Label and annotate the phloem, xylem and
advertisement
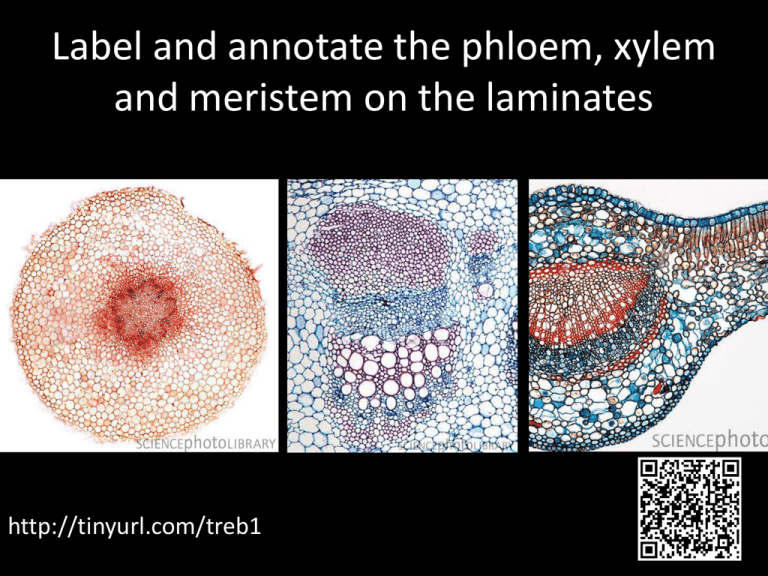
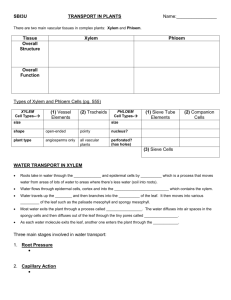
Label and annotate the phloem, xylem and meristem on the laminates http://tinyurl.com/treb1 2. Flowering plants have two tissues to transport materials, xylem and phloem. The diagram below shows the outline of a transverse section of the root of a dicotyledonous flowering plant. Sketch in and label the areas occupied by the xylem and phloem. Booklet Page 6 [Total 2 marks] Memorise this…. Recreate! Xylem Xylem Hollow Dead cells end to end Continuous Tubes (Narrow) Strengthened with Lignin Pits in wall Allow movement across No cell contents, no nucleus or cytoplasm, no end walls Page 7 How Xylem is Adapted for its role: Structure/Feature How adaptation works Dead cells aligned end to end in a continuous column Narrow tubes Lignin deposited in the walls Pits in the lignified walls No end walls or cell content Memorise this…. Recreate! Phloem Two types of cell: Sieve Tube elements and Companion Cells Sieve Tube elements: Little cytoplasm and no nucleus End to end to make a tube Cross walls perforated by pores – Sieve plates Phloem Companion Cells Large nucleus and dense cytoplasm Lots of mitochondria – ATP for active processes Linked by plasmodesmata How Phloem is Adapted for its role: Structure/Feature Sieve tube element Mitochondria in companion cell Little cytoplasm plasmodesmata How adaptation works Label diagrams in booklet and make sure key words defined On mini wb: 1. Describe the structure of a xylem vessel 2. Why do xylem vessels have pits 3. Explain why sieve tube elements are not true cells Xylem Phloem Both Xylem and Phloem Homework Using https://www.tumblr.com/ Compare and contrast the xylem and phloem in a plant and explain how they are adapted to their function