Nucleic Acids
advertisement

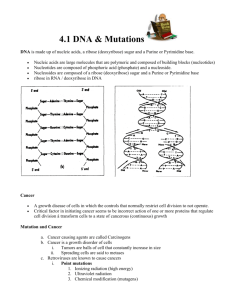
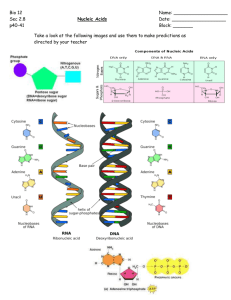
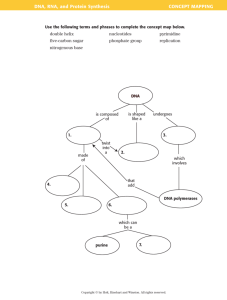
Nucleic Acids Function: Structure, Functional Structure: Varies Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides; thus nucleic acids are called polynucleotides Two major classes of nucleotides. 1) DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID (DNA) DNA is the chemical basis for the gene, the fundamental unit of inheritance; mostly found in the nuclei of cells. 2) RIBONUCLEIC ACID (RNA) RNA molecules are close copies of genes mostly found in the cytoplasm of cells. Nucleotides: A nucleotide consists of: i) a nitrogen base (either a purine or a pyrimidine) • In DNA, there are two purine bases adenine and guanine used to make nucleotides • In DNA, there are two pyrimidine bases: thymine and cytosine used to make nucleotides • In RNA, thymine does not occur--it is replaced by the pyrimidine uracil Pyrimidines (single ring) Purines (double ring) ii) a 5-carbon sugar (in DNA it is deoxyribose; in RNA it is ribose) (in RNA) (in DNA) iii) a phosphate group A nucleic acid polymer consists of alternating chains of sugar and phosphate with a nucleotide base attached to a deoxyribose sugar