Tissues - El Camino College
advertisement

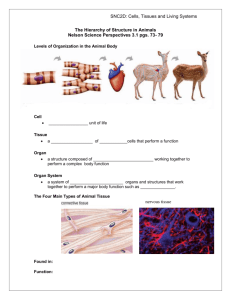
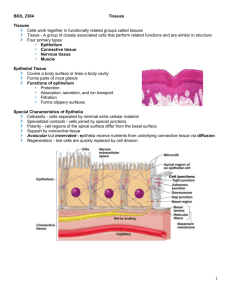
Anatomy & Physiology 34A Lecture Outline Chapter 4- Tissues I. Overview A. Definition & Classification of Tissues B. Epithelium C. Connective Tissue D. Muscle E. Nervous Tissue F. Tissue Growth, Death & Repair II. Definition & Classification of Tissues A. __________: group of closely associated similar cells that perform related functions B. ___________ - the study of tissues C. Four major body _________ types: 1. ___________ tissue ______ body surfaces; _______ hollow body tubes, body cavities and ducts; and forms glands. 2. _________ tissue protects and supports the body and its organs, ___________ organs together, stores energy reserves as fat, provides immunity. 3. __________ tissue contracts and is responsible for __________ and generation of force and heat. 4. Nervous tissue initiates and transmits electrical nerve impulses from one body part to another; controls body functions D. Body tissues are formed from 3 embryonic germ layers: 1. Ectoderm – outer layer that becomes the epidermis (epithelium) and nervous system 2. Endoderm – inner layer that becomes mucous membranes (epithelium) of the digestive, urinary, and respiratory systems 3. Mesoderm – middle layer that becomes muscle, connective tissues, and epithelium lining body cavities and blood vessels III. _____________ - includes ___________ (covering and lining), common to skin, linings of blood vessels, organs, and ____________ epithelium found in glands. A. Features of epithelial tissues: 1. ___________ or “free” surface is open to an exterior, body cavity, or lining of an internal organ. 2. __________ surface is attached to a connective tissue ________ _________ composed of a basal lamina and a deeper reticular layer. 3. 4. Many cell __________ are present, binding cells to each other 5. 6. 7. They have a __________ supply They are _____________; exchange of materials between epithelium and adjacent connective tissues is by diffusion. They usually have a high ________ rate Cancerous epithelial tissues are called carcinomas 2 B. _____________ of Membranous Epithelia 1. _____________ from pathogens, physical injury, toxins, and dessication (e.g., in the epidermis) 2. ______________ – microvilli in GI tract lining absorb nutrients and water 3. ____________ – special mucous and serous membrane cells secrete lubricating fluids 4. _______________ – kidney tubules excrete nitrogenous wastes from the body 5. __________________ – cilia on cells in lungs and reproductive tract move particles 6. _______________ - neuroepithelium in taste buds and nasal areas has a chemoreceptor function C. Epithelial tissues are classified by their cell shape and number of layers 1. Epithelial cell ___________ include: a. __________ - ______, tile-like; thin cells, usually with large nuclei; allow substances to diffuse rapidly through these cells. b. __________ - cube-shaped cells are thicker, adapted for __________ (release of a fluid by cell) and _____________ (intake of fluids or other substances by cell). c. ___________ - tall, __________ cells able to protect underlying tissues; again adapted for absorption and secretion; may have ______ or ______________ extensions on the apical surface d. ______________ - may look squamous, cuboidal, or columnar under different conditions (e. g., in urinary bladder) 2. Epithelial cell ____________ include: a. ___________ - one layer of cells. Found in areas of diffusion, osmosis, filtration, secretion, and absorption. b. ___________ - two or more layers. Protects underlying tissues from wear and tear. c. _______________ - simple columnar layer that looks like it’s stratified but nuclei are not on the same level, nor do all cells reach the apical surface. D. Epithelial Tissue _________ 1. ____________ Epithelium a. _____________ - one layer of flat, tile-like cells 1) Found in areas with little _______ and tear 2) Functions include __________ & ___________ in lungs & kidneys, osmosis & secretion in serous membranes. 3) _______________ lines heart and blood vessels 4) _______________ lines thoracic and pelvic cavities and covers organs within them. b. ______________ - one layer of cube-like cells 1) Adapted for ___________ and _____________ 2) Found covering the ovaries, in __________ and eyes, and lining some glandular ducts c. _____________ (nonciliated) - one layer of nonciliated, rectangular cells. 