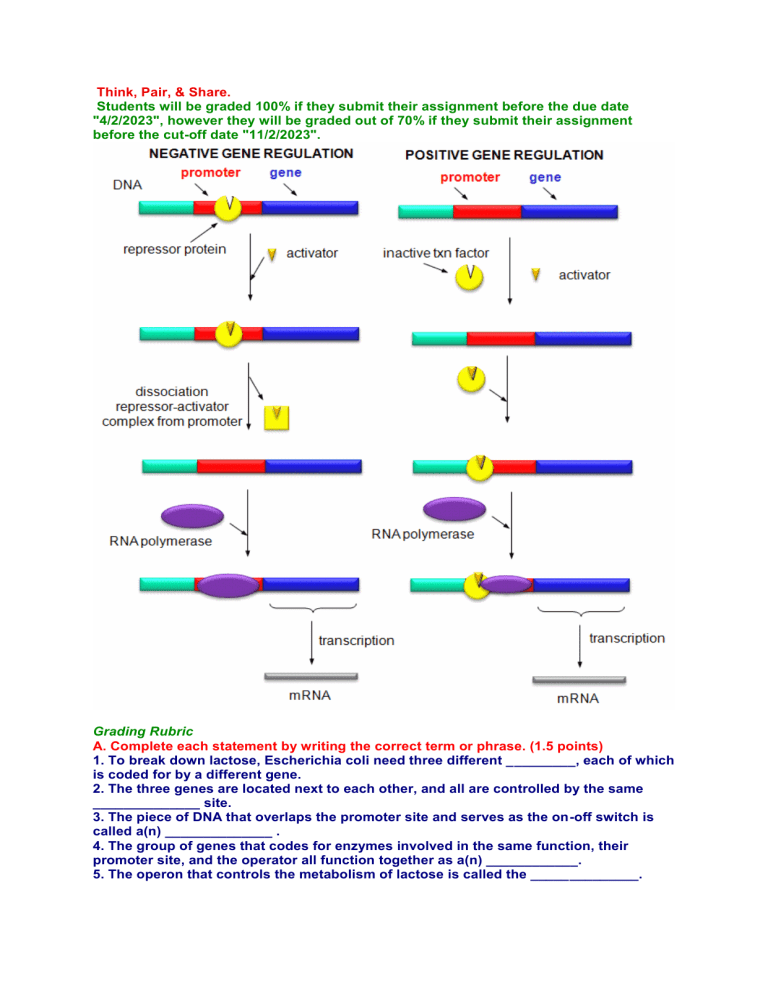
Think, Pair, & Share. Students will be graded 100% if they submit their assignment before the due date "4/2/2023", however they will be graded out of 70% if they submit their assignment before the cut-off date "11/2/2023". Grading Rubric A. Complete each statement by writing the correct term or phrase. (1.5 points) 1. To break down lactose, Escherichia coli need three different _________, each of which is coded for by a different gene. 2. The three genes are located next to each other, and all are controlled by the same ______________ site. 3. The piece of DNA that overlaps the promoter site and serves as the on-off switch is called a(n) ______________ . 4. The group of genes that codes for enzymes involved in the same function, their promoter site, and the operator all function together as a(n) ____________. 5. The operon that controls the metabolism of lactose is called the ______________. 6. A(n) ________________ is a protein that binds to an operator and physically blocks RNA polymerase from binding to a promoter site. B. Read each question, and write your answer. (1.25 points) 7. What are enhancers? 8. Why is there more opportunity for gene regulation in eukaryotic cells than in prokaryotic cells? 9. When can gene regulation occur in eukaryotic cells? 10. What are introns and exons? 11. What happens to mRNA that includes introns? C. Complete each statement by underlining the correct term or phrase in the brackets. (2.5 points) 14. Mutations can only be passed on to offspring if they occur in [gametes / body cells]. 15. Mutations that change one or just a few nucleotides in a gene on a chromosome are called [random / point] mutations. 16. If a mutation causes a gene containing the nucleotide sequence ACA to become ACTA, the mutation is called a [insertion / deletion] mutation. 17. If a mutation causes a sequence of nucleotides to change from ACGAGA to ACGGA, the mutation is called a(n) [insertion / deletion] mutation. 18. If a mutation causes a sequence of nucleotides to change from ACGAGA to ACGAGGA, the mutation is called a(n) [insertion / deletion] mutation. WORD BANK:codon gene anticodon exon intron lac genetic transc ription translation Uracil operon messenger operator repressor ribosomal polymerase ribonucleic transfer D. Completion: (4.75 points) 1. The ________ operon controls the metabolism of lactose. 2. ________ acid (RNA) is a molecule made of nucleotides linked together. 3. RNA ________ is an enzyme involved in transcription. 4. _________ RNA carries the instructions for making a protein from a gene to the site of translation 5. _________ expression is the entire process by which proteins are made. 6. The process for transferring a gene’s instructions for making a protein to an mRNA molecule. 7. A three-nucleotide sequence on the mRNA that specifies an amino acid or a “start” or “stop” signal. 8. A piece of DNA that serves as an on-off switch for transcription. 9. Long segment of DNA on a eukaryotic gene that has no coding information. 10. The nitrogen base in the nucleotides of RNA that is not present in DNA. 11. A protein that binds to an operator and inhibits transcription. 12. Portion of a eukaryotic gene that is translated. 13. A process that puts together the amino acids that make up a protein. 14. A three-nucleotide sequence on a tRNA that is complementary to one of the codons of the genetic code. 15. ________ RNA molecules are part of the structure of ribosomes. 16. ________ RNA molecules temporarily carry a specific amino acid on one end. 17. The ________ code specifies the amino acids and “start” and “stop” signals with three-part codons. 18. Collective name for a group of genes involved in a single function, along with their promoter site, and their operator.





