bsaa effect of antibiotics worksheet
advertisement

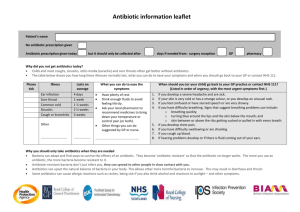
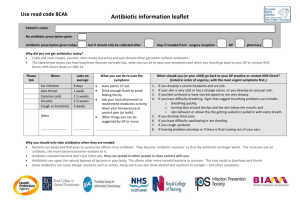
EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS ON BACTERIA Student Learning Objectives. Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives: 1 Understand the function and purpose of antibiotics. 2 Explain the way that bacteria can cause infections. 3 Understand how bacteria can be spread from host to host. Anticipated Problem: What is the function and purpose of antibiotics? I. Antibiotics are very important and powerful chemicals. A. Antibiotics are antimicrobial drugs that slow down or inhibit the growth of some kinds of microorganisms (microbes) in animals. Some microbes are beneficial while others are harmful. Antibiotics have a bacterialcidal effect, meaning they kill or inhibit the growth of other organisms. In our lab, the antibiotic discs will create a zone of inhibition, or area surrounding each disc where bacteria will be unable to grow. Illinois Biological Science Applications in Agriculture Lesson C2–10 • Page 3 B. For an antibiotic to inhibit the growth of bacteria, it must meet several criteria: 1. The antibiotic must not interfere with host’s immune system. Some antibiotics kill beneficial as well as harmful bacteria, which will slow the animal’s recovery. 2. The antibiotic should cause no direct or irreparable damage to the host. This refers to selective toxicity, or the ability of an antibiotic to kill an infection without harming the host. 3. The antibiotic should have a broad spectrum, or be effective against several types of bacteria. C. There are several types of bacteria that cause a mastitis infection, or infection of the udders of milking animals. Since there are several types of bacteria involved, it is best to use a broad spectrum antibiotic to control the infection initially. Once the specific bacteria has been controlled, the antibiotic should be changed to a narrow spectrum antibiotic to control the infection without endangering the beneficial bacteria necessary for milk production. Anticipated Problem: How does bacteria cause infection? II. Bacteria have many ways of causing infection in all animals. A. Some forms of bacteria invade host tissues directly and congregate near weak cells. Once weakened cells have been infected, the disease can spread to other body tissues and areas. Thus, it is important to keep all wounds and body injuries clean, disinfected, and bandaged to reduce the risk of bacterial infection. B. Some bacteria employ the use of microscopic “capsules” to protect them from the environment. These bacteria can survive longer on surface areas and inside the animal body before becoming active and causing infection. C. Scientists have now discovered that some bacteria may use tiny, thread-like apparatus to actually “pull” themselves into position in order to congregate and infect weak cells. D. Most bacteria rely on the method of adhesion to body tissues in order to gain a foothold for infection. Inside the urinary tract of the animal, urine flow is the primary way to rid the body of harmful bacteria. If bacteria are not adhered firmly to the urinary mucosa, they will be flushed out with the urine flow. Anticipated Problem: How can bacteria spread from host to host? III. There are several ways that bacteria can spread from host to host. A. Bacteria can be spread by using non-sterile instruments on animals, orally (by ingesting the bacteria from contaminated food or surfaces), by direct contact between an animal carrying the bacteria and a healthy animal, and through air and water. B. The most common way that bacteria can be spread from host to host is through contaminated feces. Waste management, especially in confinement operations, becomes crucial to control and minimize the spread of bacteria and disease in livestock herds. EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS ON BACTERIA Part One: Matching Instructions: Match the term with the correct response. a. Mastitis c. Bacterialcidal e. Broad Spectrum b. Antibiotic d. Selective Toxicity f. Zone of Inhibition _______1. The antibiotic affects only specific bacteria or specific species. _______2. The antibiotic will affect many different types of bacteria. _______3. A substance to kill or inhibit the growth of another organism. _______4. The area surrounding an antibiotic disc where bacteria cannot grow. _______5. An bacterial infection of the udder. _______6. Having the effect of killing or inhibiting the growth of bacteria. Part Two: Completion Instructions: Provide the word or words to complete the following statements. 1. The most common way for bacteria to spread is through animal _____________. 2. Bacteria must ___________ to body tissues before they can invade cells. 