1) Lines most of the ____ tract, where specialized cells with ____________ perform absorption and _________ cells secret mucus. 2) Forms glandular _______ and found in gall bladder. 3 d. 2. 3. Columnar (___________) - Found in _________ tubes, uterus, paranasal sinuses, and central canal of spinal cord. Associated _______ move fluids or particles. _____________ Epithelium - has 2 or more layers of cells; has a ___________ function that is enhanced by rapid cell divisions; classified according to the shape of the ___________ cells a. __________ SE- has a variable number of cell layers that are flattest at the surface; _______ occurs at the deepest layers and new cells move to the surface; two types of this tissue include: 1) _____________ SSE - contains tough keratin protein; makes up the outer layer of skin (____________); makes skin somewhat waterproof and protects from bacteria 2) _______________ SSE - lines the ______ and nasal cavities, pharynx, vagina, and anal canal; withstands moderate abrasion but not fluid loss b. __________ SE - mostly 2-3 layers of cuboidal cells; lines sweat gland ducts, salivary glands, and the _________ c. __________ SE - superficial cells are columnar, deeper cells are irregular; functions in protection and ________; found in some _____, the conjunctiva, part of urethra, and anus lining d. ______________ E - similar to nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, except the surface cells are _________ rather than flat; lines urinary ___________ and ureters; specialized for _____________ ________________ Columnar Epithelium - appears stratified because nuclei are at different levels; contains many _________ cells and may have a ciliated apical surface. a. ___________ PSE lines ______ and bronchial tubes; cilia move foreign particles in mucus from lower respiratory sys. b. __________ PSE lines male sperm ducts & large gland ducts F. _______________ Epithelia 1. ___________ are categorized as either endocrine or exocrine a. ___________ glands are _______ and secrete their hormones into the blood or surrounding extracellular fluid b. ___________ glands are connected to the epithelium by ____ and secrete their products onto body surfaces or into body cavities. The two major types of ____________ glands are: 1) Unicellular glands - ________-celled glands, such as _______ cells; these are found in linings of the respiratory and digestive systems; cells secrete ________ to lubricate and protect the linings 2) _____________ glands - composed of both secretory cells and cells of duct walls; may be classified as simple or compound, by the shape of their secretory portion, or according to the way they release their product a) ____________ glands- secrete a watery substance via exocytosis; includes salivary, pancreatic, and some sweat glands b) _____________ glands – secrete a milky substance via exocytosis; includes some sweat glands 4 c) _____________ glands – cells accumulate a product, then burst to release the product (e.g., sebaceous glands) IV. Connective tissues (___) – most abundant tissue; binds other body tissues together, protects, and provides for the metabolic needs of body organs A. __________________ of connective tissues include: 1. Most are highly ____________ (except cartilage, tendons, and ligaments) 2. They are composed of many _______ types including: a. _______________ - most common cell type in CT, secretes collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers 3. b. c. __________________ - fat cells d. e. f. g. Erythrocytes - _____ blood cells (RBCs) ________ cells - dispersed throughout CT surrounding blood vessels; they produce _____________ (an anticoagulant) and ________________, which is a vasodilator Leucocytes - _______ blood cells (WBCs) _______________ - phagocytic WBC derived from monocytes ___________ cells – WBC derived from B-lymphocytes They have a lot of noncellular ___________ between the cells. This extracellular matrix (_____) has two components: a. ____________ substance composed mainly of proteoglycans and polysaccharides (e.g.: hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate); may