Cardiovascular Pharmacology
advertisement
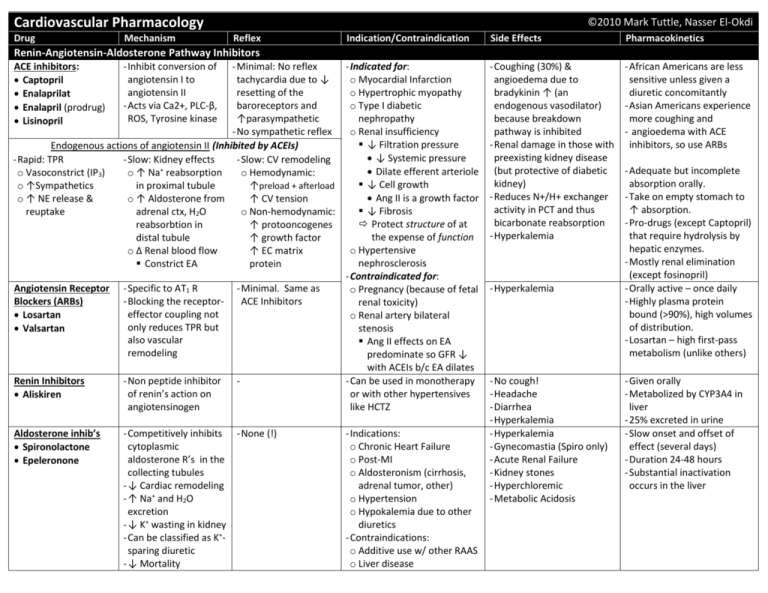
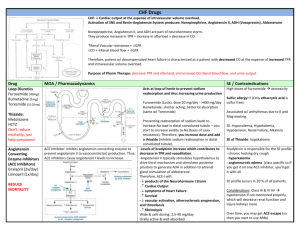
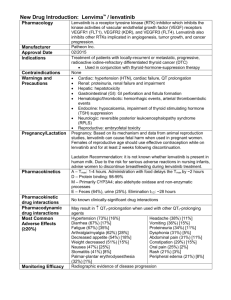
Cardiovascular Pharmacology Drug Mechanism ©2010 Mark Tuttle, Nasser El-Okdi Reflex Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Pharmacokinetics - Coughing (30%) & angioedema due to bradykinin ↑ (an endogenous vasodilator) because breakdown pathway is inhibited - Renal damage in those with preexisting kidney disease (but protective of diabetic kidney) - Reduces N+/H+ exchanger activity in PCT and thus bicarbonate reabsorption - Hyperkalemia - African Americans are less sensitive unless given a diuretic concomitantly - Asian Americans experience more coughing and - angioedema with ACE inhibitors, so use ARBs Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Pathway Inhibitors ACE inhibitors: Captopril Enalaprilat Enalapril (prodrug) Lisinopril - Minimal: No reflex - Indicated for: tachycardia due to ↓ o Myocardial Infarction resetting of the o Hypertrophic myopathy baroreceptors and o Type I diabetic ↑parasympathetic nephropathy - No sympathetic reflex o Renal insufficiency ↓ Filtration pressure Endogenous actions of angiotensin II (Inhibited by ACEIs) ↓ Systemic pressure - Rapid: TPR - Slow: Kidney effects - Slow: CV remodeling + Dilate efferent arteriole o Vasoconstrict (IP3) o ↑ Na reabsorption o Hemodynamic: ↓ Cell growth o ↑Sympathetics in proximal tubule ↑preload + afterload Ang II is a growth factor o ↑ NE release & o ↑ Aldosterone from ↑ CV tension ↓ Fibrosis reuptake adrenal ctx, H2O o Non-hemodynamic: Protect structure of at reabsorbtion in ↑ protooncogenes the expense of function distal tubule ↑ growth factor o Hypertensive o Δ Renal blood flow ↑ EC matrix nephrosclerosis Constrict EA protein - Contraindicated for: Angiotensin Receptor - Specific to AT1 R - Minimal. Same as o Pregnancy (because of fetal Blockers (ARBs) - Blocking the receptorACE Inhibitors renal toxicity) effector coupling not Losartan o Renal artery bilateral only reduces TPR but Valsartan stenosis also vascular Ang II effects on EA remodeling predominate so GFR ↓ with ACEIs b/c EA dilates Renin Inhibitors - Non peptide inhibitor - Can be used in monotherapy of renin’s action on or with other hypertensives Aliskiren angiotensinogen like HCTZ Aldosterone inhib’s Spironolactone Epeleronone - Inhibit conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II - Acts via Ca2+, PLC-β, ROS, Tyrosine kinase - Competitively inhibits - None (!) cytoplasmic aldosterone R’s in the collecting tubules - ↓ Cardiac remodeling - ↑ Na+ and H2O excretion - ↓ K+ wasting in kidney - Can be classified as K+sparing diuretic - ↓ Mortality - Indications: o Chronic Heart Failure o Post-MI o Aldosteronism (cirrhosis, adrenal tumor, other) o Hypertension o Hypokalemia due to other diuretics - Contraindications: o Additive use w/ other RAAS o Liver disease - Hyperkalemia - No cough! - Headache - Diarrhea - Hyperkalemia - Hyperkalemia - Gynecomastia (Spiro only) - Acute Renal Failure - Kidney stones - Hyperchloremic - Metabolic Acidosis - Adequate but incomplete absorption orally. - Take on empty stomach to ↑ absorption. - Pro-drugs (except Captopril) that require hydrolysis by hepatic enzymes. - Mostly renal elimination (except fosinopril) - Orally active – once daily - Highly plasma protein bound (>90%), high volumes of distribution. - Losartan – high first-pass