Classification - Mrs. Wolodkowicz`s Biological Realm
advertisement

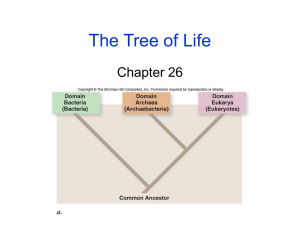
Mrs. Wolodkowicz Biology 1H Chapter 17 Classification of Organisms I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Taxonomy- branch of Biology that names & groups organisms according to their characteristics & evolutionary history or phylogeny. Aristotle- first to group organisms (either plant or animal & based on habitat (land, water, or air)) & used common names (problem: Jelly fish-not a fish at all). Linnaeus- (1707-1778) grouped organisms based on morphology. We still use his system today, but we additionally group based on phylogeny. A. Kingdom- largest group ex. Animalia. B. Phylum/Division (plants)- subset of kingdom ex. Chordata. C. Class- subset of phylum ex. Mammalia. D. Order- subset of class ex. Primates. E. Family- subset of order ex. Hominidae. F. Genus- Homo. G. Species- ex. sapiens Naming of organisms- Binomial Nomenclature. All organisms are given 2 names that make up their scientific name. The first part of the name is the Genus (always written in capitol letters). The second part of the name is the species (always written in lower case letters) and both names are underlined or written in italics. Ex. humans- Homo sapiens (species name is usually descriptive-wise). Ex. Canis lupus. Dichotomous key- written set of choices that leads to the name of an organism based on its morphology. Ex. Flower, # of petals, # of leaves, etc. Systematic taxonomy- organizes all organisms within the context of evolution. (Fossil record, morphology, embryonic developmental patterns, & molecular biology (DNA). A. Phylogenetic Tree- shows the evolutionary relationships of species in naming them. B. Cladistics- categorizes organisms based on shared derived characteristics to establish evolutionary relationships. Ex. Birds: all contain feathers; most other animals do not have feathers, thus linking all birds with a common ancestor. The kingdoms (6) A. Kingdom Archaebacteria- unicellular prokaryotes (no nucleus, no membrane organelles) that may be autotrophic or heterotrophic, aerobic or anaerobic & often live in hostile environments (most ancient of organisms. Live for about 30 min B. Kingdom Eubacteria- unicellular prokaryotes. Most are aerobic, while a few are anaerobic (bacteria). Live for about 30 min. Note: Mrs. Wolodkowicz Biology 1H VII. Archaebacteria and Eubacteria used be jointly called kingdom Monera. C. Kingdom Protista- Eukaryotic (nucleus & membrane bound organelles), mostly single-celled organisms but some are multicellular (kelp). May be heterotrophic or autotrophic Ex. Euglena’s, amoebas. D. Kingdom Fungi- Heterotrophic unicellular & multicellular Eukaryotic organisms. Ex. Mushrooms, yeast. E. Kingdom Plantae- Eukaryotic, multicellular. Most are autotrophic, a few are parasitic. Ex. ferns, moss, oak tree, rose, grass, etc. F. Kingdom Animalia- Eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic organisms. Ex. fish, dogs, worms, humans. 3-Domain System- another way of classifying organisms based on the sequences of ribosomal RNA. Even prokaryotes contain RNA. Carl Woese (1928-) used ribosomal RNA to estimate how long ago pairs of different organisms shared a common ancestor. He grouped them by domains. A. Domain Eukarya- contains Protista, Plantae, Fungi, & Animalia. B. Domain Bacteria- kingdom Eubacteria. C. Domain Archaea- kingdom Archaebacteria.