Measurement - merrylandsseniorrevision

Measurement
Content
calculate the percentage error in a measurement, eg if the measured height was 155 cm ± 0.5
cm (ie to the nearest centimetre), the percentage error for this measurement is
0.5
155
100%
calculate areas of annuluses and parts of a circle (quadrant, sector), using appropriate formulae (area of annulus:
A ( R 2 r 2 )
)
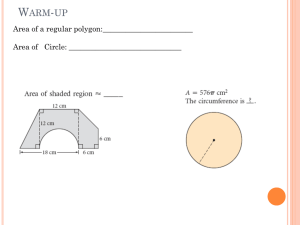
calculate areas of composite figures constructed from squares, rectangles, triangles and circles
apply Simpson’s rule over three equally spaced points, ie one application (using
A h
3
( d f
4 d m
d l
)
)
calculate the surface area of right prisms
calculate the surface area of cylinders (without ‘top’ and/or ‘bottom’) and closed cylinders (
Surface Area closed cylinder
2 r 2 2 rh
)
calculate the surface area of spheres (
Surface Area sphere
4 r 2
)
calculate the volume of a cone, square pyramid and rectangular pyramid using appropriate formulae (
Vol ume
1
3
Ah
)
calculate volumes of composite solids
calculate the volume of an annular cylinder
calculate the volume of right prisms, where the base is a composite or irregular two-dimensional shape, eg an I -beam
determine errors in calculations resulting from errors made in measurement.
Summary of the topic:
any measurement has an accuracy equal to ±
1
2
of the smallest unit marked on the scale of the measuring device and this accuracy is referred as absolute error.
𝑃𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑒𝑛𝑡𝑎𝑔𝑒 𝑒𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟 = 𝑎𝑏𝑠𝑜𝑙𝑡𝑒 𝑒𝑟𝑟𝑜𝑟
× 100% 𝑚𝑒𝑎𝑠𝑢𝑟𝑒𝑚𝑒𝑛𝑡
A composite shape is made of two or more basic shapes.
An arc is a part of the circumference of a circle. Length of an arc (l) = ᶿ
360
𝑥2
A sector is a region of a circle bounded by an arc and two radii. Its area is a fraction of the area (π 𝑟 2
). 𝐴 = ᶿ
360
X π 𝑟 2
An annulus is the ring-like shape between two concentric circles of different radii.
Simpsons’s rule is an approximate method for calculating the area of irregular shape.
The surface area of a solid is the sum of the areas of its faces. The solid can be closed or open
The volume of a prism = Area of base X height
A composite shape if made of two or more solids.