click here

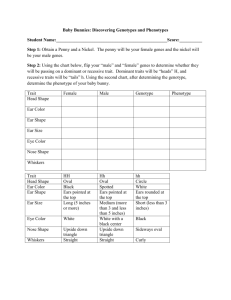
1.
Phenotype distribution for ear II: 9:3:3:1;
Ear II indicates dark and smooth is dominant;
phenotype distribution for ear I: 1:1:1:1;
Therefore:
Ear I could result from a testcross: AaBb x aabb
Kernel B is dominant for both traits: most abundant phenotype for ear II:
AaBb x AaBb
Kernel C is dominant for color but recessive for shape: about 3/16 of kernels in ear II. D is rarest phenotype.
ALL phenotypes should be in equal frequency in ear I.
Answer: (A)- all statements are correct
2. See discussion in Hartwell:
I. False; Frequency is 1/600 in U.S. populations;
II. True; educational follow up was lacking;
III. False; prenatal testing is available;
IV. True; information did get out to insurers and employers.
Answer: (D)- II and IV are correct.
3. See discussion in Hartwell:
I. False; HD is an autosomal dominant
II. True; this was one of the first human genes to be mapped to a chromo- some using molecular markers;
III. False; a cure is still unavailable.
IV. True; symptoms of HD start to appear over time.
Answer: (D)- II and IV are correct.
4. From the data, both dominant and recessive phenotypes are present in the offspring, so neither parent could be homozygous for the dominant alleles; a recessive allele would need to be passed by both parents;
The ratio of red:sepia in the offspring is 1:1, indicating a testcross: a se + /se x
se/se cross.
The ratio of normal to vestigial is 3:1, indicating a hybrid cross; vg + /vg x vg + /vg
Answer: (C)- se+/se; vg+/vg x se/se; vg+/vg.
5. Probability has no memory; what has already happened is not relevant to the problem. The two births are independent events:
P (two girls) = P(girl) x P(girl) =½ x ½ = ¼
Answer: (D)- ¼
6. P(A_B_C_D_E_ff) =
½ x ¾ x ½ x ¾ x 1 x ½ = 9/128
Answer (E): none of the above
7. P(AaBbCcDdEeff) =
½ x ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ x ½ = 1/64
Answer (B): 1/64
8. 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 2 x 1 = 32
Answer (C): 32
A a
A a
AA Aa
Aa aa
Aa Aa Aa AA
Aa Aa
½ Aa
AA AA
2/3 Aa aa aa
½ Aa ½ Aa
?
¼ Aa
9. P(III-2 is heterozygote) = ½ x ½ = ¼;
Answer (A):
10. P(IV-1 is affected) = ½ x ½ x 2/3 x ½ x ¼ = 1/48;
Answer (D).