limestone carbonate
advertisement

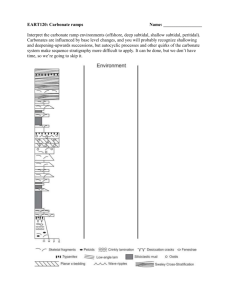
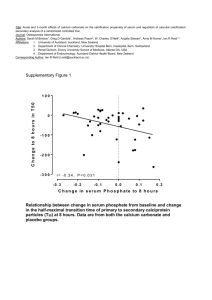
1. CALCIUM CARBONATE 1. PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Calcium carbonate occurs naturally as the principal constituent of limestone, marbel and chalk. Natural ground Calcium carbonate has been used for years as the primary constituent of putty. Since 1945, the processing of natural Calcium carbonate has seen the introduction of beneficiation by flotation to remove impurities and the development of grinding processes to manufacture finer products. The natural ground Calcium carbonate and the precipitated material compete industrially, based primarily on particle size and the characteristics imparted to the product. The precipitated types are distinguished by a finer and more uniform particle size, a narrower particle size range and a higher degree of chemical purity. Specification Calcium Carbonate finds applications in diversified sector and the specifications of the product required by different applications are marginally different. The specifications of Calcium Carbonate required for various applications are provided. Rubber industry Indian standard specification for Activated Calcium Carbonate for rubber industry IS 917-1976 revision 1980 Description The material shall consist of Precipitated Calcium Carbonate coated with thin layers of fatty acids or their salts. It shall be in the form of a free flowing, white powder, free from visible impurities. Characteristic Sieve residue on 150 micron IS Sieve % by mass. max. Hydrochloric acid insoluble % by mass, max. pH Loss on ignition, % by mass Mn % bymass max. Cu% by mass, max. Total fatty matter % by mass Requirements 0.01 0. 2 10.5 0.5 43 to 46 0.02 0.005 2 to 3.5 Mixed oxides, % by mass 1.0 CaCO3, % and MgCO3 together % by mass 92 min. Moisture content, % by mass max. 0.075 The ignition temperature shall be 950 25 deg.C Cosmetic industry IS specifications for Precipitated Calcium Carbonate for cosmetic industry IS No.918-1985 Requirements Description: The material shall be in the form of fine, white microcrystalline powder without any taste or odour. It shall be stable in air. S.No. 1. Characteristics Fineness Residue on 150- m IS sieve, % by mass, max. 2. 3. Loss on drying, % vt mass, max. Bulk density, g/ml 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. Requirement 0.1 1.0 As agreed to between the purchaser and supplier Calcium carbonate (as CaCO3), % by mass 98.0 (on dry basis), min. *Magnesium and alkali salts, % by mass 1.0 max Aluminium, iron, phosphates and matter 0.5 max. insoluble in hydrochloric acid, % by mass Iron (as Fe), % by mass, max. 0.03 Arsenic (as As2O3), parts per million, max. 2 Heavy metals (as Pb), parts/million, max. 10 Chlorides (as Cl), % by mass, max. 0.04 pH of 10% aqueous suspension 9.0 to 10.0 Barium To pass test Sulphates To pass test *Flow point As agreed to between the purchaser and the supplier Explosive and Pyrotechnic industry IS specification for Calcium carbonate for Explosive and Pyrotechnic industry IS: 7633-1982 Types The material shall be of the following two types: Type I Type II Calcium carbonate, natural Calcium carbonate, precipitated Description: Type I of the material shall be in the form of powdered calcite or limestone. It shall be white to off-white in colour. Type II of the material shall be in the form of white powder. The material shall be free from extraneous matter and grit. Requirements for Calcium Carbonate for explosive and pyrotechnic industry:S.No. Characteristics Requirement of Type I Type II Loss on drying, % by mass, max. 0.05 0.5 Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) (on dry basis), % by 98.0 98.0 mass, min. Matter insoluble in dilute Hydrochloric acid % 0.6 0.2 by mass, min. Fineness (material retained on 125-micron* IS Nil Nil sieve) % by mass Water insoluble alkali(as Na2O)% by mass.,max 0.03 0.05 Grit, % by mass, max. 0.06 0.02 Chlorides (as Cl), % by mass. max. 0.05 0.04 Total water soluble matter, % by mass, max. 0.05 0.5 i. ii iii iv. v. vi. vii viii * 90 micron for material required for use in propellants Additional requirements for Calcium Carbonate for use in propellants. S.No. Characteristics Requirement of Type I Type II Magnesium compounds (as MgCO3), % by 0.5 0.5 mass. max Iron (as Fe), % by mass, max. 0.05 0.05 Settling test (volume occupied by 5g), ml. 4 to 10 4 to 6 i. ii. iii. 2. PRODUCT APPLICATIONS Plastics As a filler in rigid and plasticized PVC to improve impact strength. As a filler in PVC footwear and cable compounds/cables to improve surface gloss and other physical properties As a filler in leather cloth sheetings Paints and surface coatings In emulsion paints as a white opacifying agent. As an antisettling agent in paints and printing inks as an extender assisting in the control of strength and body of the ink. As a polishing agent in window and mirror cleaners and polishes. In powder coatings Cosmetics/tooth paste In talcum powder, Calcium Carbonate is used to increase fluffiness and