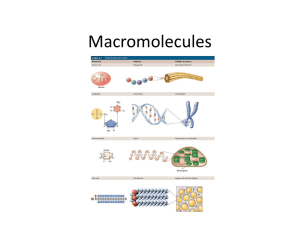
unit 1 - introduction to biology
advertisement

Name _____________________________________________________________ Test Date _Fri, 9/3______ UNIT 1 - INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY I. INTRODUCTION TO BIOLOGY (pp.16-22) A. Complexity of Life Biology is the study of _life___. To study “life” is to study a subject that is awesomely complex. Our common goal is that you _understand____ life because it is only when you understand that you can truly _learn_____ . . . And as the wise Mrs. Rice says, “If you _memorize_____, you _forget____; when you _learn______, you _remember_____! ☺ To accomplish this, there are two important keys: 1. Active Listening – Listening is not a passive activity! An active listener ________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 2. Responsible Learning - _____________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ B. Characteristics of Life 1. Living things are made of _cells___ . A cell is the _smallest working unit of life____________ 2. Living things obtain and use _energy_____. Our ultimate source of energy is the _sun_____. Plants can convert the sun’s energy into useable energy in a process called _photosynthesis____. The chemical processes that occur in an organism to convert food to _energy__ are known as _metabolism____. 3. Living things _respond to their environment_______________. Living things react to a _stimulus____; for example, _temperature, light__________. 4. Living things maintain a _constant__ internal environment. This is known as _homeostasis__ or _internal harmony____. 5. Living things _grow and develop_______. Development describes _physical changes __ that take place during the _lifetime___ of an organism. 6. Living things are based on a _universal genetic code______ - _DNA___. 7. Living things _reproduce__. If this did not occur, _species would die out____ 8. As a group, living things _evolve____; this means, _change over time______. C. Hierarchy of Life 1. _Atom____ - Smallest unit of matter that retains its elemental properties 2. _Molecule___ - Groups of atoms bonded together 3. _Cell__ - Smallest working unit of life 4. _Organism___ - Individual living thing; depending on the complexity, an organism may be composed of: a. _Tissue_______ - groups of cells working together b. _Organ____ – groups of _tissues___________ working together c. _Organ system___ - groups of _organs___ working together 5. __Population_____ - Group of organisms of one _species__ in one area 6. _Community____ - Different populations that live together in a specific area 7. _Ecosystem_____ - A community and its _non-living components___________ 8. _Biosphere______ - Earth II. THE CHEMISTRY OF LIFE (pp. 37, 38) Organisms are composed of _matter___, which is anything that takes up space and has mass. All matter is composed of _elements_____, substances that cannot be broken down by chemical reactions. A. Elements – There are 92 naturally occurring elements, 25 of which are essential to life. Four elements make up 96% of living matter. They are: _carbon___________ _hydrogen___________ _oxygen___________ _nitrogen___________ B. Compounds - Elements combine together in fixed ratios of atoms to form _compounds_______. Compounds are held together by _chemical bonds_________. The reactivity of an atom and the type of chemical bond that it forms are determined by the number of _electrons____ it has. 1. Chemical Formula - _Chemical description______ of a compound. Identifies the _number___ of _atoms____ of elements that make up the compound. Identifies the _ratio__ of _atoms__ of elements that make up the compound. H2SO4 = _2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, 4 oxygen atoms______________________________ Total number of atoms = _7__ C6H12O6 = _6 carbon atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms, 6 oxygen atoms_____________________ Total number of atoms = _24____________ 2. Chemical Equation – Provides the “_recipe__” for making a compound. The substances that go into the reaction are known as the _reactants_____. The substance(s) formed is known as the _products___. 