Standards
advertisement

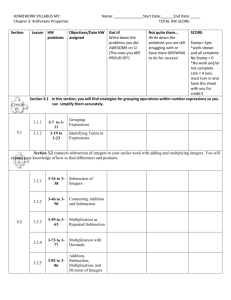
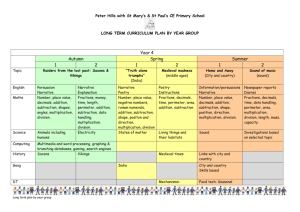
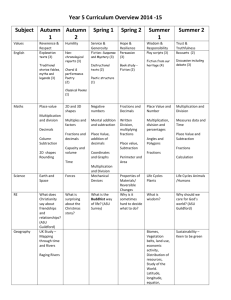
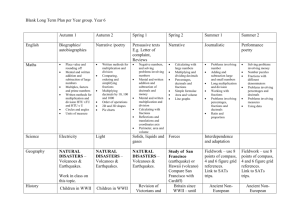
Standards Correlated to Exploring Math 8775 Level E Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) Grade 5 Mathematics TEKS STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION TX.111.17. Mathematics, Grade 5. (5.1) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student uses place value to represent whole numbers and decimals. The student is expected to: 5.1 (A) Use place value to read, write, compare, and order whole numbers through the 999,999,999,999. Correlated Lessons: 1.1 Place Value and Ordering Numbers Page 15 Objective 01: Read and order any whole number. 1.1 Place Value and Ordering Numbers Page 15 Objective 02: Order a set of whole numbers up to 10 digits. 1.4 Comparing and Rounding Whole Numbers Page 37 Objective 08: Compare and order numbers 1.4 Comparing and Rounding Whole Numbers Page 37 Objective 09: Write a large number in figures and words. 1.6 Rounding and Ordering Large Numbers Page 51 Objective 14: Order numbers to the millions place. 3.2 Multiplying by 10s, 100s, and 1,000s Page 21 Objective 75: Read large numbers GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.1 (B) Use place value to read, write, compare, and order decimals through the thousandths place. Correlated Lessons: 4.6 Ordering Decimals Page 53 Objective 133: Identify the largest and smallest decimals. 4.6 Ordering Decimals, 4.8 Working with Decimals Page 53, 69 Objective 132: Order a set of decimals. 4.8 Working with Decimals Page 69 Objective 138: Know what each digit in a decimal represents. 4.8 Working with Decimals Page 69 Objective 139: Identify a decimal that lies between two other decimals. STUDENT EXPECTATION (5.2) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student uses fractions in problem-solving situations. The student is expected to: GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.2 (B) Generate a mixed number equivalent to a given improper fraction or generate an improper fraction equivalent to a given mixed number. Correlated Lessons: 4.1 Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions Page 15 Objective 120: Recognize the relationship between improper fractions and mixed numbers. 4.1 Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions Page 15 Objective 121: Convert between improper fractions and mixed numbers. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.2 (C) Compare two fractional quantities in problem-solving situations using a variety of methods, including common denominators. Correlated Lessons: 4.2 Ordering Fractions Page 21 Objective 123: Order a set of fractions by finding a lowest common denominator or an equivalent fraction. 4.4 Equivalent Fractions and Common Denominators Page 37 Objective 128: Compare fractions by finding a common denominator. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.2 (D) Use models to relate decimals to fractions that name tenths, hundredths, and thousandths. Correlated Lessons: 4.13 Fractions, Percents and Decimals Page 109 Objective 149: Make conversions among fractions, decimals, and percents. 4.13 Fractions, Percents and Decimals, 4.14 Percent Word Problems Page 109, 119 Objective 148: Recognize the equivalence between fractions, percentages, and decimals. 4.7 Converting Decimals into Fractions Page 61 Objective 135: Convert a fraction to a decimal. 4.7 Converting Decimals into Fractions Page 61 Objective 136: Convert a decimal to a fraction. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.3) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student adds, subtracts, multiplies, and divides to solve meaningful problems. The student is expected to: 5.3 (A) Use addition and subtraction to solve problems involving whole numbers and decimals. Correlated Lessons: 2.1 Written Methods for Addition Page 15 Objective 37: Use written procedures for addition, including decimals. 2.1 Written Methods for Addition Page 15 Objective 38: Evaluate written methods of addition. 2.1 Written Methods for Addition Page 15 Objective 39: Refine written methods building on addition. 2.10 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Page 93 Objective 60: Add or subtract a pair of decimals, each less than one with up to two decimal places. 2.10 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Page 93 Objective 61: Explain in writing the process used in mental addition and subtraction. 2.11 Addition and Subtraction Using Money Page 103 Objective 62: Add and subtract using various amounts of money. 2.11 Addition and Subtraction Using Money Page 103 Objective 63: Use written methods of addition and subtraction. 2.13 Reviewing Written Methods for Addition and Subtraction Page 119 Objective 68: Add and subtract whole numbers and decimals. 