Homework 8
advertisement

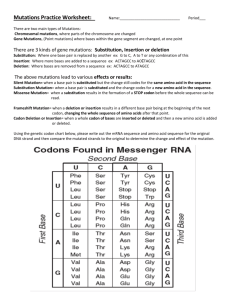
Homework 8 BIO 2 (10 points) Name ________________________ 1a. Lab Sec _____ Protein synthesis occurs with relatively high fidelity. In prokaryotes, incorrect amino acids are inserted at the rate of approximately 5 x 10-4 codons. What is the probability that an averagesized polypeptide of 300 amino acids has exactly the amino acid sequence specified in the mRNA? Show your calculation and express your final answer as a percent. 1a. The error rate of prokaryotic DNA replication is much lower than the error rate of prokaryotic protein synthesis. Why do you think the replication enzymes have evolved to have so much greater a level of fidelity than the enzymes involved in translation? 2. Bio 2 What amino acid would a tRNA with the anticodon 5’-UAG-3’ carry? Explain your logic. Page 1 Fall 2008 3. During translation, RNA:RNA base-pairing is extremely important. Describe three different stages during prokaryotic translation in which RNA:RNA base-pairing plays an important role in the process. In each case, identify the type of RNA(s) involved and the specific role that the base-pairing plays in ensuring that translation takes place properly. 4. Among Betazoids, the ability to read minds is under the control of a gene called “mindreader” (abbreviated mr). Most Betazoids can read minds, but rare mutations in the mr gene result in two alternative phenotypes: delayed-receivers and insensitives. Delayed-receivers have some mind-reading ability but perform the task much more slowly than normal Betazoids and often make mistakes. However, insensitives cannot read minds at all and are often placed in institutions at a young age, since they are unable to survive in normal Betazoid society. Betazoid genes do not have introns, 5’ UTRs, or 3’ UTRS, so the gene only contains coding DNA. It is 2,331 nucleotides in length and Betazoids, like humans, use a three-letter genetic code. The table below shows some data from a Star Fleet study in which the mutations carried by five unrelated mindreader mutants were analyzed. Bio 2 Page 2 Fall 2008 Description of mutation Phenotype Nonsense mutation in codon 774 delayed-receiver Missense mutation in codon 52 delayed-receiver Deletion of nucleotides 934-939 delayed-receiver Missense mutation in codon 192 insensitive Deletion of nucleotides 83-93 insensitive For each mutation, provide a plausible explanation for why it gives rise to its associated phenotype and not to the other phenotype. For example, hypothesize why the nonsense mutation in codon 774 gives rise to the milder delayed-receiver phenotype rather than the more severe insensitive phenotype, and then repeat this type of analysis for the other mutations. (NOTE: More than one explanation is possible in each case.) a. Nonsense mutation in codon 774 b. Missense mutation in codon 52 c. Deletion of nucleotides 934-939 Bio 2 Page 3 Fall 2008 d. Amino acid substitution mutation in codon 192 e. Deletion of nucleotides 83-93 5-6. More practice with unit conversions and common lab calculations. Try to work these problems without looking at your notes. Remember to show your entire calculation and to strike through units to receive full credit! 5. The following primer set is used during a PCR reaction. What annealing temperature would you choose to run the reaction? Show your calculations and explain your logic. forward primer: 5’ – aatgcgttatggaagagct – 3’ reverse primer: 5’ – ccacggcgattagttattga – 3’ Bio 2 Page 4 Fall 2008 6. You cut a viral genome that contains 12,344 bp with the restriction enzyme Eco RI, producing 5 bands, the shortest of which is 422 bp. What is the smallest amount of viral DNA (in ng) that you would need to cut in order to ensure that you would see the 422 bp band on a gel, given that the lower limit of detection of ethidium bromide staining is 10 ng? Bio 2 Page 5 Fall 2008