Hyperparathyroidism
advertisement
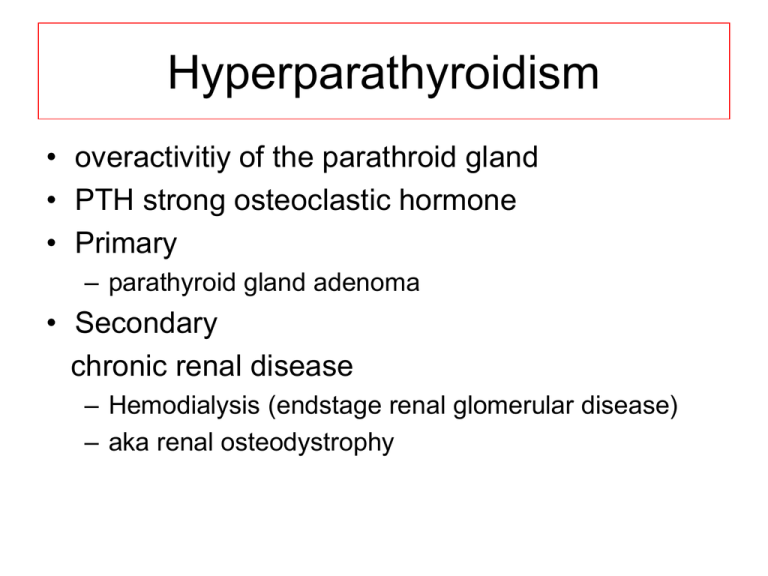
Hyperparathyroidism • overactivitiy of the parathroid gland • PTH strong osteoclastic hormone • Primary – parathyroid gland adenoma • Secondary chronic renal disease – Hemodialysis (endstage renal glomerular disease) – aka renal osteodystrophy Primary HPT • • • • most common type mc cause of hypercalcemia parathyroid adenoma 90%) carcinoma, hyperplasia, ectopic PTH producing tumors • elevated parathormone levels, hypercalcemia, hypophosphatemia Secondary HPT • complication of chronic renal disease • persist loss of calcium and phosphorus • stimulates PTH release (high PTH and low to normal calcium) • Hyperphosphatemia (kidneys can’t excrete it as well) • Tertiary HPT is seen in dialysis patients, parathryoid gland acts independent of serum calcium levels (high PTH and Calcium) • Radiographic DDx of types is difficult • 30-50 women > men • bone pain, fractures, weakness, lethargy, polydipsia, polyuria • Hypercalcemia leads to muscle weakness, hypotonia • may have renal stones • pancreatitis • hypercalcemia in primary, normal to low in secondary • elevated alkaline phosphatase • elevated PTH stones, bones, abdominal groans and psychiatric moans (renal stones, peptic ulcers, pancreatitis, confusion, lethargy, weakness) Parathormone physiology • maintains the circulating level of calcium ion • stimulates osteoclasts, which reabsorb bone and release calcium and phosphorus ion into the blood stream • increase calcium absorption through the small intestine • renal tubular phosphate excretion and calcium absorption; upsets homeostasis • in secondary HPT; calcium loss and abnormal Vit D formation leads to hypocalcemia and release of PTH Radiography - HPT • • • • • Osteopenia Subperiosteal resorption (diagnostic) Distal tuft resorption Accentuated trabeculation Brown tumors (cystic accumulations of fibrous tissue) • Loss of cortical definition • Soft tissue calcification – Metastatic calcification; eg., vascular calcification Subperiosteal resorption • most definitive radiographic sign of HPT • esp at the radial margins middle and proximal phalanges of the 2nd and 3rd digits • outer cortical erosion may appear frayed or lace like • widened joint spaces and osteolysis, esp AC and SI joints Rugger Jersey spine Sub-endplate sclerosis Salt and Pepper Skull Subchondral resorption Pre and Post treatment Renal osteodystrophy Undifferentiated seronegative spondyloarthropathy (history, clinical presentation and what is the most likely Sacroiliitis HLA -B27 Positive HLA-B27 Negative HLA-B27 Undifferentiated HPT (Calcium levels) AS* Gout (uric acid levels) Enteropathic DJD Psoriatic Infection (unilateral) Reiter’s Reactive arthritis Trauma Pregnancy DISH (upper third) OCI




![2012 [1] Rajika L Dewasurendra, Prapat Suriyaphol, Sumadhya D](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619083_1-f93216c6817d37213cca750ca3003423-300x300.png)