Eagle Physicians & Associates, PA
advertisement
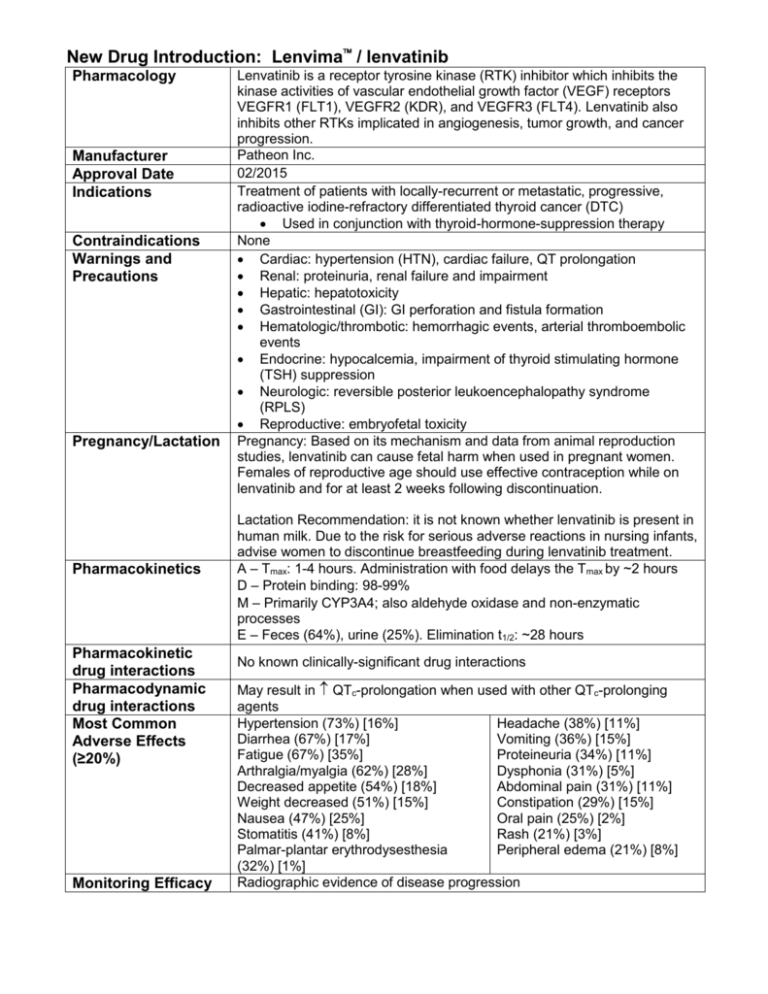
New Drug Introduction: Lenvima / lenvatinib Pharmacology Manufacturer Approval Date Indications Contraindications Warnings and Precautions Pregnancy/Lactation Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetic drug interactions Pharmacodynamic drug interactions Most Common Adverse Effects (≥20%) Monitoring Efficacy Lenvatinib is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor which inhibits the kinase activities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors VEGFR1 (FLT1), VEGFR2 (KDR), and VEGFR3 (FLT4). Lenvatinib also inhibits other RTKs implicated in angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression. Patheon Inc. 02/2015 Treatment of patients with locally-recurrent or metastatic, progressive, radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) Used in conjunction with thyroid-hormone-suppression therapy None Cardiac: hypertension (HTN), cardiac failure, QT prolongation Renal: proteinuria, renal failure and impairment Hepatic: hepatotoxicity Gastrointestinal (GI): GI perforation and fistula formation Hematologic/thrombotic: hemorrhagic events, arterial thromboembolic events Endocrine: hypocalcemia, impairment of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) suppression Neurologic: reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome (RPLS) Reproductive: embryofetal toxicity Pregnancy: Based on its mechanism and data from animal reproduction studies, lenvatinib can cause fetal harm when used in pregnant women. Females of reproductive age should use effective contraception while on lenvatinib and for at least 2 weeks following discontinuation. Lactation Recommendation: it is not known whether lenvatinib is present in human milk. Due to the risk for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, advise women to discontinue breastfeeding during lenvatinib treatment. A – Tmax: 1-4 hours. Administration with food delays the Tmax by ~2 hours D – Protein binding: 98-99% M – Primarily CYP3A4; also aldehyde oxidase and non-enzymatic processes E – Feces (64%), urine (25%). Elimination t1/2: ~28 hours No known clinically-significant drug interactions May result in QTc-prolongation when used with other QTc-prolonging agents Hypertension (73%) [16%] Headache (38%) [11%] Diarrhea (67%) [17%] Vomiting (36%) [15%] Fatigue (67%) [35%] Proteineuria (34%) [11%] Arthralgia/myalgia (62%) [28%] Dysphonia (31%) [5%] Decreased appetite (54%) [18%] Abdominal pain (31%) [11%] Weight decreased (51%) [15%] Constipation (29%) [15%] Nausea (47%) [25%] Oral pain (25%) [2%] Stomatitis (41%) [8%] Rash (21%) [3%] Palmar-plantar erythrodysesthesia Peripheral edema (21%) [8%] (32%) [1%] Radiographic evidence of disease progression Monitoring Toxicity Dosing - Initial Dosing - Usual Dosing - Max Renal Adjustment Hepatic Adjustment Toxicity Adjustment Baseline and periodically: blood pressure, proteinuria (urinalysis), liver/renal function and electrolytes/serum calcium (comprehensive metabolic panel, magnesium level), TSH levels, QTc interval (electrocardiogram), left ventricular ejection fraction (echocardiogram); symptoms of cardiac decompensation, arterial thromboembolic events, GI perforation/fistula, RPLS 24 mg PO once daily at the same time each day (not to exceed 2 doses within a 12 hour period) 24 mg PO once daily 24 mg PO once daily CrCl ≤ 30 mL/min: 14 mg PO once daily Severe (Child-Pugh C): 14 mg PO once daily Grade 2/3 adverse reaction or grade 4 laboratory abnormality: interrupt lenvatinib therapy until resolved, then resume at: 20 mg PO once daily (1st occurrence) 14 mg PO once daily (2nd occurrence) 10 mg PO once daily (3rd occurrence) Life-threatening HTN, grade 4 cardiac dysfunction, arterial thrombotic event, hepatic failure, nephrotic syndrome, severe renal impairment, GI perforation, life-threatening fistula, severe RPLS, grade 4 hemorrhage: discontinue lenvatinib Cost: Source: GoodRx.com, accessed 03/14/2015 Dose(s) Brand– Generic Lenvima- lenvatinib Caprelsa®- vandetanib Nexavar®- sorafenib 24 mg once daily 300 mg once daily 400 mg twice daily $ (30d) $14,371 $12,331 $12,588 Summary Lenvima™, lenvatinib, is an oral receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of locally-recurrent or metastatic, progressive, radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC). Lenvatinib is used in conjunction with thyroid-hormone-suppression therapy for DTC that is refractory to iodine-131 therapy. The most common adverse effects in lenvatinib-treated patients are hypertension (sometimes severe), diarrhea, and fatigue. . References: 1. http://www.lenvima.com 2. Lenvima package insert. Patheon Inc. February 2015. 3. Schlumberger M, Tahara M, Wirth LJ, et al. Lenvatinib versus placebo in radioiodinerefractory thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 2015;372(7):621-630. Date Prepared: 04/07/2015 Editor: Peter G. Koval, Pharm.D., BCPS Author: Kira Letvak, Pharm.D. Candidate, UNC Eshelman School of Pharmacy