control absorption characteristics. In depilatory creams. In face powders as a perfume carrier. In sunscreen preparations. Paper In paper coating for brightness, smoothness, opacity and ink receptivity. In cigarette paper for control of opacity and burning rate. As a cost-effective filler in alkaline sized papers giving high brightness and opacity. Food and Pharmaceuticals Pharmaceutical: As a calcium source As an antacid As a neutralisation and filtration aid in antibiotic manufacture As a buffering and dissolution aid in soluble tablets. As a bulking agent in tableting Food and Beverages As a calcium supplement In effervescent powder drinks In chewing gum To neutralise excess acid in food and wine manufacture As a filtration aid. Putty, Caulks and Sealants In PVC plastisols as a rheology modifier, particularly for car underbody. Sealant applications on polyurethane, polysulphide and silicone. Sealants for construction and insulation glass applications, as rheology modifier giving slump control. Significance of the applications Calcium carbonate is used as fillers in the above joint fillers. Caulks and sealants require less Calcium carbonate than putty due to their lower viscosity. Other miscellaneous sectors of application Printing inks - filler Joint cement compounds Flue gas desulphurisation - Calcium Carbonate traps the sulfur oxygen compounds produced in the combustion of coal. In Insecticides In polishes, shoe dressings As filler in matches, pencils, crayons etc. In linoleum, insulating compounds, welding rods For water analysis and in preparing Calcium carbonate solutions for standardising soap solutions. 3. IMPORTS Around 4000 tonnes per annum 4. EXPORTS Around 9500 tonnes per annum 5. INDIAN MANUFACTURERS Annapurna Apex Chemicals (P) Ltd., Andhra Pradesh Beautify Products, Gujarat Citurgia Bio Chemicals Ltd., Gujarat Kotak Chemicals Ltd.,Gujarat Kalpana Chemicals, Gujarat 20 Microns Limited, Gujarat Microfill Sharda Realtors Pvt. Ltd., Gujarat Sukkan Industries, Gujarat The Hindustan Mineral Products Pvt. Ltd., Gujarat Bio Chemicals Ltd. Gujarat Amgeen Aromatics, Gujarat Dinesh Chandra Industries, Gujarat Balco Chemicals, Gujarat Indimin Sales Corporation, Gujarat Kalpana Minerals Pvt. Ltd., Maharashtra Cal Chem, Maharashtra Calchem Industries (India) Ltd., Maharashtra Darsynth Chemical Industries Pvt. Ltd., Maharashtra Famous Minerals And Chemicals Co. Maharashtra Gulshan Sugars & Chemicals Ltd. Maharashtra Jaimurthi Minerals & Chemicals Pvt Ltd., Maharashtra Ramdev Chem, Maharashtra Sturdia Chemicals Ltd., Maharashtra Vineeth Chemicals, Maharashtra The Hindustan Mineral Products Co. Ltd., Chandroday Chemical Lime Inds. P.Ltd., Maharashtra Harishit Chemicals, Maharashtra Corrogard Chemicals, Maharashtra Jagrut Chemicals, Maharashtra Rashtriya Chemicals & Fertilizers Ltd., Maharashtra Aranthangi Chemicals (P) Ltd., Tamil Nadu Elf Atochem Peroxides India Ltd., Tamil Nadu Ennor Muds & Chemicals, Tamil Nadu Indian Chemicals & Minerals, Tamil Nadu K.K. Carbonates Pvt. Ltd., Tamil Nadu Merel Labs Pvt. Ltd., Tamil Nadu Kor Chemicals P.Ltd., Tamil Nadu Lime Chemicals Ltd., Himachal Pradesh Trikuta Chemicals Pvt. Ltd., Jammu & Kashmir Chemicals India, Rajasthan SBR Singhania Chemical Industries, Uttar Pradesh Rakehs Chemicals (P) Ltd., Uttar Pradesh U.P. Lime Chemicals Ltd., Uttar Pradesh Searsole Chemicals Ltd., West Bengal Around 1,75,000 tonnes per annum Indian installed capacity 6. DEMAND SUPPLY TRENDS Precipitated Calcium carbonate 84820 Activated calcium carbonate 23500 Total 108220 7. MANUFACTURING PROCESS AND TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENT Precipitated calcium carbonate is manufactured by calcining limestone and recarbonating the hydrated slaked lime in vertical carbonation towers. The reaction is exothermic and proper temperature control is maintained to get desired quality of the product. Technology developments Technology based on Crystal Morphology:A new technology based on Crystal Morphology of Precipitated Calcium carbonate (PCC) have been developed by Mineral Technologies, USA. Minerals Technologies, a company based in New York city has developed recently a patented PCC technology based on the manipulation of PCC crystal morphology. Minerals Technologies has a long experience in operating limestone and take mines, manufacturing mineral based furnace linings and producing PCC. The company has patented technology allowing for the reaction of water, limestone and carbon dioxide to produce a synthetic PCC. The company now produces the mineral in a variety of particle sizes from 0.01 to 100 um and shapes from spherical to scalenohidral and rhombhohedral. The company now offers 12 different types of PCC. This synthetic PCC has found many applications in industry. It has lowered the cost of manufacturing fine printing and writing paper. Specially engineered PCC crystals displace more expensive wood pulp and titanium dioxide and offer varying levels of gloss, light scattering or paper filling properties. Current trends in paper business in USA seem to favour increasing use of PCC. Acid Tolerant Technology The R&D of Mineral Technologies has led to the development of an acid tolerant PCC. This breakthrough could extend PCC into the market for newsprint, directory, magazine and catalog grade papers. Acid tolerant PCC opens a new paper market for PC. The new acid tolerant PCC provides a way to improve the brightness and quality of newsprint. Certain grades of PCC offer such good light scattering ability that they serve an additional benefit of replacing TiO2 in fine paper making. As PCC is much cheaper in price than TiO2, the advantage of replacing TiO2 with PCC is obvious economically. Minerals Technologies R&D has developed yet another process to produce PCC that could further endear the company to its paper industry customers. Its lime soda process yields byproduct caustic soda. In this process, soda ash can replace the carbon dioxide the company now gets from its mill host. Minerals Technologies has signed agreements with two paper companies to provide Precipitated Calcium carbonate (PCC) using its acid- tolerant technology at three ground wood paper mills in North America. 8. GLOBAL SCENARIO Global consumption pattern of Precipitated calcium carbonate Industry Paper Paints Plastics Rubber Food, cosmetics pharmaceuticals Textile packing Putties, caulks, sealants Adhesives Printing ink Consumption in % 72 8 5 4.5 and 4 2.5 2.5 1 0.5 Thrust Area for Demand in the Global Market In developed countries, the paper industry is the largest consumer of Calcium carbonate, as a filler and in coatings. Coarser particle size grades (over 2 micron) are used as fillers, where alkaline pigment with low water demand is preferred. Most of the Precipitated Calcium carbonate go into paper coatings alone or in conjunction with clay. In this application, Precipitated Calcium carbonate adds brightness, opacity and better printing ink receptivity. In developed countries, next to paper industry, paint industry is second in consumption of Calcium carbonate. They are widely used both in alkyd and latex flat wall paints. These grades provide uniform floating, as well as good colour and uniformity on recoat and overlap. The plastic industry uses Precipitated Calcium carbonate in different areas. Precipitated Calcium carbonate also finds wide use in other thermosetting plastic compounds. The printing ink industry uses the ultrafine Precipitated Calcium carbonate in high quality letter press and high quality ink. Caulks and sealants especially the higher quality elastomeric types are especially formulated with Precipitated Calcium carbonate as semi reinforcing filler types. Rubber compounding consumes a considerable amount of ultrafine Precipitated Calcium carbonate for use as reinforcing fillers. The miscellaneous end use areas are in foods and pharmaceuticals. Calcium carbonate are approved by the Foods and Drug Administration of USA, primarily for Calcium enrichment for chewing gum based and for cherry brining. 9. RECOMMENDATIONS Calcium Carbonate industry is of particular relevance to Indian conditions, in view of the adequate availability of raw material namely Lime Stone in the country and also the fact that the economic capacity of Calcium Carbonate and the project cost would not be high. This would make it possible to implement the project in medium scale sector. With regard to the cost of production, fuel and energy factors are important and such energy factors have to be maintained at competitive level. With regard to the quality of the product, international companies produce products in various grades catering to the requirements of individual user sector like PVC, Paper etc. Indian units are yet to make large number of grades of products, for meeting the specific requirements of end users. In the case of cosmetic industry, there appears to be particular preference for micronised calcium carbonate, in view of its higher surface area. In considering the Calcium Carbonate project, the factors that should be considered are the following. * Proximity to the source of good quality limestone. Most of the Calcium Carbonate units have been located near the limestone deposits. * The operating parameters of the project from the point of view of the energy requirements have to be carefully studied. * Considering the fact that the consumers of Calcium Carbonate like toothpaste would opt for good quality of the product even without consideration for marginal increase in price, ensuring adequate quality would significantly help the project in the competitive market. * It is necessary to avoid putting up small size plant, since it would make it difficult to introduce adequate energy and quality management techniques in small plants. * The scope for optimisation of the quality and energy management and also the growth rate in demand would justify a plant of large capacity. In view of the abundant availability of Limestone deposit in Tamil Nadu, Calcium carbonate project can be favourably considered. Recommended capacity 1500 tonnes per annum Estimated project cost Rs.12 crores