Water Analysis Lab: pH, Hardness, Alkalinity
advertisement

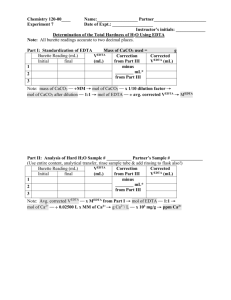
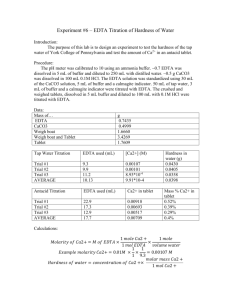
CHEMISTRY 108 LABORATORY 8 ANALYSIS OF SOLUTIONS Goals Your team is called to compare two samples of bottled water by determining the pH, water hardness and alkalinity. Materials Needed pH meters Calibration buffer pH 7 and 4 25 mL pipets (enough for five groups. Each group will need 2 pipets) 50 mL burets Buret holders and stands Magnetic stirring bars 0.0100 M Sodium EDTA solution, standardized pH 10 buffer (NH3/NH4+ buffer plus MgEDTA) Calmagite indicator 0.0100 M HCl solution, standardized Methyl orange indicator Two bottled water samples (not purified or distilled water): enough for five groups Control water sample (distilled water) Introduction Bottled water is not pure water. Since it comes from wells or springs, it often has a relatively high mineral content. It has calcium and magnesium ions, the primary sources of water hardness. It also contains bicarbonate ion, the primary sources for the alkalinity or acid neutralizing capacity of the water. In addition, bottled water contains other soluble ionic substances. We can determine the total amount of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions in water by titrating a water sample with a standardized EDTA solution. EDTA forms strong 1:1 metal-EDTA complex with Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. The indicator used in the titration is Calmagite indicator which is red/magenta in the presence of free Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions and blue in their absence. 1 Structure of EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetate) Structure of Metal-EDTA complex We commonly report water hardness as milligrams of CaCO3 per liter of water or ppm. Therefore, we calculate the number of moles of EDTA used in titration and convert it to the number of moles of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions (it is a 1:1 reaction). Then it is converted to milligrams of CaCO3. Table I. Classification of water hardness (hardness as calcium carbonate). Classification mg/L or ppm Soft 0 - 17.1 Slightly hard 17.1 - 60 Moderately hard 60 - 120 Hard 120 - 180 Very Hard 180 & over Example: A student used 11.35 mL of 0.0100 M EDTA solution to titrate 25.00 mL of the sample water. Report the hardness in milligrams of CaCO3 per liter of the sample (or ppm). What is the classification of the water sample (soft, slightly hard, moderately hard, etc.)? moles of EDTA used = 0.0100 M 0.01135 L = 0.0001135 mol moles of Ca2+ in 25 mL = moles of EDTA required = 0.0001135 mol grams of CaCO3 in 25 mL= mol of Ca2+ molar mass of CaCO3 = 0.0001135 mol 100 g/mol = 0.01135 g 2 1000mL = 0.454 g 25 mL 1000mg mg of CaCO3 in 25 mL = 0.01135 g = 11.35 mg 1g 1000mL mg of CaCO3 in 1 L = 11.35 mg = 454 mg CaCO3 in 1 L= 454 ppm 25 mL According to the classification of water, this sample is very hard (over 180 ppm). grams of CaCO3 in 1 L = 0.01135 g We can determine the amount of bicarbonate ions in water similarly by titrating a water sample with a standardized HCl solution. The indicator used in the titration is methyl orange indicator which changes color from yellow to red when an excess HCl is present and the solution pH drops below 4. It is a 1:1 reaction. HCO3- (aq) + HCl (aq) → H2O (l) + CO2 (g) + Cl- (aq) Example: A student used 5.20 mL of 0.0100 M HCl solution to titrate 25.00 mL of the sample water. Report the alkalinity in molar concentration of bicarbonate and milligrams of bicarbonate per liter of the sample (ppm). moles of HCl required = 0.0100 M 0.00520 L = 0.0000520 mole moles of bicarbonate in 25 mL = moles of HCl required = 0.0000520 mole molarity of bicarbonate = moles/L = 0.0000520 mole / 0.02500 L = 0.00208 M milligrams of bicarbonate per L= mole of bicarbonate molar mass of bicarbonate 1000 mg/g = 0.00208 M 61.02 g/mole 1000 mg/g = 127 mg/L = 127 ppm Experimental Procedure Water Hardness Test: 25 mL of water sample is combined with 2 mL of NH3/NH4+ buffer and five drops of calmagite indicator. EDTA out of the buret is added until the color goes from red to blue. The volume of EDTA required is noted and the concentration of CaCO3 is calculated. Use a 25 mL sample of distilled water as your control. Alkalinity Test: 25 mL of water sample is combined with five drops of methyl orange indicator. HCl out of the buret is added until the color goes from yellow to red. The volume of HCl required is noted and the concentration of bicarbonate is calculated. Use a 25 mL sample of distilled water as your control. Safety Precautions The fumes from the NH3/NH4Cl buffer at pH 10 are toxic, corrosive, and irritating. Dispense under a fume hood. Wash hands thoroughly before leaving the lab. 3 Pre Laboratory Questions 1. A student used 6.05 mL of 0.0100 M EDTA solution to titrate 25 mL of the sample water. Report the hardness in milligrams of CaCO3 per liter of the sample. What is the classification of the water sample (soft, slightly hard, moderately hard, etc.)? 2. Is it better to drink hard water or soft water? Explain your answer. 3. Is acidic water or basic water better for our health? Explain your answer. 4 REPORT SHEET LABORATORY 8: ANALYSIS OF SOLUTIONS Name:______________________________ Section:_____________ Date:__________ Partner:___________________________ Bottled water sample 1 Bottled water sample 2 Distilled water Identification _____________ _____________ _____________ pH ____________ ____________ ____________ Water Hardness Bottled water sample 1 Volume of water sample titrated, mL __________________ Trial# Volume of EDTA required, mL Number of moles of EDTA, mol Number of moles of Ca2+, mol Water hardness, mg CaCO3 in L sample 1 ________ ________ ________ ________ Average Total Hardness, mg CaCO3/L ________ Classification of your water sample _______________ Bottled water sample 2 Volume of water sample titrated, mL __________________ Trial# Volume of EDTA required, mL Number of moles of EDTA, mol Number of moles of Ca2+, mol Water hardness, mg CaCO3 in L sample 1 ________ ________ ________ ________ Average Total Hardness, mg CaCO3/L ________ Classification of your water sample _______________ Distilled water Volume of water sample titrated, mL __________________ Trial# Volume of EDTA required, mL Number of moles of EDTA, mol Number of moles of Ca2+, mol Water hardness, mg CaCO3 in L sample 1 ________ ________ ________ ________ 5 2 ________ ________ ________ ________ 2 ________ ________ ________ ________ 2 ________ ________ ________ ________ Label ____________ ____________ ____________ 3 ________ ________ ________ ________ 3 ________ ________ ________ ________ 3 ________ ________ ________ ________ Average Total Hardness, mg CaCO3/L ________ Classification of your water sample _______________ Alkalinity Bottled water sample 1 Volume of water sample titrated, mL __________________ Trial# Volume of HCl required, mL Number of moles of HCl, mol Number of moles of bicarbonate, mol alkalinity, mg bicarbonate in L sample 1 ________ ________ ________ ________ Average alkalinity, mg bicarbonate/L ________ Bottled water sample 2 Volume of water sample titrated, mL __________________ Trial# Volume of HCl required, mL Number of moles of HCl, mol Number of moles of bicarbonate, mol alkalinity, mg bicarbonate in L sample 1 ________ ________ ________ ________ Average alkalinity, mg bicarbonate/L ________ Distilled water Volume of water sample titrated, mL __________________ Trial# Volume of HCl required, mL Number of moles of HCl, mol Number of moles of bicarbonate, mol alkalinity, mg bicarbonate in L sample 1 ________ ________ ________ ________ Average alkalinity, mg bicarbonate/L ________ 2 ________ ________ ________ ________ 2 ________ ________ ________ ________ 2 ________ ________ ________ ________ 3 ________ ________ ________ ________ 3 ________ ________ ________ ________ 3 ________ ________ ________ ________ POST-LABORATORY PROBLEMS: Must be included in your lab report. 1. The pH of water for human consumption should be close to neutral. How closely do your samples compare with this goal? 2. Report the water hardness in ppm and molar concentration of CaCO3. How would you classify your water samples according to table 1? 6 3. Report the bicarbonate concentrations in ppm and molar concentration. 4. Compare the water hardness and alkalinity of two water samples. Which one has higher water hardness? Which one has higher alkalinity? Can you decide which one is better? 7