metabolism (unlike others) - Given orally - Metabolized by CYP3A4 in liver - 25% excreted in urine - Slow onset and offset of effect (several days) - Duration 24-48 hours - Substantial inactivation occurs in the liver Drug Mechanism Reflex Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Pharmacokinetic - ↓CO via β1 in heart via ↓ and ↓ PKA - ↓ BP from ↓RAAS activity via β1 in kidney mesangial cells - Prevent NE effects o ↓ Cardiac remodel o ↓ Cell death - CV ↓ initially, but CV ↑ in long term - Baroreceptor reflex blocked postural hypotension - Indicated for: o Hypertension o Heart disease o Angina Pectoris o Arrhythmias - Contraindicated for: o Type I diabetes bc it masks hypoglycemic tachycardia o Asthma o Heart block o Peripheral vascular disease o Variant (Prinzmetal) angina - Oral - Duration of action is 10-12 hours - Once-a-day treatment α1-Blockers Doxazoxin Prazosin Terazosin Mixed α/β-Blockers Carvedilol (β > α) Labetalol (β > α1) Partial β2 agonist - - Orthostatic hypotension - LDL and triglycerides ↑ - Bronchospastic disease - Bradycardia, AV block, MI - Acute cardiac decompen. - Withdrawal syndrome o Can lead to myocardial ischemia since β1 Rs have been up-regulated - Fatigue - Cold hands - Central actions: Sedation, Depression, vivid dreams - Impotence - Abrupt discontinuation can lead to myocardial ischemia since β1 Rs have been up-regulated - - - Central α2 agonists α-methyldopa Clonidine Peripheral antagonist Reserpine - Inhibits adrenergic neuronal outflow from brainstem - Inhibit vesicular uptake of NE - Indicated for: o Pheochromocytoma - Contraindicated for: o Decompensated HF o Asthma o 2nd/3rd degree AV block - - Depression - Ulcers - - Helps block pseudohypertension, but no end-organ protection - Depression, more so than the Central α2 agonists - Ulcers - ©2010 MT,NE Adrenergic Drugs β-Blockers Metoprolol (β1 » β2) Nadolol (β1 = β2) Propanolol (β1 = β2) - ↑ Exercise tolerance in angina patients since limiting factor was chest pain - ↓ exercise tolerance in normal patients since CO is limiting - Better than α /βblocker alone because of α-block: ↓afterload - Also an antioxidant - Monotherapy may increase risk of CHF, but LDL ↓ and HDL ↑ - Direct Vasodilators Drug K+ Channel Openers Diazoxide Minoxidil (Rogaine) Mechanism - ↓ afterload (selective for arterial vascular beds) - K+ leak hyperpolarizes smooth m., relaxing Reflex - Severe reflex hypertension pseudohypertension - Use in combination with a drug that opposes this reflex Organic Nitrates Isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN) Isosorbide-5mononitrate (oral) Amyl Nitrate Nitroglycerin - ↓ preload - Peripheral veins > resistance vessels - Large arteries > small arteries - NO ↑, cGMP ↑, activating Protein Kinase G which dePlates part of the myosin light chain, relaxing the muscle - Hypotension - Tachycardia o ↓ Perfusion time - Contractility ↑ o ↑ O2 demand Inorganic Nitrates Sodium Nitroprusside - ↓ preload and ↓ afterload (act arterial + venous) - Donates NO, same mechanism as organic nitrate - Na+ and H2O retention Nesiritide Synthetic Brain Natriuretic Pept (BNP) - ↑cGMP relaxes arteries - 2nd Messenger Inhibs Hydralazine and veins Indication/Contraindication - Contraindicated as monotherapy due to pseudohyptertension - Indicated for heart failure patients with renal dysfunction that can’t tolerate ACE inhibitiors - Indicated for: o Acute MI o Heart failure o Malignant hypertension