Mitosis and Meiosis Unit 3 Portfolio
advertisement

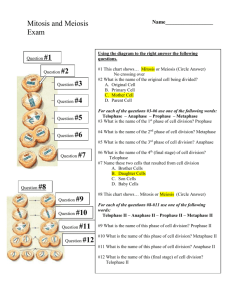
Mitosis and Meiosis Unit 3 Portfolio Part 1 Mitosis (6 points) Section 1 Match the name of the phase with the description. Phases include: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase Metaphase 2.Prophase 3.Telophase 4.Anaphase The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome attaches to the spindle fibers by its centromere. Chromosomes at each end begin to unwind (lose their rod-like appearance). This occurs in 2 regions at the ends of the cell. A nuclear envelop forms around each region of the chromosome The chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. Structures called spindle fibers from at the ends of cells. The nuclear envelope breaks down The centromeres split. The two chromatids separate. One chromatid moves to one end of the cell and the other to the opposite end of the cell. The cell becomes stretched. Section 2 Match the name of the phase with the picture. Phases include: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase 1. __________Telophase_____________________ 2. __________metaphase______________________ 3. _________prophase_______________________ 4. _anaphase________ Part 2 Meiosis (8 points) Section 1: Match the name of the meiosis phase with the description. Phases include Prophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase I, Metaphase II, Anaphase I, Anaphase II, Telophase I, and Telophase II. 1.Metaphase I 2. 3.Anaphase I 4.Metaphase II 5. 6. 7. 8. The chromosome pairs line up in the center of the cell The chromatids separate, forming single chromosomes and move toward opposite ends of the cells. The chromosome pairs separate and move to the opposite ends of the cell The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell The nuclear envelope breaks down Nuclear membranes form around each set of chromosomes. The cell separates into two daughter cells. Each cell has half the original number of chromosomes but each chromosome still has two chromatids. Nuclear envelops form around each set of chromatids. Each cell separates into 2 daughter cells which results in four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes of the original parent. Chromosomes of the parent cell pair up. (They can exchange genetic material) Section 2: Match the name of the meiosis phase with the picture. Phases include Prophase I, Prophase II, Metaphase I, Metaphase II, Anaphase I, Anaphase II, Telophase I, and Telophase II. Part 3 Analysis of Mitosis and Meisois (5 points) 1. Why is mitosis important? 2. Why is meiosis important? 3. Name one similarity of mitosis and meiosis? 4. Name one major difference between mitosis and meiosis? 5. How does meisois increase genetic variation?