Key from 3/9

Chapter 7
1. Some genes and mutations vary in the phenotypic expression depending on the sex of the parent from whom the gene is inherited. This phenomenon is know as:
A. Imprinting
B. Penetrance
C. Genetic anticipation
D. Sex-linked inheritance
Pg. 124-125
2. A ratio of 12:3:1 is most characteristic of:
A. Recessive epistasis
9:3:4 (Pg. 111-113)
B. Dominant epistasis
12:3:1 (Pg. 113)
C. Duplicate recessive epistasis
9:7 (Pg. 113-115)
D. None of the above
3. For the following pedigree, determine the type of inheritance, and explain that determination
=
Autosomal recessive inheritance (Pg. 142-143)
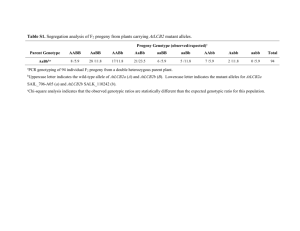
4. What are the expected ratios of gametes from crossing Ab x aB with and without linkage
Fig. 7.5
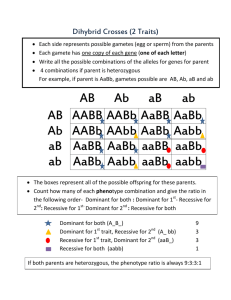
5. The expected phenotype ratio is a dihybrid cross (AaBb x AaBb) is 9:3:3:1. What is a likely explanation if the results of such a cross are significantly different than the expected 9:3:3:1 ratio?
A. The genes A and B are located near each other on the same chromosome
B. The genes A and B are located on separate chromosomes
C. One of the genes does not cause a phenotype
D. The two genes assort independently
E. Mendel was wrong
Pg. 166-167
6. From the cross AaBb x aabb, what is the recombination frequency if the progeny numbers are 72 AaBb, 68 aabb, 17 Aabb, 21 aaBb
A. 0.213
B. 0.271
C. 0.500
D. 0.787
E. Cannot be determined
Recombination frequency (RF): # recombinant progeny/total progeny * 100
= 0.213
Pg. 171
7. In a cross between AaBb and aabb, the following progeny were recovered.
73 Aabb
80 aaBb
12 AaBb
9 aabb
A. Coupling
B. Repulsion
C. Both coupling and repulsion
D. Neither coupling nor repulsion
E. Cannot tell from the information given
Pg. 172