ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
advertisement

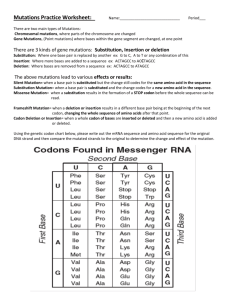
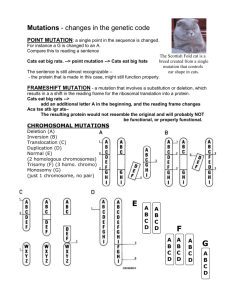
ANSWERS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS CHAPTER 12 1. A mutation occurs in less than 1 percent of the population. A SNP occurs in more than 1 percent of the population. 2. A germinal mutation occurs in a gamete or a fertilized ovum, and therefore affects all the cells of an individual and is more serious than a somatic mutation, which affects only some tissues and is not transmitted to future generations. 3. Collagen’s conformation and assembly is very precise and sensitive to disruption by slight alterations. 4. Gaucher disease is a metabolic disorder that causes fat buildup in bone marrow, liver, and spleen and Parkinson disease is a neurodegenerative movement disorder. Both can be caused by deficiency of an enzyme, glucocerebrosidase. 5. A spontaneous mutation can arise if a DNA base is in its rare tautomeric form at the instant when the replication fork arrives. A wrong base inserts opposite the rare one. 6. Alpha and beta rays do not often harm health unless inhaled or eaten. Gamma radiation can penetrate the body, damaging tissues. 7. Mutational hot spots are direct repeats or symmetrical regions of DNA. 8. Frameshift, deletion, duplication, insertion, transposable element 9. a. A degenerate codon b. A mutation that replaces an amino acid with a structurally similar one c. A mutation that replaces an amino acid in a nonessential part of the protein d. A mutation in an intron 10. A jumping gene can disrupt gene function by altering the reading frame or shutting off transcription. 11. The gene is expanding. 12. Short repeats can cause mispairing during meiosis. Long triplet repeats add amino acids, which can disrupt the encoded protein's function, often adding a function. Repeated genes can cause mispairing in meiosis and have dosage-related effects. 13. Copy number variants (CNVs) differ by the number of copies of genes. Missense mutations are single DNA base pair changes that alter the amino acid sequence of a peptide. 14. Retention of an intron and expanding triplet repeats may provide a new function for a gene, which may cause disease. 15. Mutations in the 3rd codon position can be silent. Mutations in the 2nd position may replace an amino acid with a similarly-shaped one. 61 codons specify 20 amino acids. 16. A conditional mutation is only expressed under certain conditions, such as increased temperature or exposure to particular drugs or chemicals. 17. Excision repair corrects ultraviolet-induced pyrimidine dimers. Mismatch repair corrects replication errors. They use different enzymes. 1 18. The parental DNA strand is retained in the stem cell. ANSWERS TO APPLIED QUESTIONS 1. a. AUGUCGUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, substitutes serine for leucine. b. AUGUAGUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, changes second codon to a stop codon. c. AUGAAUUGUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, shifts reading frame. d. AUGUUAUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, no consequence e. AUGUUCUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, substitutes phenylalanine for leucine. f. AUGUUAUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, no consequence g. AUGUUGUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCAAUGUUGUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA h. AUGUGUCAAAAGCAUGGCGGCCA, shifts reading frame. 2. The frameshift mutation can create a stop codon, leading to a shortened polypeptide. 3. Any change that produces UAA, UAG, or UGA 4. a. Methionine-Threonine–Histidine-Arginine-Cysteine-Serine-Leucine-Arginine b. Methionine-Threonine–Histidine-Serine-Cysteine-Serine-Leucine-Arginine c. A nonsense mutation that causes a premature stop and shortens the peptide. d. A frameshift mutation changes the sequence and creates a premature stop. e. Insertion of two bases in a row 5. GAU to AAU or GAC to AAC 6. The second boy's second mutation, further in the gene, restores the reading frame so that part of the dystrophin protein has a normal structure, providing some function. 7. Asn to lys: AAU to AAA AAC to AAG ile to thr: AUU to ACU AUC to ACC AUA to ACA 8. a. GCG to GAC or GGU to GAU b. missense 9. The drug causes a tRNA bearing an amino acid to bind to a “stop” codon, enabling the part of the mRNA past the stop codon to be translated. A full protein is made. Such an effect could be used to “read through” stop codons in the middle of genes that cause diseases. 10. Nonsense 11. Arg to his: CGU to CAU or CGC to CAC 12. The repair enzymes could correct UV-induced pyrimidine dimers. ANSWERS TO WEB ACTIVITIES 1. a. de novo, because it is not in parents b. The mutation creates an intron splice site c. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy, dilated cardiomyopathy, Dunnigan-type familial partial lipodystrophy, limb girdle muscular dystrophy, obesity, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. 2 2. Beneficial: identification of fatal “double dominants.” Harmful: screening and termination of all affected pregnancies. 3. Answers vary with image selected. Albinism causes white hair, very pale skin, and red irises. 4. Repeat disease fragile X syndrome Friedrich ataxia Haw River syndrome Jacobsen syndrome spinal + bulbar muscular atrophy spinocerebellar ataxia Repeat CGG or CCG GAA CAG CGG CAG CAG Normal # 6-50 6-29 7-25 11 14-32 4-44 Disease # 200-2,000 200-900 49-75 100-1,000 40-55 40-130 ANSWERS TO FORENSICS FOCUS 1. Somatic mutation ANSWERS TO CASE STUDIES AND RESEARCH RESULTS 1. Keyshauna’s case is more severe because she has short CFTR proteins in all her cells, whereas Latika is missing part of the protein in some cells. 2. Marshall and Angela shouldn't be concerned, because they have mutations in two different genes. 3. a. Autosomal recessive. Both sexes are affected and it skips generations. b. Consanguinity. Blood relatives share alleles inherited from common ancestors increasing the risk of passing the same recessive alleles to children c. No difference in the amino acids. 4. The second amino acid is proline in healthy members and eucine in those with heart failure. 5. Helpful: early identification so that individualized treatments can begin early. Ability to make lifestyle changes and limit environmental exposures that increase risks. Harmful: may subject individuals to stigmatization, genetic discrimination or emotional harm. 3