2.2 Written Methods for Subtraction Page 23 Objective 40: Subtract whole numbers and decimals using a variety of methods. 2.2 Written Methods for Subtraction Page 23 Objective 41: Evaluate written methods of subtraction. 2.2 Written Methods for Subtraction Page 23 Objective 42: Refine written methods of building on subtraction. 2.3 Mental Strategies for Addition Page 29 Objective 43: Use number facts and place value to understand and do mental addition. 2.3 Mental Strategies for Addition Page 29 Objective 44: Add four-digit multiples of 100. 2.3 Mental Strategies for Addition Page 29 Objective 45: Count on to add decimals with units, tenths, and hundredths to make the next higher whole number or tenth. 2.4 Mental Strategies for Subtraction Page 37 Objective 46: Use a variety of mental strategies to calculate the difference between two numbers. 2.5 Mental Strategies for Addition and Subtraction Page 47 Objective 48: Use a variety of strategies to add two numbers mentally. 2.6 Subtraction Using Multiples of 100 Page 57 Objective 51: Subtract four-digit multiples of 100. 2.6 Subtraction Using Multiples of 100, 2.10 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Page 57, 93 Objective 50: Use number facts and place value to understand and do mental subtraction. 2.7 Addition and Subtraction as Inverse Operations Page 65 Objective 55: Use revisions of written methods of addition and subtraction. 2.8 Adding Decimals Page 77 Objective 57: Add two or more decimals up to four digits and up to two decimal places. 2.8 Adding Decimals, 2.13 Reviewing Written Methods for Addition and Subtraction Page 77, 119 Objective 56: Develop and refine written methods for addition. 2.9 Subtracting Decimals Page 85 Objective 59: Subtract decimals with up to four digits and up to two decimal places. 2.9 Subtracting Decimals, 2.13 Reviewing Written Methods for Addition and Subtraction Page 85, 119 Objective 58: Develop and refine written methods for subtraction. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.3 (B) Use multiplication to solve problems involving whole numbers (no more than three digits times two digits without technology). Correlated Lessons: 1.5 Number Operations using 10, 100, or 1,000 Page 43 Objective 12: Multiply a whole number by 10, 100, and 1,000. 3.1 Multiplication and Division Facts Page 15 Objective 70: Use knowledge of factors and closely related facts for mental calculation. 3.1 Multiplication and Division Facts Page 15 Objective 71: Explain methods and reasoning about numbers orally and in writing. 3.15 Review Written Methods of Multiplication Page 117 Objective 110: Understand the standard written mehtod for long multiplication. 3.15 Review Written Methods of Multiplication Page 117 Objective 111: Use the standard written method for long multiplication to solve problems. 3.6 Using a Grid and Partitioning Method in Simple Problems Page 49 Objective 83: Develop written methods for multiplying a three-digit number by a two-digit number. 3.7 Using a Grid and Partitioning Method in Complex Problems Page 55 Objective 84: Develop written methods to find the product of two numbers. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.3 (C) Use division to solve problems involving whole numbers (no more than two-digit divisors and three-digit dividends without technology) , including interpreting the remainder within a given context. Correlated Lessons: 3.1 Multiplication and Division Facts Page 15 Objective 70: Use knowledge of factors and closely related facts for mental calculation. 3.1 Multiplication and Division Facts Page 15 Objective 71: Explain methods and reasoning about numbers orally and in writing. 3.10 Using Different Methods of Division Page 79 Objective 93: Use written methods to find the quotient of two numbers. 3.12 Using Simple Division Page 95 Objective 100: Write a quotient as a decimal when dividing by a whole number. 3.12 Using Simple Division Page 95 Objective 99: Write a quotient as a fraction when dividing by a whole number. 3.13 More Division Problems with Remainders Page 103 Objective 102: Understand the concept of a remainder. 3.16 Review Written Methods of Division Page 125 Objective 113: Understand the standard written method for long division. 3.16 Review Written Methods of Division Page 125 Objective 114: Use the standard written method for long division to solve problems. 3.8 Using Written Methods of Division Page 61 Objective 87: Use written methods to divide a three-digit number by a two-digit number. 3.8 Using Written Methods of Division Page 61 Objective 88: Write a remainder as a fraction. 3.9 Division Problems with Remainders Page 67 Objective 89: Use division strategies to establish answers. 3.9 Division Problems with Remainders Page 67 Objective 90: Find and express a quotient with a remainder as a fraction. 3.9 Division Problems with Remainders Page 67 Objective 92: Express an answer as a fraction and as a decimal. STUDENT EXPECTATION (5.4) Number, operation, and quantitative reasoning. The student estimates to determine reasonable results. The student is expected to use strategies, including rounding and compatible numbers to estimate solutions to addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division problems. Correlated Lessons: 1.7 Rounding Large Numbers Page 59 Objective 17: Use rounding to estimate the answers to calculations. 1.7 Rounding Large Numbers Page 59 Objective 18: Use vocabulary for estimating and approximating. 1.8 Estimation and Rounding Page 69 Objective 19: Make a sensible estimate of a range of objects. 1.8 Estimation and Rounding Page 69 Objective 20: Use estimation to make an approximation of the answer. 3.7 Using a Grid and Partitioning Method in Complex Problems Page 55 Objective 85: Use estimation before working out an accurate answer. 3.9 Division Problems with Remainders Page 67 Objective 91: Round products and quotients to the nearest whole number. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.5) Patterns, relationships, and algebraic thinking. The student makes generalizations based on observed patterns and relationships. The student is expected to: 5.5 (A) Describe the relationship between sets of data in graphic organizers such as lists, tables, charts, and diagrams. Correlated Lessons: 1.6 Rounding and Ordering Large Numbers Page 51 Objective 15: Interpret information in a table. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.5 (B) Identify prime and composite numbers using concrete objects, pictorial models , and patterns in factor pairs. Correlated Lessons: 1.10 Number Sense and Division Page 85 Objective 23: Solve problems using factors and divisiblity. 1.9 Rules of Divisibility and Prime Numbers Page 79 Objective 22: Find prime numbers and prime factors. STUDENT EXPECTATION (5.7) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student generates geometric definitions using critical attributes. The student is expected to identify essential attributes including parallel, perpendicular, and congruent parts of two- and three-dimensional geometric figures. Correlated Lessons: 5.1 Properties of 3-Dimensional and 2-Dimensional Shapes Page 15 Objective 153: Recognize features of two dimensional and three dimensional shapes. 5.1 Properties of 3-Dimensional and 2-Dimensional Shapes Page 15 Objective 155: Use correct vocabulary when describing features of shapes. 5.1 Properties of 3-Dimensional and 2-Dimensional Shapes Page 15 Objective 156: Describe characteristics of two dimensional and three dimensional shapes. 5.10 Identifying Shapes by Plotting Points on a Grid Page 75 Objective 179: Use the properties of quadrilaterals to answer specific questions. 5.2 Sorting Shapes Using a Venn Diagram Page 23 Objective 159: Use statements to define shapes. 5.3 Circles Page 31 Objective 160: Know the vocabulary relating to circles. 5.4 Making a Cube Page 37 Objective 162: Describe solids in terms of vertices, edges, and faces. 5.5 Types of Triangles Page 43 Objective 164: Identify and name triangles. 5.5 Types of Triangles Page 43 Objective 165: Know the definitions of different triangles, e.g. equilateral, isosceles, and scalene, and identify their attributes. 5.5 Types of Triangles Page 43 Objective 166: Measure length to identify different triangles. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.8) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student models transformations. The student is expected to: 5.8 (A) Sketch the results of translations, rotations, and reflections on a Quadrant I coordinate grid. Correlated Lessons: 5.17 Rotation Page 125 Objective 207: Use coordinates in all four quadrants. 5.9 Reflective Symmetry on a Grid Page 69 Objective 177: Reflect shapes on the x- and y-axes, including two reflections. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.8 (B) Identify the transformation that generates one figure from the other when given two congruent figures on a Quadrant I coordinate grid. Correlated Lessons: 5.17 Rotation Page 125 Objective 205: Identify a rotation. STUDENT EXPECTATION (5.9) Geometry and spatial reasoning. The student recognizes the connection between ordered pairs of numbers and locations of points on a plane. The student is expected to locate and name points on a coordinate grid using ordered pairs of whole numbers. Correlated Lessons: 5.6 Parts of a Coordinate System Page 49 Objective 167: Recognize position and direction and use coordinates. 5.6 Parts of a Coordinate System, 5.9 Reflective Symmetry on a Grid Page 49 Objective 169: Plot coordinates on a pair of axes. 5.7 Plotting Coordinates on a Grid Page 55 Objective 170: Plot points in all four quadrants. 5.7 Plotting Coordinates on a Grid Page 55 Objective 171: Read coordinates in all four quadrants. 5.7 Plotting Coordinates on a Grid Page 55 Objective 172: Complete a shape by plotting the missing point. 5.9 Reflective Symmetry on a Grid Page 69 Objective 176: Plot coordinates on a pair of axes. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.10) Measurement. The student applies measurement concepts involving length (including perimeter), area, capacity/volume, and weight/mass to solve problems. The student is expected to: 5.10 (A) Perform simple conversions within the same measurement system (SI (metric) or customary). Correlated Lessons: 6.2 Estimating, Measuring, and Recording Lengths Page 21 Objective 212: Convert customary units of measurement. 6.2 Estimating, Measuring, and Recording Lengths Page 21 Objective 213: Convert metric units of measurement. 6.3 Measuring Weight Using Metric and U.S. Customary Scales Page 27 Objective 216: Convert small units to larger units and vise versa. 6.4 Using Scales for Measurement Page 35 Objective 219: Use metric and customary conversions. 6.5 Measuring Capacity, 6.6 Length, Weight, and Capacity Page 41, 47 Objective 221: Use conversions for metric and customary units. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.10 (B) Connect models for perimeter, area, and volume with their respective formulas. Correlated Lessons: 6.10 Calculating Volumes Page 77 Objective 230: Know and use formulas for finding the volume of cubes, rectangular prisms, and cylinders. 6.10 Calculating Volumes Page 77 Objective 231: Use correct units when calculating volume. 6.10 Calculating Volumes Page 77 Objective 232: Apply knowledge of volume to real-life situations. 6.7 Calculating Perimeter and Area Page 59 Objective 225: Use formulas for perimeter and area of rectangles. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.10 (C) Select and use appropriate units and formulas to measure length, perimeter, area, and volume. Correlated Lessons: 6.1 Metric and Customary Units of Measurement Page 15 Objective 209: Know and use standard metric units for length. 6.1 Metric and Customary Units of Measurement Page 15 Objective 210: Know and use customary units for length. 6.10 Calculating Volumes Page 77 Objective 230: Know and use formulas for finding the volume of cubes, rectangular prisms, and cylinders. 6.10 Calculating Volumes Page 77 Objective 231: Use correct units when calculating volume. 6.10 Calculating Volumes Page 77 Objective 232: Apply knowledge of volume to real-life situations. 6.11 Real-Life Problems Involving Measurement Page 85 Objective 233: Identify appropriate units of measurement and equipment for measuring. 6.2 Estimating, Measuring, and Recording Lengths Page 21 Objective 211: Estimate, measure, and record lengths. 6.7 Calculating Perimeter and Area Page 59 Objective 225: Use formulas for perimeter and area of rectangles. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.12) Probability and statistics. The student describes and predicts the results of a probability experiment. The student is expected to: 5.12 (C) List all possible outcomes of a probability experiment such as tossing a coin. Correlated Lessons: 7.11 Using Probability Diagrams Page 91 Objective 263: Know that probability folllows a particular set of outcomes. 7.9 Probability Page 77 Objective 257: Know that events have an outcome. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.13) Probability and statistics. The student solves problems by collecting, organizing, displaying, and interpreting sets of data. The student is expected to: 5.13 (A) Use tables of related number pairs to make line graphs. Correlated Lessons: 7.6 Line Graphs Page 55 Objective 252: Collect and organize data on a line graph. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.13 (B) Describe characteristics of data presented in tables and graphs including median, mode, and range. Correlated Lessons: 7.1 Mode, Range, and Median Page 15 Objective 241: Find the mode, range and median of a set of data. 7.2 Mode, Range, Median, and Mean Page 23 Objective 242: Find the mode, range, median, and mean of a set of data. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.13 (C) Graph a given set of data using an appropriate graphical representation such as a picture or line graph. Correlated Lessons: 7.6 Line Graphs Page 55 Objective 252: Collect and organize data on a line graph. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.14) Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student applies Grade 5 mathematics to solve problems connected to everyday experiences and activities in and outside of school. The student is expected to: 5.14 (B) Solve problems that incorporate understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness. Correlated Lessons: 1.10 Number Sense and Division Page 85 Objective 27: Use inverse operations to calculate and check answers. 1.14 Reasoning About Numbers Page 115 Objective 34: Make decisions about how to approach mathematical problems. 2.12 Magic Squares, 3.6 Using a Grid and Partitioning Method in Simple Problems Page 111, 49 Objective 66: Choose the most appropriate method to solve problems. 2.6 Subtraction Using Multiples of 100 Page 57 Objective 52: Apply mental strategies in problem solving situations. 2.6 Subtraction Using Multiples of 100 Page 57 Objective 53: Explain the problem solving process used to solve problems. 2.7 Addition and Subtraction as Inverse Operations Page 65 Objective 54: Use addition and subtraction as inverse operations to check the accuracy of an answer. 2.7 Addition and Subtraction as Inverse Operations Page 65 Objective 55: Use revisions of written methods of addition and subtraction. 3.11 Multiplication, Addition, and Division Page 85 Objective 97: Choose the appropriate strategy to solve problems. 3.11 Multiplication, Addition, and Division Page 85 Objective 98: Check calculations using equivalent or inverse operations. 3.12 Using Simple Division Page 95 Objective 101: Use the inverse operations to check results. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.14 (C) Select or develop an appropriate problem-solving plan or strategy, including drawing a picture, looking for a pattern, systematic guessing and checking, acting it out, making a table, working a simpler problem, or working backwards to solve a problem. Correlated Lessons: 1.14 Reasoning About Numbers Page 115 Objective 34: Make decisions about how to approach mathematical problems. 2.12 Magic Squares, 3.6 Using a Grid and Partitioning Method in Simple Problems Page 111, 49 Objective 66: Choose the most appropriate method to solve problems. 2.6 Subtraction Using Multiples of 100 Page 57 Objective 52: Apply mental strategies in problem solving situations. 2.6 Subtraction Using Multiples of 100 Page 57 Objective 53: Explain the problem solving process used to solve problems. 3.11 Multiplication, Addition, and Division Page 85 Objective 97: Choose the appropriate strategy to solve problems. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.15) Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student communicates about Grade 5 mathematics using informal language. The student is expected to: 5.15 (A) Explain and record observations using objects, words, pictures, numbers, and technology. Correlated Lessons: 1.12 Number Patterns, 3.18 Solving Money Word Problems Page 99, 139 Objective 31: Explain and record how a problem was solved. 2.1 Written Methods for Addition Page 15 Objective 37: Use written procedures for addition, including decimals. 2.10 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Page 93 Objective 61: Explain in writing the process used in mental addition and subtraction. 2.11 Addition and Subtraction Using Money Page 103 Objective 63: Use written methods of addition and subtraction. 2.12 Magic Squares Page 111 Objective 67: Explain reasoning when making a choice. 2.2 Written Methods for Subtraction Page 23 Objective 40: Subtract whole numbers and decimals using a variety of methods. 2.8 Adding Decimals, 2.13 Reviewing Written Methods for Addition and Subtraction Page 77, 119 Objective 56: Develop and refine written methods for addition. 2.9 Subtracting Decimals, 2.13 Reviewing Written Methods for Addition and Subtraction Page 85, 119 Objective 58: Develop and refine written methods for subtraction. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.15 (B) Relate informal language to mathematical language and symbols. Correlated Lessons: 1.12 Number Patterns, 3.18 Solving Money Word Problems Page 99, 139 Objective 31: Explain and record how a problem was solved. 2.10 Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Page 93 Objective 61: Explain in writing the process used in mental addition and subtraction. 2.12 Magic Squares Page 111 Objective 67: Explain reasoning when making a choice. STUDENT EXPECTATION GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION (5.16) Underlying processes and mathematical tools. The student uses logical reasoning. The student is expected to: 5.16 (A) Make generalizations from patterns or sets of examples and non-examples. Correlated Lessons: 1.10 Number Sense and Division Page 85 Objective 24: Make predictions and find patterns. GRADE LEVEL EXPECTATION 5.16 (B) Justify why an answer is reasonable and explain the solution process. Correlated Lessons: 1.10 Number Sense and Division Page 85 Objective 27: Use inverse operations to calculate and check answers. 2.1 Written Methods for Addition Page 15 Objective 38: Evaluate written methods of addition. 2.2 Written Methods for Subtraction Page 23 Objective 41: Evaluate written methods of subtraction. 2.7 Addition and Subtraction as Inverse Operations Page 65 Objective 54: Use addition and subtraction as inverse operations to check the accuracy of an answer. 2.7 Addition and Subtraction as Inverse Operations Page 65 Objective 55: Use revisions of written methods of addition and subtraction. 3.11 Multiplication, Addition, and Division Page 85 Objective 98: Check calculations using equivalent or inverse operations. 3.12 Using Simple Division Page 95 Objective 101: Use the inverse operations to check results.