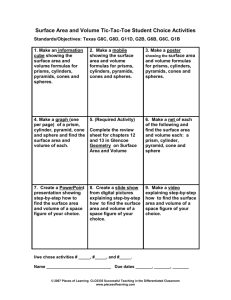
Surface area and volume
advertisement

HEATHCOTE HIGH SCHOOL YEAR 10 MATHEMATICS PROGRAM 2006 TOPIC: Surface Area and Volume SUGGESTED TIME: CONTENT Key Ideas for Stage 4 1. Find the surface area of rectangular and triangular prisms 2. Find the volume of right prisms and cylinders 3. Convert between metric units of volume OUTCOMES: Stage 4: MS4.2 Calculates surface area of rectangular and triangular prisms and volume of right prisms and cylinders (p 131) Stage 5.2: MS5.2.2 Applies formulae to find the surface area of right cylinders and volume of right pyramids, cones and spheres and calculates the surface area and volume of composite solids (p 132) Stage 5.3: MS5.3.1 Applies formulae to find the surface area of pyramids, right cones and spheres (p 133) KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS identifying the surface area and edge lengths of rectangular and triangular prisms finding the surface area of rectangular and triangular prisms by practical means eg from a net calculating the surface area of rectangular and triangular prisms converting between units of volume using the kilolitre as a unit in measuring large volumes constructing and drawing various prisms from a given cross-sectional diagram identifying and drawing the cross-section of a prism developing the formula for volume of prisms by considering the number and volume of layers of identical shape calculating the volume of a prism given its perpendicular height and the area of its cross-section RESOURCES New Century 10 Advanced Ch New Century 10 Intermediate Ch Maths Works 10 Intermediate Ch Spectrum 10 Standard Ch New Century 9 Advanced Ch New Course Mathematics 9 Advanced Ch New Century 9 Intermediate Ch Maths Works 9 Intermediate Ch Spectrum 9 Standard Ch TERMINOLOGY area, surface, volume, formulae, prisms, pyramids, capacity, milli, kilo, mega, right figures, composite solids, spheres, cones, edges, net, cross section, perpendicular, slant, dissection, cylinders, quadrilaterals, sectors, intervals, Pythagoras Theorem New Century 10 Adv & Int BLM Excel 10 Advanced New Century 9 Adv & Int BLM Excel 9 Advanced Excel 8 Workbook 1 Excel 8 Workbook 2 Literacy in Maths Book calculating the volume of prisms with crosssections that are rectangular and triangular calculating the volume of prisms with crosssections that are simple composite figures that may be dissected into rectangles and triangles developing and using the formula to find the volume of cylinders Heathcote High School 533568763 Page 1 of 3 Key Ideas for Stage 5.2 1. Find surface area of right cylinders and composite solids 2. Find the volume of right pyramids, cones, spheres and composite solids developing a formula to find the surface area of right cylinders finding the surface area of right cylinders calculating the surface area of composite solids involving right cylinders and prisms using the fact that a pyramid has one-third the volume of a prism with the same base and the same perpendicular height using the fact that a cone has one-third the volume of a cylinder with the same base and the same perpendicular height using the formula to find the volume of pyramids and cones using the formula to find the volume of spheres finding the dimensions of solids given their volume and/or surface area by substitution into a formula to generate an equation finding the volume of prisms whose bases can be dissected into triangles, special quadrilaterals and sectors finding the volume of composite solids Key Ideas for Stage 5.3 identifying the perpendicular and slant height of pyramids and right cones using Pythagoras’ theorem to find slant height, base length or perpendicular height of pyramids and right cones devising and using methods to calculate the surface area of pyramids developing and using the formula to calculate the surface area of cones using the formula to calculate the surface area of spheres finding the dimensions of solids given their surface area by substitution into a formula to generate an equation establishing and applying the fact that in two similar figures with similarity ratio 1: k 1. Apply formulae for the surface area of pyramids, right cones and spheres 2. Explore and use similarity relationships for area and volume Heathcote High School 533568763 WORKING MATHEMATICALLY DIAGNOSIS/ASSESSMENT recognise, giving examples, that prisms with the same volume may have different surface areas, and prisms with the same surface area may have different volumes (Reasoning, Applying Strategies) solve practical problems related to surface area eg compare the amount of packaging material needed for different shapes (Applying Strategies apply Pythagoras’ theorem to problems involving surface Page 2 of 3 Heathcote High School - matching angles have the same size matching intervals are in the ratio 1: k matching areas are in the ratio 1: k2 matching volumes are in the ratio 1: k3 533568763 area (Applying Strategies) solve problems involving the similarity ratio and areas and volumes (Applying Strategies) Page 3 of 3