Introduction
advertisement

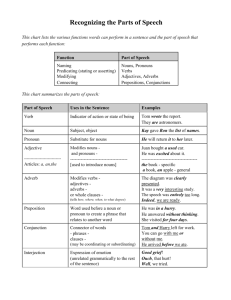
Introduction Sentences are made up of different types of words and each type has its own job to do in the sentence. This section includes: Nouns and pronouns Adjectives Prepositions, articles and conjunctions Nouns and pronouns Nouns Common nouns are the names of things, for example, people, places or objects. A proper noun is the name of a particular person, place or thing, and always begins with a capital letter. Amy went to France on Saturday and took her camera with her. Amy, France and Saturday are proper nouns and camera is a common noun. Pronouns A pronoun is a word that takes the place of nouns, for example: he she them there it Amy took her camera to France. She took it there. She is a pronoun that takes the place of Amy, it takes the place of camera, and there takes the place of France. Adjectives An adjective is a word that describes a noun (the name of a thing or a place). It was a terrible book. The word terrible is an adjective. It tells us what the book (the noun) was like. Where can I put an adjective? Adjectives can come before or after a noun. The book he read on holiday was terrible. He read a terrible book on holiday. Try putting adjectives in different places in your sentences to make your writing more interesting. Using more than one adjective If you want to describe a noun in detail, you can use more than one adjective. He had a mouldy, smelly, overpriced sandwich for lunch. When you have a list of adjectives like this, separate them with commas. Prepositions, articles and conjunctions Prepositions A preposition is a word that tells you where or when something is in relation to something else, for example: after before on under inside outside After walking for miles she rested on a small hill. After tells you when she rested and on tells you where she rested. Articles An article is a word that tells you whether a noun is specific or general, for example a, an, the. She took a big suitcase on holiday. A tells you that the noun suitcase is general. It’s not talking about any particular suitcase, it’s any old big suitcase. She took the big suitcase on holiday. The tells you it was a particular suitcase. Perhaps she has a big suitcase and a small one. She took the big suitcase. Conjunctions A conjunction is a word that joins two sentences or clauses, for example: and but although whenever He went to the cinema and she went swimming. Amy took her mp3 player with her but she forgot to put any batteries in it. 1. What is an adverb? a word that describes an adjective a word that describes a verb a word that describes noun 2. What is an adjective? a doing word a word that describes a noun when you use two words together that start with the same sound 3. An article (e.g. a, an, the) tells you whether a noun is specific or general where something is in relation to something else how big something is in relation to something else 4. What is a verb? it tells you whether a noun is specific or general a describing word a doing word 5. What sort of word is 'nose'? A noun An adverb An adjective 6. What is a pronoun? a word that takes the place of a noun the name of a place, a person or a thing a word that describes a noun 7. What is an adverbial phrase? more than one word doing the job of an adverb an adverb and an adjective used together an adverb placed after the verb it describes 8. What type of word is 'inside'? verb pronoun preposition 9. Why do we use conjunctions? to describe nouns to join sentences together to shorten a sentence 10. What is a clause? something you find on a cat's paw a doing word a short sentence