twisted ladder shape called a double helix. The two strands are held together by complementary bases on opposite strands. Thymine has a shape that complements (fits together like a puzzle) adenine. So every nucleotide that has a thymine base has an adenine base across from it. Cytosine and guanine are also complementary in shape and they fit together like puzzles pieces. RNA is a nucleic acid that is a single strand of nucleotides that are in straight chain. Its job is to be the copy of a section DNA that gets used to make the cell’s proteins. DNA’s role is to be the master copy that stores all the genetic information of a cell. Matching _____ 1. proteins a. molecules that store a code _____ 2. amino acids b. ribonucleic acid _____ 3. nucleic acids c. deoxyribonucleic acid _____ 4. DNA d. building blocks of DNA and RNA _____ 5. RNA e. adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine _____ 6. nucleotides f. building blocks of a protein _____ 7. nitrogen bases g. fit together like a puzzle _____ 8. complementary bases h. molecules built to have a special shape to do _____ 9. double helix their job i. shape of a DNA molecule True or False _____ 1. Proteins have to have a special shape to do their job. _____ 2. The shape of a protein is determined by the order of their nucleotides. _____ 3. The shape of a protein is determined by the order of their amino acids. _____ 4. If the arrangement of amino acids is changed, the shape of a protein may also change. _____ 5. The code in DNA helps the cell arrange its amino acids together in the correct order to make its proteins. _____ 6. The two types of nucleic acids are DNA and RNA. _____ 7. Amino acids are the building blocks of nucleic acids. _____ 8. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. _____ 9. A nucleotide is made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a nitrogen base. _____ 10. There are three different nitrogen bases. _____ 11. Adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine are the four different types of nitrogen bases. _____ 12. Thymine is complementary to guanine. _____ 13. Thymine is complementary to adenine. _____ 14. RNA is made of two strands of nucleotides. _____ 15. A double helix is like a twisted ladder. _____ 16. DNA’s shape is a double helix. _____ 17. On a DNA molecule, cytosine would have a guanine across from it. _____ 18. RNA’s job is to store genetic information in the nucleus of a cell. _____ 19. DNA’s job is to allow parents to pass on their genetic information to their offspring. _____ 20. RNA’s job is to help use the code in the DNA to make a cell’s proteins. Completing Sentences proteins DNA adenine thymine nitrogen base amino acids RNA guanine sugar double helix nucleic acids nucleotides cytosine phosphate group 1. The two types of nucleic acids are _____________ and _______________. 2. __________________________ are the building blocks of nucleic acids. 3. Each nucleotide is made of a __________________, a _________________________ and a _____________________________. 4. Two complementary bases are _______________ and ________________________. 5. Two other complementary bases are ____________________ and _______________. 6. The shape of a DNA molecule is called a ____________________________. 7. __________________________ are molecule that help the cell makes its proteins correctly. 8. _______________________ are vital to a cell, and they must be made to have a specific shape to do their job. 9. The shape of a protein is determine by the sequence of its _____________________. Nucleic Acid – Short Answer 1. Name and describe the function of the previous 3 organic molecules. 2. What macromolecule is used to make proteins with the proper amino acid sequence? 3. What are two types of nucleic acids? 4. What are the building blocks of nucleic acids? 5. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? 6. What are the four types of nitrogen bases? 7. What is the shape of a DNA molecule? 8. How are RNA and DNA different?