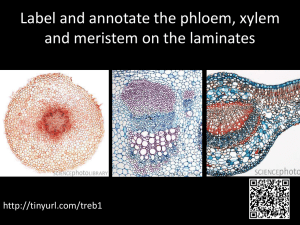
Vascular Tissues
advertisement

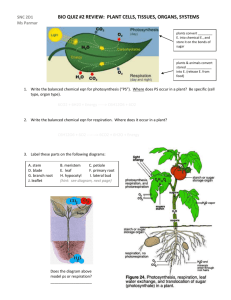
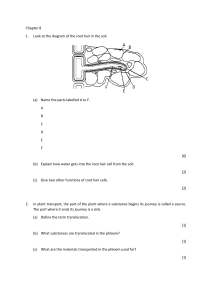
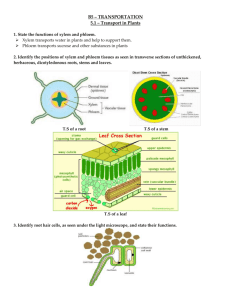
SBI3U TRANSPORT IN PLANTS Name:________________ There are two main vascular tissues in complex plants: Xylem and Phloem. Tissue Overall Structure Xylem Phloem Overall Function Types of Xylem and Phloem Cells (pg. 555) XYLEM Cell Types-- (1) Vessel Elements (2) Tracheids size PHLOEM Cell Types- (1) Sieve Tube Elements (2) Companion Cells size shape open-ended pointy nucleus? plant type angiosperms only all vascular plants perforated? (has holes) (3) Sieve Cells WATER TRANSPORT IN XYLEM Roots take in water through the _____________ and epidermal cells by __________ which is a process that moves water from areas of lots of water to areas where there’s less water (soil into roots). Water flows through epidermal cells, cortex and into the __________________________ which contains the xylem. Water travels up the ________ and then branches into the __________ of the leaf. It then moves into various _________ of the leaf such as the palisade mesophyll and spongy mesophyll. Most water exits the plant through a process called _________________. The water diffuses into air spaces in the spongy cells and then diffuses out of the leaf through the tiny pores called ________________. As each water molecule exits the leaf, another one enters the plant through the ____________. Three main stages involved in water transport: 1. Root Pressure 2. Capillary Action 3. TRANSPIRATIONAL PULL (or Cohesion-Tension) Transpiration is the ____________________________________________________________________________ Because water is POLAR, the water molecules in the xylem are connected by COHESIVE FORCES so the upward movement of water causes another water molecule to move into the root (by osmosis) as one leaves the leaf. What are factors that affect the rate of transpiration? The rate of transpiration is greatest on ________, _________, ________ days. NUTRIENT (SUGAR) TRANSPORT IN PHLOEM: TRANSLOCATION Translocation is the downward transport of carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis through the ________________. Sugars move from the “source” or _______________________________________________ to organs in the plant, which rapidly consumes sugars OR stores the sugars, which is called the _____________. Examples: source: _____________ sink: __________________ Translocation 1. Carbohydrates (glucose sugars) produced in the leaf palisade cells by photosynthesis ( a source) move into the phloem. 2. The solute concentration inside the phloem’s sieve tubes increases then water moves into the phloem by osmosis. (Water comes from the _______________.) 3. This increases the pressure in the phloem so water is pushed down and carries the sugars with it (mass-flow theory) 4. The dissolved sugars move to various sinks such as the roots, developing flowers and fruits (a meristem called the bud primordium) or rapidly dividing cells in the plant responsible for growth in diameter (__________________________) or height/length (_____________________________). In root cells, glucose is converted into starch and stored. Draw a visual that may help you picture translocation in the box provided. (pg. 569) Home Fun : Read pages 564-570. Answer #4, 6 on pg. 570.