be liquid, semisolid, gel-like, or hard b. Protein __________ provide support and include collagen (white), elastic (yellow), and reticular (fine collagenic) fibers B. ____________ syndrome is a genetic disorder of connective tissue 1. ______________ protein in elastic fibers is defective 2. Results in ________-jointedness, long limbs, fingers and toes, visual problems, and weakened blood vessels (esp. the ___________) C. The major ____________ of CT include: 1. Embryonic ____________- undifferentiated tissue from which other CTs are derived 2. Connective tissue ___________ - areolar, adipose, reticular; regular, irregular, and elastic dense fibrous CT D. 3. 4. 5. ____________ - hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage 1. ________ __________ Connective tissue, which has 3 types ________ (osseous) tissue ________ Connective Tissue ___________ includes: a. _________ CT - has gel-like matrix with all three fiber types; cells are fibroblasts, macrophages, mast cells, plasma cells, other WBCs, & adipocytes. Locations include: 5 1) Composes ________ that binds the skin to underlying muscle and is highly 2) 3) 2. vascular Surrounds blood ____________ and nerves Wraps & cushions _________ b. _____________ tissue - contains numerous adipocytes 1) Functions in _________ reserve, support and protection of organs 2) Found in skin __________, around kidneys, heart surface, omentum, around joints, in women’s breasts c. Reticular CT - has a network of _____________ fibers in a gel matrix and phagocytic cells; found in lymph nodes, bone marrow, spleen _________ ____________ CT also has 3 types: a. __________ - composed primarily of parallel collagen fibers and some fibroblasts; found in _________ that attach muscle to bone and ______________ that attach bone to bone b. _____________ - mostly irregularly arranged collagen fibers and some fibroblasts; found in skin ________, submucosa of the GI tract, and fibrous capsules of organs and joints c. Elastic - has yellowish, irregular __________ fibers; found in large artery walls, larynx, trachea, and bronchial tubes D. ________ - has a semisolid matrix (chondroitin sulfate) containing collagen or elastic fibers and _________cytes; it is surrounded by a __________________ (of dense irregular connective tissue) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Chondro__________ produce the matrix and give rise to chondrocytes Chondro____ occur within spaces called lacunae in the matrix Chondro________ break down cartilage Cartilage has no ________ vessels or nerves Three major _________ of cartilage are: a. ___________ C. - most abundant cartilage in body; has fine collagen fibers in a ______ matrix 1) Found in embryonic skeleton, at ends of bones, _________ cartilage, in _______, and in respiratory structures 2) Allows smooth movement at ________, provides support. b. _________cartilage - contains bundles of collagen in matrix 1) Found in pubic symphysis, intervertebral discs, and _____ menisci – areas subject to compression 2) Acts as a “shock absorber” c. ____________ C. - contains elastic fibers in the matrix 1) Found in ext. _____, epiglottis, Eustachian tubes 2) Provides flexible support and maintains ________ 6 E. Bone (__________ tissue) - has a ________ matrix containing calcium phosphate and collagen fibers and cells called _____cytes; surrounded by a peri___________ of fibrous CT a. Osteo_______ build bone tissue and give rise to osteocytes; osteo________ break down bone b. _________ (Haversian system) is basic unit of compact bone, consists of a central __________ canal surrounded by _______ rings interspersed with ____________ containing ______cytes; _____________ extend between lacunae to connect osteocytes c. Functions: supports, protects, stores __________, houses blood forming tissue (bone marrow). F. _________ (vascular tissue) - has liquid matrix called _________ and formed elements that include: 1. _________cytes - RBCs lack a nucleus; function to transport O2 to cells and CO2 away from cells 2. _________cytes – WBCs have a nucleus; involved in phagocytosis, allergic reactions, and immunity 3. 4. _____________ - cell fragments that function in blood clotting. Cancers of WBCs are called leukemia G. _____________ - epithelial layer + underlying connective tissue = epithelial membrane. 