3. Waste management becomes crucial in _______________ operations. Part Three: Multiple Choice Instructions: Circle the letter of the correct answer. _______1. The ability of an antibiotic to inhibit an infection without negatively affecting the host is known as: a. bacterialcidal effect b. zone of inhibition c. E. Coli d. selective toxicity Illinois Biological Science Applications in Agriculture Lesson C2–10 • Page 7 _______2. A chemical that is produced by certain microorganisms in nature that inhibit the growth of other microorganisms is called: a. bacteria b. E. Coli c. an antibiotic d. all of the above _______3. When an antibiotic or other agent has caused the death of the organism it is known as: a. selective toxicity b. zone of inhibition c. gram positive bacteria d. bacterialcidal effect _______4. A clear area surrounding the antibiotic disk where the bacteria are unable to grow is called: a. selective toxicity b. the zone of inhibition c. the bacterialcidal effect d. none of the above _______5. What ways can bacteria can pass through an animal? a. by mouth b. through air and water c. urinary tract d. all of the above Part Four: Short Answer Instructions: Provide information to answer the following question. What are the three conditions that antibiotics must meet to inhibit the growth of bacteria? Illinois Biological Science Applications in Agriculture Lesson C2–10 • Page 8 Assessment Illinois Biological Science Applications in Agriculture Lesson C2–10 • Page 21 TS–A Technical Supplement EFFECT OF ANTIBIOTICS ON BACTERIA 1. What are some necessary characteristics an antibiotic must have to inhibit the growth of bacteria? Antibiotic compounds are called antimicrobial drugs because they kill or slow down the growth of some kinds of microorganisms (microbes) that live in animals. Some of these microbes are beneficial to animals, while others are harmful. When livestock are raised in confinement, there is a greater potential for the spread of harmful microbes among the animals because they are crowded more closely together. The use of antimicrobial drugs or antibiotics helps to keep these harmful microbes under control. For an antibiotic to inhibit the growth of bacteria, it must meet several criteria: It must not interfere with the host’s immune system. Some antibiotics kill not only bad bacteria, but also harm good bacteria, thus slowing the animal’s recovery. It should cause no direct or irreparable damage to the host. This involves selective toxicity: the ability of the antibiotic to exhibit an infection without harming the host. It should have a broad spectrum or be effective against several types of bacteria. These types of antibiotics can take care of several species of bacteria. Illinois Biological Science Applications in Agriculture Lesson C2–10 • Page 22 2. How does a broad spectrum of antibiotics help to cure a disease like mastitis? Different types of antibiotics vary in the range of microorganisms that they control. Some control many types of different microorganisms and are thus called broad spectrum antibiotics. Those antibiotics that control only a few microorganisms are called narrow spectrum antibiotics. Since there are several types of bacteria involved in a mastitis infection, such as strep. and staph., a broad spectrum antibiotic should be used. A broad spectrum antibiotic will not only inhibit the bacteria or microorganisms responsible, but also aid in the cow’s speed to recovery by improving the animal’s health. After the specific bacteria have been controlled, the antibiotic should be changed to a narrow spectrum antibiotic to control the problem without endangering the beneficial bacteria necessary for milk production. 3. How is selective toxicity important in an antibiotic? Selective toxicity becomes very important in an antibiotic when you want to control or inhibit one type of bacteria without decreasing the animal’s health by damaging its immune system. 4. Why is the bacteria’s ability to adhere so important? The ability of bacteria to adhere to tissues/cells is important because if bacteria do not adhere to these structures, the animal’s defense system will be weakened. The advantageous bacteria need to adhere for growth, reproduction, and immunity. The harmful bacteria need to adhere for the infection to invade cells and spread to other body tissues. If bacteria fail to adhere to tissues/cells, they will be flushed out of the body through the urinary tract. Antibiotics need to adhere also, or they won’t be effective. 5. How are bacteria spread from host to host? Bacteria are spread from animal to animal through feces, non-sterile instruments, orally, by direct contact, and through air and water. The most common way bacteria are spread from animal to animal is through feces. Therefore, waste management becomes very critical, especially in confinement. Illinois Biological Science Applications in Agriculture Lesson C2–10 • Page 23