o Stable angina Dilation of veins: ↓preload N.C. in coronary flow, but ↑ subendocardial flow Non-ischemic is unaffected: no coronary “steal” like with dipyridamole o Variant angina: Prinzmetal Relieve vasospasm ↑ epicardial flow o Unstable angina Unclear, but platelets ↓ - Contraindicated with: o Concurrent ED drugs (Sildenafil citrate, Vardenafil, Tadalafil) - Indicated for: o Hypertensive emergency o Severe heart failure - Contraindicated for: o Renal insufficiency - Endogenous BNP is a marker for HF! > 100pg/dl Side Effects - Lupus-like Syndrome - Angina - Tachycardia - Headache - Nausea - Anorexia - sweating/flushing - Orthostatic hypotension o Venous dilation - Throbbing headaches o Arteriolar dilation - Inhibit platelet aggregation via ↑ cGMP - Relaxation of non-vascular smooth mm (ex. GI, airway) - Tolerance develops rapidly, so best to have 8 hour periods of non-use - Cyanide intoxication o Antidote: Sodium thiosulfate or Hydroxycobalamin - Arrhythmias - Hypotension (shock) - Hypothyroidism (rare) - Pharmacokinetic ©2010 MT,NE - 16% in fast acetylators - 35% in slow acetylators - High first-pass metab: 90% - Nitroglycerin t½: 1-3 min - ISDN t½: ~40 min - Transdermal Nitrog.t½:6-10h - Preparations o Prophylaxis Oral o Acute Sublingual o ACS Intravenous - Intravenous - Short duration (minutes) - Metabolized by uptake into RBC mitochondria and liberation of cyanide - Drug Mechanism Reflex Indication/Contraindication Side Effects Pharmacokinetic ©2010 MT,NE 2+ - Generally selective for arterial smooth muscle - Neurons: N/P-type Ca channels, but these drugs only act on L-Type Ca2+ channels Calcium Channel - ↓afterload, not preload - Skeletal muscle relies on [Ca2+]intracellular but cardiac/smooth m rely on [Ca2+]extracellular Antagonists Atherosclerosis ↓via non-channel effects—antioxidant? ↓ Non-voltage gated Ca2+ channel (TRPC3), TNFα-NFκB pro-inflam. signaling ↓, VCAM-1 ↓, monocytes ↓ Dihydropyridine - Vasculature > Cardiac - Over-use results in - Stable and prinzmetal angina - Migraine - Oral/IV preparations - Blocks L-type Ca2+ ch. dominance of reflex - Hypertension - Preterm labor - High first-pass metabolism Amlodipine mechanism Supraventrical tachycardia Stroke - CytP450 3A4 inhibited by Nifedipine o ↑End Diastolic (arrhythmias) - Raynaud’s phenomenon o Grapefruit juice (Anti-taste) “-ines” Pressure and o Diazepam (Anti-anxiety) Non-Dihydropyridine - Vasculature = Cardiac - Contraindicated with: - Atrioventricular block 2+ ejection time, while o Ketoconazole (Antifungal) - Blocks L-type Ca ch. o β-blockers: CO - Acute heart failure Diltiazem decreasing heart - Duration of action: 4-8 hrs - ↓vascular resistance, o ↑ [Digoxin] to toxic level - Constipation Verapamil rate, contractility - t½: 3-6 hrs cardiac rate and o Heart block - Edema and arterial - Significant binding to plasma cardiac force result in o Sick sinus syndrome - Nausea pressures proteins (77-99%) ↓O2 demand o CHF - Flushing o Hypotension - Dizziness Inotropic Agents Cardiac glycosides: - ↓Cardiac Na+/K+ pump - Sensitize - Indicated for: - AV blockade - Sugar residues control o Digitalis competes w/K+ parasympathetic o Heart failure - Ventricular tachycardia pharmacokinetics Digoxin (-OH @ 12) o Hyperkalemia: ↓ efx tone ↑ o CHF with A-fib GI effects Digitoxin is more lipid-soluble Digitoxin o Hypokalemia: ↑ efx - ↓ Sympathetic o CHF with dilated heart o Vomitting since it has no OH @ pos 12. Ouabin (possible) - ↑ intracellular Ca2+ via activity - Contraindicated with: o Diarrhea o t ½: 168h ↓ Na+/Ca2+ activity - (may) sensitize o Quinidine use - CNS: hallucinations o Mostly in blood No effect on overall baroreceptors o Amiodarone use - EKG changes: o 90% bound to pp mortality, but may Contractility, SV ↑ Heart rate ↓ o Verapamil use o PR int. ↑, QT int. ↓ Digoxin is more water-soluble improve quality of AV-conduction rate ↓ o Loop diuretics (since o T-wave inversion since it has an OH @ pos 12 life they ↓ K+) At toxic levels: o t ½: 40h Used when diuretic Pre/afterload ↓ - Arrhythmia: delayed after o Mostly in cells and ACE inhibitor repolarization o 20% bound to pp fail to control - Hypokalemia Low therapeutic - Reduced renal clearance index w/quinidine + verapamil - Treat with: o K+, lidocane, Anti-digoxin Abs Newer Anti-Angina Drugs Metabolic modulators (Trimetazine, ranolazine): pFOX inhibitors ischemic myocardium shifts to FAO metabolism over glucose which has higher O2 requirement Direct bradycardic agents: Ivabradine K+ channel activators: Nicorandil Rho kinase inhibitors: Fasudil NO donors: L-arginine Capsaicin Amiloride PKG facilitators: Detanonoate Thiazolinediones Diuretics Drug Mechanism Thiazides: - ↓ NaCl reabsorption in distal convoluted Chlorothiazide tubule Hydrochlorothiazide - ↓Cardiac O2 consum. Chlorothalidone Loop Diuretics: - ↓ NaCl and KCl reabsorption in thick Furosemide ascending limb Bumetanide Blocks Na/K/2Cl transporter - ↓Cardiac O2 consum. Reflex - Stimulation of sympathetic activity - Activation of RAAS - Strong reflex response rules out mono therapy with diuretics Indication/Contraindication - Indicated for: o Renal failure o Heart failure, hypertension o Edematous conditions o Hyperkalemia/calcemia - Chlorothalidone no diff than amlodipine/lisinopril, but better than α-blker doxazosin - Contraindicated with: o Diabetes (high doses) o Dyslipidemia (high doses) Side Effects - Hypokalemia o Increases digitalis, quinidine toxicity (torsades de points) o V-fib - Hyperuricemia (gout) - Hyperglycemia - Sexual impotence - Ototoxicity (loop only) - Teratogenic (loop only) Pharmacokinetic ©2010 MT,NE - Chlorothiazide o 9-56% bioavailable o 1.5h t½ - Hydrochlorothiazide o 70% bioavailable o 2.5h t½ - Chlorothalidone o 65% bioavailable o 47h t½ - Loop: ~ 4h t½ Overall Treatment Notes Hypertension Common Drug combinations: Racial considerations - Reserpine, hydralazine, HCTZ - African Americans: - β-blockers and diuretics Ca2+ antagonists + diuretics - ACE inhibitors/ARBs + diuretics - Asian Americans: ARBs - ACE inhibitors + Ca2+ antagonists Initial drug choices - Uncomplicated: diuretics, β-blockers - Diabetes w/proteinuria: ACE inhibitor - Heart failure: ACE inhibs, diuretics Heart Failure - - - Angina Chronic Stable Angina - Nitrates - Ca2+ Channel Antagonists - β-Blocker Vasospastic (Prinzmetal’s) Angina - Nitrates - Ca2+ Channel Antagonists High filling pressure, dyspnea o Venous dilators: Long-acting nitrates relieve filling pressures and pulmonary congestion Fatigue, low LV output o Arteriolar dilators: Hydralazine (2nd messenger inhibitor/Direct vasodilator) Chronic failure o Need to relieve both Unstable Angina - - Isolated systolic hypertension (older persons) Diuretics or long-acting DHP-Ca2+ blockers - MI: β-blockers (non-ISA), ACE I’s Platelet inhibitors Heparin Nitrates β-Blocker Ca2+ Channel Antagonists Non-pharmacologic intervention (CABG etc)