1. _________ M. - lines tubes that open to the exterior (i.e., digestive, respiratory, and urogenital tracts); underlying connective tissue is called ________ _______; secretes mucus 2. ___________ M. - (pleura, pericardium, peritoneum) lines body cavities (____________) that do not open to exterior and covers organs (____________) within the cavities; secretes serous fluid. 3. __________ M. - line joint cavities, bursae, and tendon sheaths; do not contain epithelium; secrete lubricating _________ fluid. V. ____________ Tissue contractile tissues; consists of 3 types: A. __________Muscle - multinucleated, _________, cylindrical fiber that form fascicle bundles 1. 2. Spans joints of skeleton via ___________ Function is ______________ movement of the skeleton. B. __________ Muscle - Branched, striated fiber, each with a single nucleus and __________ ___________ between cells 1. 2. Found in __________ wall Function in _________________, rhythmic heart contractions C. ___________ Muscle - elongated, spindle-shaped cell fibers with a single nucleus (nonstriated) 1. 2. Found in walls of hollow internal _________ Function in _____________ movements of internal tubes (digestive, respiratory, and urinary tracts) 7 VI. ___________ Tissue is found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, and is composed of neurons and neuroglia A. ____________ have long processes that extend from their cell body 1. Cell __________ contains most of the cellular organelles 2. ________________ are processes that receive and respond to stimuli 3. ___________ is a single process that transmits nerve impulses away from the cell body to other cells and organs B. ______________ (glial cells) are smaller cells that nourish, insulate, and support neurons VII. Tissue Growth, Development, Death, & Repair A. ___________ in Tissue Type – some tissues can change from one form to another 1. _____________________ occurs in the embryo when mesenchyme tissue becomes specialized into other tissue types 2. ______________ is the change of one mature tissue type to another, as when cuboidal epithelium lining a girl’s vagina changes to stratified squamous epithelium at puberty B. Tissue Growth 1. Hyper_________ is tissue growth via mitotic cell division, as in the growth of a child 2. Hyper____________ is the enlargement of existing cells, such as muscle cell growth during exercise 3. __________________ is the development of a tumor (neoplasm), benign or malignant, composed of abnormal, nonfunctional tissue C. Tissue Shrinkage & Death 1. ______________ is the shrinkage of a tissue via loss in cell mass or number 2. _______________ is the death of tissue due to trauma, toxins, infection, etc. a. ________________ is tissue necrosis due to an insufficient blood supply b. ________ gangrene is necrosis of a wound resulting from infection by Clostridium bacteria c. ________________ is the sudden death of tissue that occurs when its blood supply is cut off (e.g., myocardial infarction) d. _______________ ulcer (bed sore) occurs when continual pressure to an area cuts off blood flow to part of the body D. Tissue ______________ can occur in two ways, regeneration and fibrosis 1. _______________ – replacement of dead or damaged cells by new cells identical to the original cells. (e.g., repair of minor skin injuries and liver damage) 2. _____________ is the replacement of damaged tissue with scar tissue, which holds an organ together but does not restore its function. (e.g., repair of severe cuts and burns) 3. _____________ of cut healing involve inflammation, fibrosis and regeneration: a. Bleeding in the cut causes mast cells to release ______________, which increases blood flow and makes capillaries “leaky” b. Blood plasma carries antibodies, _______ proteins, and blood cells into the wound c. A blood ________ forms and hardens into a scab over the wound. d. _________________ clean up tissue debris under the scab e. New capillaries and fibroblasts form a soft mass called ________________ tissue under the scab f. ______________ occurs as macrophages dissolve the blood clot, while fibro_____ deposit collagen to replace it g. __________________ takes place as epithelial cells multiply beneath the scab, and the scab sloughs off. 8