Unit 8-Volume and Surface Area
advertisement

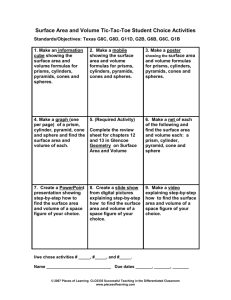
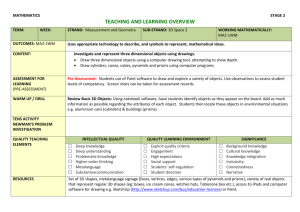
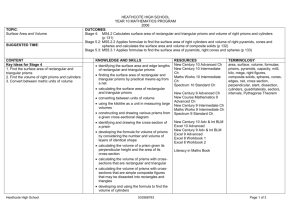
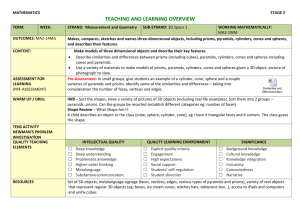
Unit Overview Content Area: Math Unit Title: Volume and Surface Area Unit: 8 Target Course/Grade Level: Seventh Grade Timeline: 3 weeks Unit Summary: Students explore the concepts of surface area and volume of three-dimensional shapes including prisms, cylinders, pyramids, and cones. They will discover relationships between the volumes of prisms and pyramids and cylinders and cones to justify and apply surface area and volume formulas. Students will also use the formulas to find volume and surface areas of three-dimensional composite shapes. Students will build on these concepts as they work with similar solids. Primary interdisciplinary connections: Language Arts, Science, and Technology 9.1 21st-Centuries Life & Career Skills Standard 9.1 All students will demonstrate the creative, critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills needed to function successfully as both global citizens and workers in diverse ethnic and organizational cultures. Strand: A. Critical Thinking and Problem Solving B. Creativity and Innovation C. Collaboration, Teamwork and Leadership Content Statement: 9.1.8: A The ability to recognize a problem and apply critical thinking skills and problem solving skills to solve the problem is a lifelong skill that develops over time. 9.1.8: B Gathering and Evaluating knowledge and information from a variety of sources, including global perspective, fosters creativity and innovative thinking. 9.1.8: C Collaboration and team work enable individuals or groups to achieve common goals with greater efficiency. Leadership abilities develop over time through participation in group and or teams that are engaged in challenging or competitive activities. 21st Century themes and skills: Critical Thinking and Problem Solving, Collaboration, Teamwork and Leadership, Creativity and Innovation Mathematical Practices: 7.MP.1 Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them. 7.MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 7.MP.3 Construct viable arguments and critique the reasoning of others. 7.MP.4 Model with mathematics. 7.MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. 7.MP.6 Attend to precision. 7.MP.7 Look for and make use of structure. 7.MP.8 Look for and express regularity in repeated reasoning. Domain: Geometry Cluster: Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving angle measure, area, surface area, and volume. Standard # Standards 7.G.4 Know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle and use them to solve problems; give an informal derivation of the relationship between the circumference and area of a circle. 7.G.6 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, volume and surface area of two-and three-dimensional objects composed of triangles, quadrilaterals, polygons, cubes, and right prisms. 9.1.8.A.1 Develop strategies to reinforce positive attitudes and productive behaviors that impact critical thinking and problem-solving skills. 9.1.8.A.2 Implement problem-solving strategies to solve a problem in school or the community. 9.1.8.B.2 Assess data gathered to solve problems for which there are varying perspective (e.g., cross cultural, gender specific, generational, etc.) and determine how the data can best be used to design the multiple solutions. 9.1.8.C.1 Determine an individual’s responsibility for personal actions and contributions to group activities. 9.1.8.C.2 Demonstrate the use of compromise, consensus and community building strategies for carrying out different task, assignments and projects. 9.1.8.C.3 Model leadership skills during classroom and extracurricular activities. Unit Essential Questions How are volume and surface used in the real world? How are two-dimensional representations of three-dimensional figures useful? How is finding the volume of a composite figure different than finding the surface area of a composite figure? How is it similar? Unit Enduring Understandings Volume is the measure of space occupied by a three-dimensional region. It is measured in cubic units. Surface area is the sum of the areas of all the surfaces, or faces of a three-dimensional figure. It is measured in square units. A composite figure is made up of two or more three-dimensional figures. Unit Learning Targets Students will ... Justify formulas for the volume of prisms Find the volumes of rectangular and triangular prisms Find the volumes of cylinders. Justify formulas for the volume of pyramids and cones. Find the volume of pyramids. Find the volume of cones. Find the surface area of prisms and cylinders using models and nets. Find the surface area of prisms. Find the surface area of a cylinder. Compare surface area and volume of rectangular prisms and cylinders. Find the surface area of pyramids. Justify the formula for the surface area of a cone by using a net Solve problems by solving a simpler problem. Explore volume and surface area of composite figures. Find the volume and surface area of composite figures. Evidence of Learning Summative Assessment Justify and apply formulas for surface area and volume of pyramids, prisms, cylinders, and cones. Use formulas to find surface areas and volumes of three-dimensional composite shapes. Equipment needed: Teacher Instructional Resources: Textbook - TBD Study Island Khan Academy Videos Formative Assessments Skill sheets Quizzes/Tests Student workbook Homework Math games Study Island Integration of Technology: Smart Board to play online games, utilize online resources, generate models with Smart Software. Kahn Academy Videos Elmo – for demonstration Study Island Technology Resources: http://www.purplemath.com http://www.khanacademy.org – Interactive 2.0 instructional and practice site. Students can view instructional videos and complete practice modules for additional practice/remediation. http://www.studyisland.com/ - Web-based instruction, practice, assessment and reporting built from NJ standards. http://www.ixl.com/math/grade-7 - IXL 7th grade online interactive activities for the students to complete http://www.aaamath.com/grade7.html - AAA math 7th grade – online interactive activities and problems for the student to complete. http://www.adaptedmind.com/Math-Worksheets.html?type=hstb – Grade level material for practice, lessons, games, etc. Opportunities for Differentiation: Decelerate: Use base-ten unit cubes to assist in determining volume. Have students use empty boxes to create a net to assist in finding surface area. Create composite figures by using cereal boxes and card stock to create a model. Accelerated: Have students write a formula for a volume of a trapezoidal prism. Students use base-ten blocks to find integer dimensions rectangular prisms with a given volume. Students will write real-world problems that can be solved by finding volume of a composite figure and one solved by finding surface area. Include a drawing for each. Teacher Notes: