Review Mitosis Meiosis and Cell Communication
advertisement

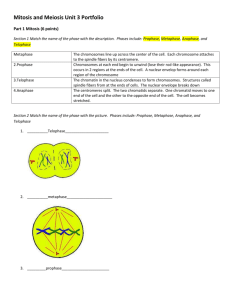
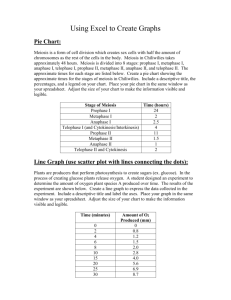
1 NAME: _______________________________________ DATE: __________ BLOCK: _____ Use the first two meiosis diagrams to show independent assortment without any crossing over. Use your third set to show how crossing over can change the sex cells. For all three diagrams, use 2 big chromosomes and 2 small chromosomes and 2 colors. Use two colors to indicate maternal and paternal chromosomes. Use the following key to see which alleles are found on each chromosome. For each sex cell in all 3 diagrams, list the allele possibilities (letter combinations) on the line below each sex cell. MEIOSIS Independent Assortment 2 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II MEIOSIS Independent Assortment 3 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II MEIOSIS Crossing Over 4 Interphase Prophase I Metaphase I Anaphase I Telophase I Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II 5 1. Look at the cells below. Identify the phase in which each cell is and then number the phases #1-5 in the order that they occur. 2. Label the following cell features: nucleus, spindle fiber, chromatin, chromatid, cell wall, and cell plate. Label each structure only one time even though you may see it more than one time. 3. Below is a diagram of a signal transduction pathway that uses cAMP as a second messenger. Label the parts. 6 4. Explain how the toxin from Vibrio chloerae (which causes cholera) causes severe diarrhea. You should include G protein, adenylyl cyclase, and cAMP in your answer. 5. Label the diagram of the cell cycle below. Describe the relative concentrations of MPF and its constituent molecules throughout the cell cycle. 6. Describe the G1, G2, and M checkpoints. What happens after each checkpoint? For G2 and M what must happen to pass each checkpoint? 7 7. Match the terms with the correct definition by writing the letter in front of each term. protein kinases protein phosphatases phosphodiesterase A. enzymes that rapidly remove P B. an enzyme in cell membranes that converts ATP into cAMP C. enzymes that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to a protein adenylyl cyclase D. an enzyme that converts cAMP into AMP tyrosine kinase receptor E. signals cause dimerization and phosphorylation to activate apoptosis F. a very common second messenger cAMP G. triggered by signals that activate cell suicide 8. Match the terms with the correct definition by writing the letter in front of each term. centromere A. the pairing of homologous chromosomes density dependent inhibition B. when normal cells stop mitosis if the area is too crowded C. the region in which sister chromatids are attached angiogenesis sporpphyte karyotype gametophyte synapsis D. a multicellular haploid stage of a life cycle E. A picture of homologous chromosomes; can be used to analyze chromosomes of fetuses F. the recruitment of new blood vessels for growing, cancerous cells G. a multicellular diploid stage of a life cycle 9. Assume that a plant has a chromosome number of 2n = 24. Calculate the following: diploid number = haploid number = n= chromosome number in a gametophyte cell = chromosome number in a gamete = 8 10. For normal humans, calculate the following: chromosome number in G0 = chromatid number at the end of S = chromosome number in somatic cells = chromosome number in gametes = 11. Explain the two differences between plant and animal cell division. 12. If an organism’s somatic cells have 10 chromosomes, how many would the gametes have? 13. For alternation of generations life cycles: What follows the formation of a zygote? What process makes spores into a gametophyte? What process makes gametes? 14. In which phase does crossing over occur in meiosis? 15. In which phase does DNA replicate? 16. If an organism has 30 chromosomes, how many genetically different sex cells can it make? 17. What are the three main stages of cell signaling? 18. What is a centromere? 19. How does the tyrosine kinase receptor work?