2H2 + O2 2H2O Reactant = __H2 and O2_____ Product = _ H2O________ C. Chemical Bonds (pp. 37-38) 1. Ionic Bond – Weaker bond in which electrons are _transferred______- that is, one atom _strips____ an electron(s) away from the other. Results in 2 oppositely-charged particles called _ions____ that are attracted to each other due to the difference in _charges___. Examples include _Na+Cl-_______________ 2. Covalent Bond– Strong chemical bond in which electrons are _shared________. Results in a very stable compound called a _molecule____. Examples include _water, glucose, DNA_____________. III. THE IMPORTANCE OF CARBON (pp. 44-45) Although a cell is composed of 70% to 95% _water____, most of the rest consists of carbon-based compounds. Carbon can form very large, complex molecules called _organic____ compounds due to its number of electrons. Organic molecules important in organisms are called _biomolecules_____. A. Polymers - Most biomolecules are _polymers____. The prefix “poly” means _”many”______. A polymer is a large molecule composed of _many__ identical or similar building blocks. The sub-units, or building block molecules, of a polymer are called _monomers___. B. Classes of Biomolecules: 1. _Carbohydrates________________ 2. _Lipids_______________________ 3. _Proteins_____________________ 4. _Nucleic Acids_________________ IV. CARBOHYDRATES (p. 45-46) Carbohydrates are used for immediate and stored _energy____ and as a _building material____________. Carbohydrates contain the elements _C_, _H__, and _O___. The ratio of _H___ atoms to _O___ is _2 : 1____. In other words, for every _2 hydrogens__ in a carbohydrate, there is _1 oxygen____. There are three groups of carbohydrates: A. Monosaccharides – “_One__ Sugar”. Simplest of all sugars. Although they vary in the number of _C___ atoms, the ratio of _2 H : 1 O_____ is always present. Monosaccharides are the building blocks, or _monomers_____, for the more complex carbohydrates. Examples of monosaccharides include 1. _Glucose____ – Six-carbon monosaccharide that is the preferred _energy source ___ for most organisms, including _humans______. The chemical formula of glucose is _C6 H12 O6________. 2. _Deoxyribose_____ - Five-carbon monosaccharide; important component of _DNA_____. B. Disaccharides - _Two__ monosaccharides _covalently____ bonded together. Examples include 1. Sucrose - _table sugar____________. 2. Lactose - _milk sugar_____________. C. Polysaccharides - _Many __ monosaccharides _covalently___bonded together. They are divided into two groups based on function - _energy storage____ polysaccharides and _structural_____ polysaccharides. 1. Storage Polysaccharides – Long _polymers___ of _glucose__ broken down as needed for _energy____ a. Glycogen – Storage form of _glucose___ in _animals___. In humans, most glycogen is stored in _liver___ and _muscle___ cells. b. Starch – Storage form of _glucose____ in _plants___. Humans are able to break down starch to its monomers of _glucose_____ for energy. 2. Structural Polysaccharides – Used as a _building material____ in many organisms a. Cellulose – Major component of _plant cell walls______. Composed of monomers of _glucose___. Humans are unable to break the bonds in cellulose; therefore it cannot be used for _energy___ but it is still important to our diet as a source of _fiber____. b. Chitin – Major component of _fungal__ cell walls and the _exoskeletons___ of insects and other arthropods. V. LIPIDS (p. 46-47) Known for their _insolubility____ in water. Made up of _C__, _H___, and _O___, but lipids do not have the _2H : 1O____ ratio found in carbohydrates. Our bodies need lipids for _energy storage, insulation and cushioning__. There are 3 important groups: A. Fats & Oils – Characterized by presence of _three fatty acid tails____. Generally referred to as _fat___ if lipid is solid at room temperature and an _oil___ if lipid is liquid at room temperature. Fats and oils are classified as _saturated ___ or _unsaturated_, depending on the type of covalent bonds in the fatty acids. _Saturated ___ fats have been linked to heart disease. B. Phospholipids – Unique lipid found in every living _cell membrane______. C. Steroids – An important example of a steroid is _cholesterol____. Used for _hormone____ production and animal cell structure. VI. PROTEINS (pp. 47-53) Proteins are instrumental in _support, structure, movement, and metabolism________________________. In addition to _C___, _H____, and _O___, proteins contain _N___. A. Amino Acids - The monomers of proteins are _amino acids______. There are _20___ amino acids that combine together in different _numbers_, _patterns__, and _arrangements___ to form proteins. B. Enzymes - One very important function of proteins is to act as _enzymes__. Enzymes are biological _catalysts_____, meaning they _trigger_____ chemical reactions. An organism could not maintain _homeostasis____ without functioning enzymes. VII. NUCLEIC ACIDS (p. 47) Nucleic acids are _polymers_____ composed of monomers called _nucleotides____. There are three important molecules in this group: A. DNA - Contains the _genetic instructions_____ for the cell. B. RNA - _Carries out __ the instructions in DNA. C. ATP – Provides useable _energy__ in all cells