Ch. 13
advertisement

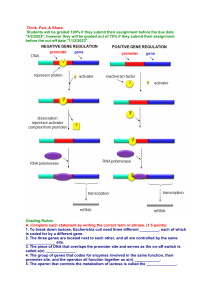
Discussion Guide Chapter 13 Mader 10th Edition 1. Describe what occurs in an E. coli cell in the absence of lactose versus the presence of lactose, in terms of gene control. 2. Distinguish between negative gene control and positive gene control. Give examples of each. 3. If all the cells in your body start out life with the same inherited information on how to build proteins, then what causes the differences between a nerve cell and a muscle cell? 4. Relate heterochomatin and euchromatin to levels of chromatin organization. 5. X chromosome inactivation causes the formation of _________ __________________. 6. Explain how X inactivation leads to the development of a calico cat. 7. According to the theory of dosage compensation (Sam Rhine talked about this), why is the shut down of one X chromosome important? 8. Describe the role of transcription factors and enhancers in eukaryotic cells. 9. Explain how alternative processing of mRNA lead to genetic and phenotypic diversity. 10. Describe how a eukaryotic cell can control the translation of mRNA transcripts after the mRNA have been transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. 11. Compare prokaryotes and eukaryotes control of gene expression. 12. Contrast mutations that occur in a somatic cell from one that arises in a germ cell. 13. Explain how base-pair substitutions, such as a point mutation and frameshift mutation (deletion), can change the final protein product of a gene. 14. The nucleotide sequence of a hypothetical eukaryotic nuclear gene is: TAC ATA CTA GTT ACG TCG CCC GGA AAT ATC If a mutation in this gene were to change the fifteenth nucletide (underlined) from guanine to thymine, what effect do you think it might have on the expression of this gene? 15. Explain how a mutation in p53 can contribute to the development of cancer. 16. When boiled down to its essential parts, evolution is about who survives and who reproduces. How can mutations play a role in the survival and reproduction of a species?