questions that may be used for the genetics term test
advertisement

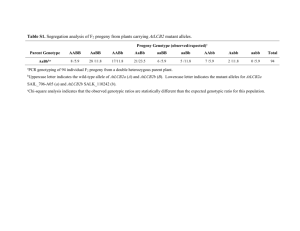
QUESTIONS THAT MAY BE USED FOR THE GENETICS TERM TEST Twenty questions will be pulled from this list of questions for the test. Each student must pass the test with a “B” grade or higher in order to continue on and take other genetic’s tests. This is a quality assignment. Those who do not pass, will have to retake a different test until they do pass. In studying for this test, you may use any possible means to learn the material. Matching 1. Dominant or recessive form that gene may take recessive 2. Condition in which one allele is not dominant allele to the other and three phenotypes result punnett square 3. genetic trait dominates or prevents the expression co-dominant of the recessive phenotype 4. unit responsible for the transmitting of hereditary dominant traits; segments of a DNA molecule homozygous 5. science of heredity gene 6. particular combination of alleles of an organism heterozygous 7. having two different alleles for a given charecter trait genetics at the corresponding sites on homologous chromosomes genotype 8. having two identical allesles for a given trait at the corresponding sites on homologous chromosomes 9. physical or visible charecteristic that the genotype determines 10. chart uses to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring of a cross 11. form of a trait that is dominated by another form 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. The cells of a body are all: 1n, 2n, 3n, monoploid All normal gametes are : 1n, 2n, 3n, diploid Circle the homozygous genes: Aa, BB, AaBb, Bb Circle the herozygous genes: Aa, BB, AABB, Bb Circle the gametes for this individual AABB A, Aa, AB, Ab, AaBb, ba How many different gametes are possible from a parent AaBb? Which is properly written for a heterozygote cross with a homozygote? Bb x Bb, Bb x BB, AaBb x AABb, AABB x AABB For this genetic cross, AabbCc x AaBbCc, the gametes will all be? 1n, 2n, 3n, diploid, triploid How does one figure out the F2 generation? F1 x F1, Parent x F1, P1 x P1, P1, x P2, F1 x F2 Circle the alleles in this cross. AABBCc x aabbCC What do these symbols mean? ¼= __________, F= _________ parent, filial, phenotype, family, probability, phooey Circle all the gametes this individual can provide: AABb A, B, AB, Ab, AA, Bb, Abb Which of these are homozygous for two traits? AABB, AaBb, AABb, aabb, MmFf, aaBb How many different gametes are possible form a parent who is DdEe? 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 26. Which is properly written for a homozygous cross with a heterozygous? AA x aa, Aa,x Aa, BB x Bb, bb x bb, AABB x aabb, AaBb x AaBb 27. For this genetic cross, DDEeRr x ddeeRR, the gametes will all be: diploid, triploid, 1n, 2n, 3n, unknown 28. AABB (gametes) AA, AB, BB (circle correct ones) 29. AaBbCC (gametes) AaBC. ABC. AbC. Abc (circle correct ones ) 30. Circle the homozygous (for each trait) Underline the heterozygous (for each trait) HHNN, UuYy, J, Aabb, Aa, BB 31. Parents are all: 1n, 2n, 3n, monoploid 32. Gametes are all: 1n, 2n, 3n, diploid 33. F1 (progeny) are all: 1n, 2n, 3n, haploid 34. Your body cells are all: 1n, 2n, 3n, haploid 35. Your sex cells are all: 1n, 2n, 3n, diploid 36. Write out a gamete for this person: AaBbCcDd 37. How many different gametes can these people produce: AaBB = ____, Aa= _____, AABB = _____, AaBBcc= _____ 38. Circle the phenotypes: AABB, AB, ½ AB, green eyes, Tall, recessive, dominant XX, female 38. Circle all the gametes this individual can provide: BBYy BB, BY, Yy, By 39. How many different gametes could this person make? BbYyGG 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 40. Gametes for this person BbYy will all be? Diploid, haploid, triploid, 2n, 4n 41. Circle the homozygous trait. A, AA, Aa, AABb 42. Circle the homozygous for two traits. AABB, AaBb, AABa AaBb, AA 43. Circle the heterozygous trait. A, AA, Aa, AABb 44. Circle the hereozygous for two traits. AABB, AaBb, AABb, AaBb, Aa 45. Circle all the alleles in this cross: AaBb x AABB 46. Circle the genotype(s) . Brown hair, female, AaBb, ½ tall 47. Circle the phenotype(s) . Brown hair, female, 2n, AA, Aa, ½ BB 48. When doing a genetic cross, what do these symbols mean? ¼= _____, F= _____ Parent, filial, phenotype, family, probability, phooey, final 49. Circle ALL of the recessive genes in this genetic cross. AABbCc x AaBBCC 50. How does one find the F2 generation? F1 x F1, F1 x parent, P1 x P1, P1 x F1 Answer the questions below using this genetic problem B = brown, b = blue BB x bb 4/4 Bb 4/4 offspring will be brown eyed. BB bb b b B B BB Bb Bb Bb Bb 51. Circle the recessive gametes. 52. Underline all homozygous offspring. 53. Put a square around a phenotype. 54. Write out the cross for how you would figure out the F2 generation for the above example. B=Black, b= brown Bb x Bb ¾ black, ¼ brown b 55. Circle a genotype. 56. Cross out a homozygous recessive progeny. 57. underline a recessive phenotype. T = tall, t = short TT x tt b B Bb Bb BbB B Bb 4/4 Tt, 4/4 tall Bb TT tt 58. Circle all the gametes that have recessive alleles T 59. Put a box around all heterozygous genotypes. 60. Underline all phenotypes. T 61. Put an X through all parents. 62 For this example, how would you find the F2 generation? t t Tt Tt Tt Tt Use the two genetic crosses below for your answers Bb x Bb ½ Bb, ½ bb AABB x aabb 16/16 AaBb 63. Circle all the genes of the parents 64. Underline all the recessive genes in both crosses. 65. Put a box around the F1 generation of both crosses. B = brown, Bb x Bb 66. 67. 68. 69. 70. 71. b = white ¼ BB, ½ Bb, ¼ bb ¾ brown, ¼ white Circle the parents. Underline the phenotypes. Square in the herozygous progeny Cross out all the diploid cells. Double underline the symbols. Color in all the alleles. 72. How many gametes are seen in the problem above. Understanding the punnett square. For all of the following questions, you will be asked to circle the correct answer in the genetic problem and on the punnett square. Be sure and circle ALL possible answers. T = tall t = short TT Tt T Tt x TT Bb t TT TT Tt TT Tt TT, TT, Tt, Tt T 73. Circle all dominant gametes on the punnett square. 74. Cross out all homozygous dominant parents. 75. Put a box around the progeny. 76. Scratch out all heterozygous offspring. B = brown eyes b = blue eyes T Bb B b B BB Bb b Bb bb ¼ = BB ½ = Bb ¼ = bb Bb x Bb = BB, Bb, Bb, bb ¾ = Brown eyes ¼ = blue eyes 77. Circle a homozygous dominant progeny inside of the punnett square and one outside of the punnett square. 78. Underline a phenotype. 79. Cross out a genotypic ratio. 80. Square a genotype for a person with blue eyes. (not the symbol for blue eyes.) 81. Color in all the progeny that are carriers for the blue eyed trait. Genetic crosses Use the genetic cross below to answer the questions. AABB x aabb = 16/16 AaBb 82. Circle the genes of the parents. 83. Put a box around the F1 generation. 83. Underline all heterozygous genotypes.